
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The solid shaft is fixed to the support at C and subjected to the torsional loadings and axial load P as shown.
a. Determine the torsional shear stress at Point A (50mm from the center) and Point B (on the Surface)
b. Determine the absolute maximum torsional shear stress in the shaft.
c. sketch the state of stress at point A and draw its corresponding Mohr’s Circle of stress. compute the principal stresses and maximum in-plane stress.
T=10.38kN-m
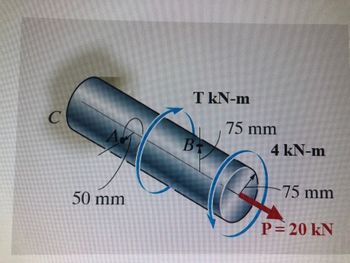
Transcribed Image Text:C
50 mm
T kN-m
B₁
75 mm
4 kN-m
Q
75 mm
P= 20 kN
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- - once answered correctly will UPVOTE!!arrow_forward1.1 Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown. Knowing that d₁ = 30 mm and d₂ = 50 mm, find the average normal stress at the midsection of (a) rod AB, (b) rod BC. d₂ 125 kN B 60 kN 125 kN 1.2 m 0,9 marrow_forwardAll forces applied in the system are in the (x - y) plane. The material point B at the top of the beam is rotated at an angle of 15° counterclockwise. It is required that the shear stress is 17.5 MPa for this rotated material point B. At the bottom point A of the beam it is required that the maximum tensile stress is 110 MPa. Determine the load P and the length d that satisfies these constraints defined for points A and B. Given data: L= 4 b, t = b / 25, c = 2b, b = 1000 mm, e = 12, f=5 b/4- q = 2P/L b/ 4 -b/4- Parrow_forward
- Problem 2. [Concepts: Internal forces in 2D and average normal stress] The bars of the truss each have a cross-sectional area of 1.25 in². a) Determine the average normal stress in each member due to the loading P = 8 kip. State whether the stress is tensile or compressive. b) If the maximum average normal stress in any bar is not to exceed 20 ksi, determine the maximum magnitude P of the loads that can be applied to the truss. 4 ft 4 ft 4 E 0.75 P 0arrow_forwardDetermine the shear stress in pin A (double shear) and the normal stress in DE. The diameter of pin A is 0.125" and the cross section of DE is 0.15"x0.25". -2 ft -2 ft C A E 3 ft 600 lbarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning