
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
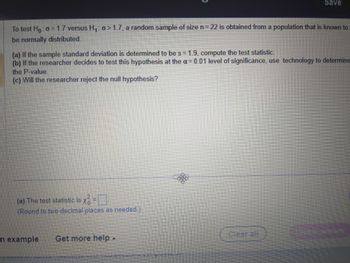
Transcribed Image Text:To test Ho: o = 1.7 versus H₁: o>1.7, a random sample of size n = 22 is obtained from a population that is known to
be normally distributed.
(a) If the sample standard deviation is determined to be s = 1.9, compute the test statistic.
(b) If the researcher decides to test this hypothesis at the a= 0.01 level of significance, use technology to determine
the P-value.
(c) Will the researcher reject the null hypothesis?
(a) The test statistic is x =
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
n example
Get more help.
Save
ER SANS PENSE)
Clear all
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- To test Ho: o = 2.4 versus H₁: o>2.4, a random sample of size n=23 is obtained from a population that is known to be normally distributed. (a) If the sample standard deviation is determined to be s= 3.3, compute the test statistic. (b) If the researcher. decides to test this hypothesis at the x = 0.05 level of significance, use technology to determine the P-value. (c) Will the researcher reject the null hypothesis? (a) The test statistic is x² =. A (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Help me solve this View an example Get more help. Clear all Type here to search Bi C a R T O (2 96°F Sunny Final check 4:15 PM E 6/18/2022arrow_forwardLet x = age in years of a rural Quebec woman at the time of her first marriage. In the year 1941, the population variance of x was approximately σ2 = 5.1. Suppose a recent study of age at first marriage for a random sample of 41 women in rural Quebec gave a sample variance s2 = 3.0. Use a 5% level of significance to test the claim that the current variance is less than 5.1. Find a 90% confidence interval for the population variance. Find the requested confidence interval for the population variance. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) lower and upper limitarrow_forwardIt was reported that last year the average price of gallons of gasoline in a city X was $3.15. This year a sample of 50 gas stations had an average price of $3.10 for a gallon. We assume that the population standard deviation of prices is $0.15. We are interested in determining whether this year's mean price is less than last year. Perform a hypothesis test at the level of significance α=0.05.arrow_forward
- A repeated-measures study with a sample of n=16 participants produces a mean difference of MD=4with a standard deviation of s=8. Use a two-tailed hypothesis test with a=.05 to determine whether it is likely that this sample came from a population with μD=0. b. Now assume that the sample mean difference is MD=10, and once again visualize the sample distribution. Use a two-tailed hypothesis test with α=.05 to determine whether it is likely that this sample came from a population with μD=0. c. Explain how the size of the sample mean difference influences the likelihood of finding a significant mean difference.arrow_forwardMore than 100 million people around the world are not getting enough sleep; the average adult needs between 7.5 and 8 hours of sleep per night. College students are particularly at risk of not getting enough shut-eye. A recent survey of several thousand college students indicated that the total hours of sleep time per night, denoted by the random variable X, can be approximated by a normal model with E(X) = 6.62 hours and SD(X) = 1.13 hours. Question 1. Find the probability that the hours of sleep per night for a random sample of 4 college students has a mean x between 6.57 and 6.93. (use 4 decimal places in your answer) Question 2. Find the probability that the hours of sleep per night for a random sample of 16 college students has a mean x between 6.57 and 6.93. (use 4 decimal places in your answer) Question 3. Find the probability that the hours of sleep per night for a random sample of 25 college students has a mean x between 6.57 and 6.93. (use 4 decimal places in your answer)arrow_forwardAn inventor has developed a new, energy-efficient lawn mower engine. He claims that the engine will run continuously for 5 hours (300 minutes) on a single gallon of regular gasoline. From his stock of 2000 engines, the inventor selects a simple random sample of 40 engines for testing. The engines run for an average of 295 minutes, with a standard deviation of 20 minutes. Test the null hypothesis that the mean run time is µ = 305 minutes against the alternative hypothesis that the mean run time is not 305 minutes. Use p = .08. (Assume that run times for the population of engines are normally distributed.) SE = s / √( n ) t = (x - μ) / SE Compute the standard error (SE) _____________ Degrees of freedom (df) ___________________ t-test statistic (t) __________________________arrow_forward
- In a lake pollution study, the concentration of lead in the upper sedimentary layer of a lake bottom is measured from 25 sediment samples. The sample mean and the standard deviation of the measurements are found to be 0.38 and 0.06, respectively. Suppose Ho : u = 0.34 H1: u# 0.34 (a) State Type I and Type Il errors. (b) Conduct a hypothesis test at 0.01 level of significance by doing the seven-step classical approach. (please show all seven steps, formulas, calculations and the curve)arrow_forwardThe average age at which adolescent girls reach their adult height is 16 years. Suppose you have a sample of 29 adolescent girls who are developmentally delayed, and who have an average age at which they reached their adult height of 17.8 years and a sample variance of 77.4 years. You want to test the hypothesis that adolescent girls who are developmentally delayed have a different age at which they reached their adult height than all adolescent girls. In order to calculate the t statistic, you first need to calculate the estimated standard error. The estimated standard error SM= (round to four decimals)arrow_forwardData provided by the National Association of College Employers indicated that the average starting salary for graduates with a Bachelors Degree in Accounting was $37,000 in 2008. In June 2010 a sample of 48 graduating accounting majors provided a sample average starting salary of $38,100, with a sample standard deviation of $5200. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if it can be assumed that accounting graduates in 2010 had higher average salaries than graduates in 2008, using α = .05.arrow_forward
- To evaluate the effect of a treatment, a sample of n = 8 is obtained from a population with a mean of μ = 40, and the treatment is administered to the individuals in the sample. After treatment, the sample mean is found to be M = 35. (Use the 4-step procedure to conduct the hypothesis test) If the sample variance is s2 = 32, are the data sufficient to conclude that the treatment has a significant effect using a two-tailed test with α = .05? If the sample variance is s2 = 72, are the data sufficient to conclude that the treatment has a significant effect using a two-tailed test with α = .05? Comparing your answer for parts a and b, how does the variability of the scores in the sample influence the outcome of a hypothesis test?arrow_forwardThe college bookstore tells prospective students that the average cost of its textbooks is $92 per book, with a standard deviation of $15. The engineering students think that the average cost of their books is higher than the average for all students. To test the bookstore’s claim against their alternative, the engineering students collect a random sample of size 45, and calculate x = $97.34. Conduct a hypothesis test with α = 0.05 to see if the students’ claim is supported. Use the classical approach.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman