
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
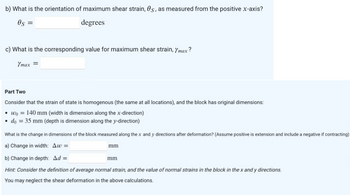
Transcribed Image Text:b) What is the orientation of maximum shear strain, 0s, as measured from the positive x-axis?
0s =
degrees
c) What is the corresponding value for maximum shear strain, Ymax?
Ymax =
Part Two
Consider that the strain of state is homogenous (the same at all locations), and the block has original dimensions:
wo 140 mm (width is dimension along the x-direction)
• do = 35 mm (depth is dimension along the y-direction)
What is the change in dimensions of the block measured along the x and y directions after deformation? (Assume positive is extension and include a negative if contracting)
a) Change in width: Aw=
b) Change in depth: Ad=
Hint: Consider the definition of average normal strain, and the value of normal strains in the block in the x and y directions.
You may neglect the shear deformation in the above calculations.
mm
mm
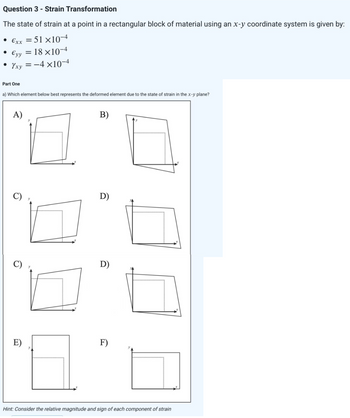
Transcribed Image Text:Question 3 - Strain Transformation
The state of strain at a point in a rectangular block of material using an x-y coordinate system is given by:
• €xx = 51×10-4
€yy = 18 ×10-4
Yxy=-4x10-4
●
●
Part One
a) Which element below best represents the deformed element due to the state of strain in the x-y plane?
6
2
B)
D)
D)
F)
Hint: Consider the relative magnitude and sign of each component of strain
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Thin square plate PQRS is symmetrically deformed into the shape shown by the dashed lines in the figure.[a = 200 mm, b = 202.1 mm, c = 198.9 mm] For the deformed plate, determine the normal strain of diagonal PR? In micro £ For the deformed plate, determine the shear strain xy at corner P?in micro radarrow_forwardA thin rectangular plate ABCD is deformed into a parallelogram as shown in the figure below. The width of the plate is w = 1300 mm, and the height of the plate is h = 1700 mm. The shear strain at A is known to be +4172 μrad. Assume a = 2.9 mm. Calculate the magnitude of dimension b in the figure.arrow_forwardThe hydrostatic represented by oij given below is 100 50 50 50 125 75 50 75 75 σij stress for the state of stress MPa = MPaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning