
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
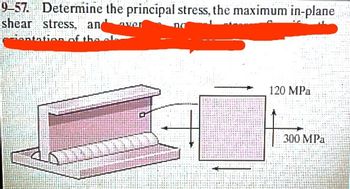
Transcribed Image Text:9-57. Determine the principal stress, the maximum in-plane
shear stress, an
over
120 MPa
STIL
300 MPa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. In the structure below, the vertical bar A has a modulus of elasticity of 210 GPa, a length of 475 mm, and a cross-sectional area of 260 mm². The post B has a modulus of elasticity of 14 GPa, a length of 450 mm, and a cross-sectional area of 5300 mm². The rigid bar CDE is horizontal before the load P = 222 kN is applied. Determine a) b) The axial stress in the vertical bar A and post B; The deflection at point D. C Smooth A pins 480 mm D 870 mm P E Barrow_forwardProblem 9 Consider a thin rectangular cantilever beam of length I, thickness 2c and unit with (t-1). Investigate what problem of plane stress is solved by stress function: 3F 3carrow_forwardWhat are appropriate relations established from the calculation of maximum shear stress in a thin circular tube? 4 (b) t = (a) Tmax Tavg 3 'avg max 3 4 S Rỉ + R2R1+ R3 (c) Tmax when (R, = = 2avg - R.) (d) Tmax 3 A Rỉ + R? Here, (R, > R1) and S is shear force at the cross sectional and A is cross sectional area.arrow_forward
- - once answered correctly will UPVOTE!!arrow_forwardThe question is in the picture. Thanksarrow_forwardAll forces applied in the system are in the (x - y) plane. The material point B at the top of the beam is rotated at an angle of 15° counterclockwise. It is required that the shear stress is 17.5 MPa for this rotated material point B. At the bottom point A of the beam it is required that the maximum tensile stress is 110 MPa. Determine the load P and the length d that satisfies these constraints defined for points A and B. Given data: L= 4 b, t = b / 25, c = 2b, b = 1000 mm, e = 12, f=5 b/4- q = 2P/L b/ 4 -b/4- Parrow_forward
- 3. For the given state of stress, determine the principal planes, the principal stresses, the max shear stress. You must use Mohr's Circle. 20 MPa 32 MPa 55 MPaarrow_forwardDetermine the length of the cantilevered beam so that the maximum bending stress in the beam is equivalent to the maximum shear stress. L Uarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning