
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
The motor shown in the figure produces a torque of 225 N·m in shaft (1). If the shear stress in shaft (1) must be limited to 56 MPa, determine the minimum acceptable diameter that may be used. Determine the magnitude of the internal torque in shaft (1). Assume that shaft (1) will have a solid circular cross section.
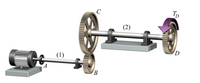
Transcribed Image Text:C
TD
(2)
'D
(1)
A
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The torsional assembly shown in the figure consists of a solid 60-mm diameter aluminum [G = 28 GPa] segment (2) and two bronze [G = 45 GPa] tube segments (1) and (3), which have an outside diameter of 75 mm and a wall thickness of 5 mm. If concentrated torques of TB = 9 kN-m and TC = 9 kN-m are applied in the directions shown, determine the following: 1. Calculate the polar moment of inertia of the bronze tube in mm^4. 2. Calculate the polar moment of inertia of the aluminum tube in mm^4. 3. Calculate the internal torque in the aluminum segment in kN.m 4. Calculate the internal torque in the bronze segment in kN.m 5. Calculate the maximum shear stress in bronze tube segments in MPa. 6. Calculate the maximum shear stress in aluminum tube segment in MPa. 7. Calculate the absolute value of the angle of twist of bronze tube in radian. 8. Calculate the absolute value of the angle of twist of aluminum tube in radian. Kindly answer all questions with complete solution pleasearrow_forwardFor the shaft shown, a. Determine the maximum stress on the shaft and the maximum angle of twist of end D relative to end A. b. If the stress in every section must not exceed 25 MPa, what should be the uniform diameter of the shaft? dAB = 100mm, dbc = 80mm, dcd = 50mm G for the shaft is 80GPa. Consider clockwise torques as negative.arrow_forward5. A 1 cm² rod L is suspended vertically as shown in the figure. The unit weight of the material is y. Determine the normal stress in this rod using differential equations of equilibrium. L X уarrow_forward
- A cylindrical pressure vessel having a radius r = 14 in. and wall thickness t = 0.375 in. is subjected to internal pressure p = 375 psi. In addition, a torque T = 90 kip-ft acts at each end of the cylinder (see figure). (Assume that the structures behave linearly elastically and that the stresses caused by two or more loads may be superimposed to obtain the resultant stresses acting at a point. Consider both in-plane and out-of-plane shear stresses unless otherwise specified.) (a) Determine the maximum tensile stress omay and the maximum in-plane shear stress Tmay in the wall of the cylinder. (Enter the magnitudes in ksi.) o, = ksi Tmax ksi (b) If the allowable in-plane shear stress is 4.5 ksi, what is the maximum allowable torque T? (Enter the magnitude in kip-ft.) kip-ft (c) If T = 150 kip-ft and allowable in-plane shear and allowable normal stresses are 4.5 ksi and 11.5 ksi, respectively, what is the minimum required wall thickness (in inches)? in.arrow_forwardSolve the Problem, Thanksarrow_forward3. A 3-m-long aluminum tube with the cross section shown carries a 200-N-m torque. a. The maximum shear stress in the tube. b. The relative angle of rotation of the ends of the tube. For aluminum, use G = 28 GPa. 100 mm 2.4 mm 2.4 mm 2.4 mm 50 mm 1. 12 mmarrow_forward
- W/FBD,thank youarrow_forwardThe tubular shaft shown in the figure has an external diameter of D = 5.5 in. and an internal diameter of d = 2.75 in. and is subjected to a torque of T= 6825 lb-in. [theta = 31 deg] What is the shear stress at A?in psi What is the shear stress at B?in psi What is the shear stress at C? What is the shear stress at D?in psi What is the shear stress at E?in psiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning