
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
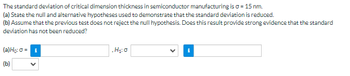
Transcribed Image Text:The standard deviation of critical dimension thickness in semiconductor manufacturing is o = 15 nm.
(a) State the null and alternative hypotheses used to demonstrate that the standard deviation is reduced.
(b) Assume that the previous test does not reject the null hypothesis. Does this result provide strong evidence that the standard
deviation has not been reduced?
(a) Ho: 0 = i
(b)
.H₂:0
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- To test Ho: o=2.8 versus H₁: <2.8, a random sample of size n=21 is obtained from a population that is known to be normally distributed. CITE (a) If the sample standard deviation is determined to be s = 1.3, compute the test statistic. = 4.311 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) If the researcher decides to test this hypothesis at the α=0.10 level of significance, determine the critical value. The critical value is (Round to three decimal places needed.) 4 Clear all View an example Get more help. a Et H Help me solve this Type here to search 4 R F 5 T 7 8 96°F Mostly sunny Check answ G 3:54 PM 6/18/202arrow_forwardJust question 3 fill in the blankarrow_forwardTo test Ho: o = 2.1 versus H: 0+2.1, a random sample of size n = 17 is obtained from a population that is known to be normally distributed. (a) If the sample standard deviation is determined to be s = 1.8, compute the test statistic. = 11.755 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) If the researcher decides to test this hypothesis at the a = 0.05 level of significance, determine the critical values. .2 The critical values are x6 025 and x6.975 %3D %3D (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- A population of values has a distribution with μ=52.4μ=52.4 and σ=72.7σ=72.7. You intend to draw a random sample of size n=205n=205.According to the Central Limit Theorem:(a) What is the mean of the distribution of sample means?μ¯x=μx¯= (b) What is the standard deviation of the distribution of sample means?(Report answer accurate to 2 decimal places.)σ¯x=σx¯=arrow_forwardQ1: Lifetimes of a certain component are lognormally distributed with parameters u = 1 day and o = 0.5 days. Find the mean lifetime of these components. 1-Find the standard deviation of the lifetimes. 2-Find CDF 3- Find reliability at t= 4 day Q2: The lifetime (in days) of a certain electronic component that operates in a high-temperature environment is lognormally distributed with u = 1.2 and o = 2. a. Find the mean lifetime. b. Find the probability that a component lasts between three and six days. c. Find the 95th percentile of the lifetimes. d- find CDF Q3: The authors suggest using a Weibull distribution to model the duration of a bake step in the manufacture of a semiconductor. Let T represent the duration in hours of the bake step for a randomly chosen lot. If T Weibull(0.3, 0.1), what is the probability that the bake step takes longer than four hours? What is the probability that it takes between two and seven hours? What reliability at t= 0.8 hoursarrow_forward(3) The weights of adult black squirrels are known to be normally distributed with mean µ and standard deviation o = 0.12 lbs. A random sample of nine black squirrels gave their average weight to be o.78 lbs. It is hypothesized that due to various reasons the black squirrels are becoming heavier. If the null hypothesis is Ho : H s 0.75 lbs, versus H1 : µ > 0.75 find the p-value The following``answers" have been proposed. (a) By consulting a standard normal table, the p-value is sup P(X9 2 0.78) = P(Z > 1.645) = 0.05. HS0.75 (b) By consulting a standard normal table, the p-value is sup P(X9 2 0.78) = P(Z > 1.00) = 0.1587. HS0.75 (c) By consulting a standard normal table, the p-value is sup P(X9 2 0.78) = P(Z > 0.75) = 0.2266. µ 0.50) = 0.3085. µ<0.75 (e) None of the above The correct answer is (a) (b) (d) N/A (Select One)arrow_forward
- A company claims that the mean monthly residential electricity consumption in a certain region is more than 860 kilo Watt-hours (kWh). You want to test this claim. You find that a random sample of 69 residential customers has a mean monthly consumption of 890 kWh. Assume the population standard deviation is 123 kWh. At α=0.05, can you support the claim? Complete parts (a) through (e). (b) Find the critical value(s) and identify the rejection region(s). Select the correct choice below and fill in the answer box within your choice. Use technology. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) A. The critical values are ±enter your response here. B. The critical value is enter your response here.arrow_forwardTo test Ho: o=2.4 versus H₁: o>2.4, a random sample of size n = 16 is obtained from a population that is known to be normally distributed. Complete parts (a) through (d). CIER (a) If the sample standard deviation is determined to be s=2.2, compute the test statistic. x 12.604 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (b) If the researcher decides to test this hypothesis at the a= 0.01 level of significance, determine the critical value. X.01 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) 4 Check answer Help me solve this View an example Get more help. a 3:55 PM 6/18/2022 O Ei = Type here to search G B K ? Clear all 96°F Mostly sunnyarrow_forwardA population of values has a distribution with μ=5.6μ=5.6 and σ=28.5σ=28.5. You intend to draw a random sample of size n=22n=22. According to the Central Limit Theorem: (a) What is the mean of the distribution of sample means? μ¯x=μx¯= (b) What is the standard deviation of the distribution of sample means? (Report answer accurate to 2 decimal places.) σ¯x=σx¯= (c) In a random sample of n=22, what is the probability that its sample mean is more than 4.6? Round to three decimal places. (d) In a random sample of n=22, what is the probability that its sample mean is less than 17.9? Give your answer to three decimal places. Submitarrow_forward
- You may need to use the appropriate appendix table or technology to answer this question. Given are five observations for two variables, x and y. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) xi 1 2 3 4 5 yi 4 8 5 11 15 (a) Use sŷ* = s 1 n + (x* − x)2 Σ(xi − x)2 to estimate the standard deviation of ŷ* when x = 5. (b) Use ŷ* ± t?/2sŷ* to develop a 95% confidence interval for the expected value of y when x = 5. to (c) Use spred = s 1 + 1 n + (x* − x)2 Σ(xi − x)2 to estimate the standard deviation of an individual value of y when x = 5. (d) Use ŷ* ± t?/2spred to develop a 95% prediction interval for y when x = 5. to I need all the parts, I attached a picture of the whole question in case the one I copied above was not clear enough.arrow_forwardConsider a paint-drying situation in which drying time for a test specimen is normally distributed with o = 6. The hypotheses H,: µ = 74 and H: µ < 74 are to be tested using a random sample of n = 25 observations. (a) How many standard deviations (of X) below the null value is x = 72.3? (Round your answer to two decimal places.) 1.42 standard deviations (b) If x = 72.3, what is the conclusion using a = 0.004? Calculate the test statistic and determine the P-value. (Round your test statistic to two decimal places and your P-value to four decimal places.) z = p-value = State the conclusion in the problem context. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean drying time is less than 74. O Do not reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean drying time is less than 74. O Reject the null hypothesis. There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean drying time is less than 74. O Reject the null…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman