
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
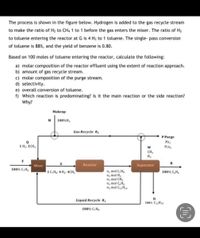
Transcribed Image Text:The process is shown in the figure below. Hydrogen is added to the gas recycle stream
to make the ratio of H2 to CH4 1 to 1 before the gas enters the mixer. The ratio of H2
to toluene entering the reactor at G is 4 Hz to 1 toluene. The single- pass conversion
of toluene is 88%, and the yield of benzene is 0.80.
Based on 100 moles of toluene entering the reactor, calculate the following:
a) molar composition of the reactor effluent using the extent of reaction approach.
b) amount of gas recycle stream.
c) molar composition of the purge stream.
d) selectivity.
e) overall conversion of toluene.
f) Which reaction is predominating? Is it the main reaction or the side reaction?
Why?
Makeup
M 100%H,
Gas Recycle R.
P Purge
YH2
1 H2: 1CH,
YCH,
CH
H2
Mixer
Reactor
Separator
100% C,H,
n, mol C,H,
nz mol H2
n, mol CH,
n, mol C,H.
ng mol C H10
1C,H: 4 H3: 4CH,
100% C,H
Liquid Recycle R
100% C12H10
100% C,H

Transcribed Image Text:Q3: Toluene (C;Hs) reacts with H2 to form benzene (CoHs desired product), but a side
reaction occurs in which diphenyl (C12 H10, undesired product), is formed.
C,H
+
H2 -
C,H, + CH,
20,H.
H2 →
C2H10 + 2CH,
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 21 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I don’t understand thisarrow_forwardBenzene vapor is burned in air. Find the molar enthalpy of the reactants and the products if all heat is extracted from the reaction and the initial and final temperatures are equal. (Assume the H2O product is a liquid)arrow_forwardPlease show every step you used to solve each problem. A vapor mixture of 100 mol/s comprising 55 mol% benzene and 45 mol % toluene is sent to a partial condenser operating at 760 mm Hg. 75 mol% of the toluene in the feed is recovered in the liquid product. Determine all unknown flow rates, compositions, and required heat removal. and do a degree a. Draw a process flow diagram of freedom analysis b. Write out equations used to solve and to calculate all specifications used in Excel Solver unknown flow rates, compositions, C. F Specify the temperature and pressure of the feed as T₁ = 102°C and P₁ = 760 mm Hg. Choose the lowest enthalpy stream (liquid product stream) for a reference condition. Calculate the required heat removal analytically by hand (No Excel Solver). d. Create Enthalpy Tablearrow_forward
- One of the ways that benzene is produced on a large scale is the hydrodealkylation of toluene. C,H,CH; + H, C,H, + CH4 A stream of toluene is mixed with a recycle stream and enters a reactor along with a stream of pure hydrogen. The reaction products at 550 °C enter a condenser, where they are cooled to 41.0 °C. A vapor stream containing Y5CH, = 0.600 mol CH,/mol leaves the process, and a liquid stream containing x66 = 0.810 mol benzene/mol and x6 = 0.190 mol toluene/mol enters a distillation column. The distillate of the column leaves the process at n7 = 668.0 mol/h and contains y7h = 0.9000 mol benzene/mol and y7 = 0.1000 mol toluene/mol. The bottoms of the column contains X8b = 0.250 mol benzene/mol and xgt = 0.750 mol toluene/mol and is recycled back to the fresh feed. Hydrogen is fed into the process at ni = 1183 mol H,/h. This process is carried out at 760 mmHg. A n, mol/h mol H/mol YSH2 YSCH, mol CH_/mol Ysh mol b/mol Ys mol t/mol n̟ mol/h n, mol/h Condenser Улн, тol H/mol Усн,…arrow_forward11.7 mole dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) enter a reactor with 21.6 mole hydrogen (H2) and 37.5 mole oxygen (O2). The following reaction takes place: CH2Cl2 + H2 + 3/2 O2 → COCl2 + 2 H2O 6.4 mole of H2O are produced. Calculate the extent of the reaction.arrow_forwardFresh methanol (CH3OH) reactant is combined with recycled reactant and vaporized before being sent to a fixed-bed reactor. The reactor effluent is then cooled before being sent to the first of two distillation columns. DME (CH3)2O product is taken overhead from the first column. The second column separates the water from the unused methanol. The methanol is recycled back to the front end of the process, and the water is sent to wastewater treatment to remove trace amounts of organic compounds. Draw a block flow diagram for this process. The main reaction is 2CH3OH → (CH3)2O + H2Oarrow_forward
- Aniline is produced by the hydrogenation of nitrobenzene. A small amount of cyclohexylamine is produced as a by-product. Nitrobenzene is fed to the reactor as a vapor with three times the required stoichiometric amount of hydrogen. The conversion of nitrobenzene to the products is 96% and the selectivity to aniline is 85%. Unreacted hydrogen is separated from the reaction products and recycled to the reactor. From the recycle line it is purged to keep the inerts in the recycle stream below 5%. The fresh hydrogen that is fed is 99.5% pure and the rest is inert. Calculate the adiabatic outlet temperature of the reaction products and indicate the relationship with respect to the reference temperature (298.15) (in K):arrow_forwardCalculate the amount of heat required to pass through each section of the graph. Here are the heat capacities and phase change enthalpies of water. ΔHfus or enthalpy of fusion or the first phase change from solid to liquid ΔHfus = 6.01kJ/mol ΔHvap or enthalpy of vaporization or the second phase change from liquid to gas ΔHvap = 40.7kJ/mol cliquid water or specific heat of water in the liquid phase cliquid water = 4.184J/g℃ cice or specific heat of water in the solid phase cice = 2.108J/g℃ cwater vapor or the specific heat of water in the gas phase cwater vapor= 1.996J/g℃arrow_forward4. At 1084 °C solid copper melts to form a liquid. The phase change can be described as Cu(s) → Cu(t). The density of solid and liquid copper are 8.96 g/cm' and 7.75 g/cm' respectively. The enthalpies of combustion of the solid and liquid are -156.06 kJ/mol and -167.92 kJ/mol respectively. The product of combustion of both the solid and liquid is CuO(s). Calculate the standard enthalpy changes for the fusion process in kJ/mol. Calculate the change in internal energy when the sample is under a pressure of 500 kbar. Cu(s) → Cu(e) Solid copper liquid copper enthalples of combustion 8.96 g/cm3 7.75 g 1cm² said: -156.06 kJ/mol liquid-162.42 kJ/molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The