
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
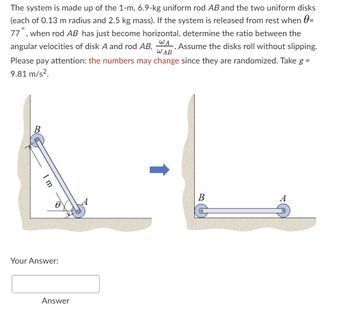
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
The system is made up of the following components:
- A 1-meter, 6.9-kg uniform rod \( AB \).
- Two uniform disks, each with a 0.13 m radius and 2.5 kg mass.
**Initial Condition:**
- The system is released from rest when \( \theta = 77^\circ \).
**Objective:**
- Determine the ratio between the angular velocities of disk \( A \) and rod \( AB \), denoted as \( \frac{\omega_A}{\omega_{AB}} \), when rod \( AB \) has just become horizontal.
- Assume the disks roll without slipping.
**Important Note:**
- The numbers may change since they are randomized.
- Use \( g = 9.81 \, \text{m/s}^2 \).
**Diagram Explanation:**
1. **Left Side Diagram:**
- Shows rod \( AB \) inclined at an angle \( \theta \) from the vertical.
- The length of the rod is marked as 1 meter.
- Points \( A \) and \( B \) are shown as pivot points connecting the rod and the disks.
2. **Right Side Diagram:**
- Illustrates the rod \( AB \) in the horizontal position after release.
- Points \( A \) and \( B \) remain in contact with the disks.
**Calculation Area:**
- A field marked "Your Answer:" followed by a text box labeled "Answer" is provided for inputting the calculated ratio of angular velocities.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The 150 kg spool below is initially at rest and has a radius of gyration of kg 0.5 m. The force Pis applied at B and causes the spool to begin rotating. The rope attached to point A does not slip at its contact point with the spool, meaning that point is an instantaneous center of zero velocity as shown. However, the bottom of the spool slips against the ground, causing a frictional force which acts to the right. After 5 s the angular velocity of the spool is -27 rad/s (using the coordinate system shown, meaning the spool rotates in the clockwise direction). Based on this information: a) Find the moment of inertia of the spool at the instantaneous center of zero velocity. b) Calculate the frictional force exerted on the spool by the ground. c) Using the principal of angular impulse and momentum, determine the coefficient of kinetic friction, r, between the bottom of the spool and the ground. IC 0.75 m 0.25 m P = 800 N 0.5 m Barrow_forwardThe spring is uncompressed when the uniform sender bar AB is in the vertical position shown. Bar AB with a mass of 50 kg and a length of 1 m is released from rest in the position where the bar has been rotated 30° clockwise from the position shown. This initial position of the bar AB is illustrated using the dashed line in the figure. Neglect any sag of the spring as well as the spring mass. (b) Find the angular velocity of the bar when it reaches the vertical position. A Initial position of the bar AB when it is released from rest k=12 kN/m Answers: (a) a = 198.951 rad/s² (b) 2 = 10 rad/s 30º Barrow_forwardThe 35 lb slender rod AB is 277 in. long and at rest in a horizontal position supported by a spring located at h = 226 in. from the suspension cable at B. If the cable at B fails, answer the following 1) Part A: Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of end A. 2) Part B: Determine the magnitude of the acceleration of end B. 3) Part C: Determine the angular acceleration of the rod.arrow_forward
- The system is at rest with the spring unstretched when theta = 0. the 5.3 kg uniform slender bar is then given a slight clockwise nudge. The value of b is 0.45 m. (a) if the bar comes to momentary rest when theta = 58, determine the spring constant k. (b) for the value k = 65 N/m, find the magnitude of the angular velocity of th ebar when theta = 38 degrees.arrow_forwardThe slotted circular disk whose mass is 4.9 kg has a radius of gyration about O of 230 mm. The disk carries the four steel balls, each of mass 0.17 kg and located as shown, and rotates freely about a vertical axis through O with an angular speed of 164 rev/min. Each of the small balls is held in place by a latching device not shown. If the balls are released while the disk is rotating and come to rest relative to the disk at the outer ends of the slots, compute the new angular speed N of the disk. Also find the magnitude |AE| of the energy loss due to the impact of the balls with the ends of the slots. Neglect the diameter of the balls and discuss this approximation. 164 rev/min 145 mm 305 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY