
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A thin sheet of rubber in the form of a square is uniformly deformed into the parallelogram shape as
shown in the figure. All edges remain the same length ?, as the sheet deforms. Determine the average normal
strain along the diagonal ??. Length ? is in millimeter (mm). Answer in 4 decimal places
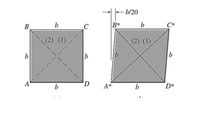
Transcribed Image Text:b/20
B
b.
B*
(2)
(2) (1),
A'
b
A*
D*
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A circular bar of magnesium alloy is 390 mm long. The stress-strain diagram for the material is shown in the figure. 70 63 56 49 O (MPa) 42 35 28 21 14 7 0.002 0.004 0.006 0.008 0.01 The bar is loaded in tension to an elongation of 2.34 mm, and then the load is removed. Hint: Use the concepts illustrated in the figures below. (Assume the curve in the figure above is linear between (0, 0) and (0.001, 28), and curves with a gradually decreasing slope otherwise.) F В E F Loading CD Loading Residual Elastic strain recovery (a) What is the permanent set of the bar (in mm)? 2.184 X mm (b) If the bar is reloaded, what is the proportional limit (in MPa)? 55 X MPaarrow_forwardThe assembly shown in the figure consists of an aluminum tube AB and a steel rod BC. The rod is attached to the tube through the rigid collar at B and passes through the tube. The cross-sectional area of the rod is 75 mm2 and the cross-sectional area of the tube is 400 + UV in mm2, where UV is 99. A tensile load of 80 kN is applied to the rod. Take Est = 200 GPa for the steel rod, Eal = 70 GPa for the aluminum tube. Determine: (a) the displacement of end C with respect to end B (i.e., the elongation of the steel rod), (b) the displacement of end B with respect to the fixed end A (i.e., the shrink of the aluminum tube), (c) the displacement of the end C of the rod (i.e., (a) + (b)).arrow_forwardA thin rectangular plate ABCD is deformed into a parallelogram as shown in the figure below. The width of the plate is w = 1200 mm, and the height of the plate is h = 2000 mm. The shear strain at A is known to be +3650 µrad. Assume a = 1.8 mm. Calculate the magnitude of dimension b in the figure. D Answer: b= i W B a mm Xarrow_forward
- Question 1: The piece of plastic is originally rectangular. Given LCD and LAD are 400 and 300 mm, respectively. If the plastic distorts as shown by the dashed lines, a) Determine the average normal strain that occurs along CD. b) Determine the average normal strain that occurs along AD. c) Determine the shear strain Yxy at corner C. 2 mm LCD 2 mm D LAD mm B 12 mm 3 mm mmarrow_forwardA round steel alloy bar with a diameter of 19mm and a gauge length of 76mm was subjected to tension, with the results shown in Table. Using a computer spreadsheet program, plot the stress–strain relationship. From the graph, determine the Young’s modulus of the steel alloy and the deformation corresponding to a 37kN load.arrow_forwardThin square plate PQRS is symmetrically deformed into the shape shown by the dashed lines in the figure.[a = 200 mm, b = 202.1 mm, c = 198.9 mm] For the deformed plate, determine the normal strain of diagonal PR? In micro £ For the deformed plate, determine the shear strain xy at corner P?in micro radarrow_forward
- A thin rectangular plate ABCD is deformed into a parallelogram as shown in the figure below. The width of the plate is w = 1300 mm, and the height of the plate is h = 1700 mm. The shear strain at A is known to be +4172 μrad. Assume a = 2.9 mm. Calculate the magnitude of dimension b in the figure.arrow_forwardA brass alloy rod having a cross sectional area of 0.24 in.2and a modulus of 16 * 106 psi is subjected to a tensile load. Plastic deformation was observed to begin at a load of 8,944 lb.a. Determine the maximum stress that can be applied without plastic deformation.b. If the maximum length to which a specimen may be stretched without causing plastic deformation is 3.28 in., what is the original specimen length?arrow_forwardA thin rectangular plate ABCD is deformed into a parallelogram as shown in the figure below. The width of the plate is w = 1400 mm, and the height of the plate is h = 1900 mm. The shear strain at A is known to be +4294 μrad. Assume a = 2.4 mm. Calculate the magnitude of dimension b in the figure. D h Answer: b= i A W Ta mm 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning