
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
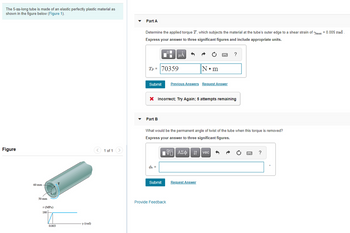
Transcribed Image Text:The 5-m-long tube is made of an elastic perfectly plastic material as
shown in the figure below (Figure 1).
Figure
60 mm -
50 mm
7 (MPa)
180
0.003
T
y (rad)
< 1 of 1 >
Part A
Determine the applied torque T, which subjects the material at the tube's outer edge to a shear strain of max = 0.005 rad.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units.
O
Fi
Tp = |70359
Part B
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
μA
Φ Ξ
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
Submit
N•m
What would be the permanent angle of twist of the tube when this torque is removed?
Express your answer to three significant figures.
Provide Feedback
www
VAΣo↓ vec
ΑΣΦΑ
Request Answer
?
wwwww
F
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Thin square plate PQRS is symmetrically deformed into the shape shown by the dashed lines in the figure.[a = 200 mm, b = 202.1 mm, c = 198.9 mm] For the deformed plate, determine the shear strain xy at corner P?in micro radarrow_forward2.25. A system consists of two rigid end-plates, tied together by three horizontal bars as shown in Fig. 2-42. Through a fabrication error, the central bar, ②2, is 0.0005L too short. All bars are of identical cross section and of steel having E = 210 GPa. Find the stress in each bar after the system has mechanically been pulled together so that the gap A is closed. Ans σ-35 MPa σ = 70 MPa Fig. 2-42arrow_forwardFor the state of stress given in the illustration below, determine the normal and shear stresses on plane A. = -29000 psi A 20° T xy 8 = 7250 psi = 11600 psiarrow_forward
- A solid circular steel shaft of 50 mm diameter, fixed at one end, is subjected to torques as shown below. The shearing modulus of the material is 80 GPa. 500 Nm 250 Nm 500 mm 500 mm 500 mm The rotation of the free end S due to torsion isarrow_forwardA load of 1000 N is applied as shown in figure, given cross-sectional area of bar 1 & 2 is 100 mm² & 80 mm2, young modulus of elasticity E₁ = 120 GPa, E₂ = 150 GPa. Calculate the minimum normal stress (in MPa) (1) (2) P= P= 1000 Narrow_forwardA circular steel tube of length L = 1.5 m is loaded in torsion by torques T (see figure). T r2 (a) If the inner radius of the tube is r, = 41 mm and the measured angle of twist between the ends is 0.5°, what is the shear strain y, (in radians) at the inner surface? (Enter the magnitude.) rad (b) If the maximum allowable shear strain is 0.00026 rad and the angle of twist is to be kept at 0.45° by adjusting the torque T, what is the maximum permissible outer radius (r,)may (in mm)? mm Enter a number.arrow_forward
- The rectangular plate is subjected to force P that causes elongation in the horizontal direction and shrinking in the vertical direction as shown with the dashed line in the figure. Assume a = 550 mm, Δx = 2 mm, and Δy = 1.1 mm. Determine the shear strain γxy at point A? Determine the shear strain γnt at point A? In micro rad What is the normal strain in the x-direction? What is the normal strain in the y-direction? What is the normal strain in the n-direction? Answer in clear way pleasearrow_forwardSOLVE THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM AND SHOW YOUR COMPLETE SOLUTIONS FOR BETTER UNDERSTANDING. ILLUSTRATE FREE BODY DIAGRAM.arrow_forwardA punch for making holes in steel plates is shown in Figure 3. Assume that a punchhaving diameter d = 20 mm is used to punch a hole of 8 mm plate. If force, V = 110 kNis required to create the hole, determine the shear stress in the plate.arrow_forward
- The assembly shown in figure below consists of a light rigid bar AB, pinned at O, that is attached to the steel and aluminum rods. In the position shown, bar AB is horizontal and there is a gap, A = 5 mm, between the lower end of the steel rod and its pin support at C. Compute the stress in the aluminum rod when the lower end of the steel rod is touch to its support. A 0.75 m Steel A = 250 mm E = 200 GPa *i* O 1.5 m Aluminum L = 2m A = 300 mm' E = 70 GPa B Darrow_forwardA 52-kip force acts on a machine part at point A as shown below. The diagram shows the internal normal force, shear force and bending moment acting on a particular RECTANGULAR Cross section. -30in N 10in 26in F=52 kip The value of the bending moment M you would use to find the bending stress on a stress element located 2 inches up from the bottom of the rectangular cross section is closest to: 264 kip-in O a. 408 kip-in Ob. 1,464 kip-in O c. 1,608 kip-inarrow_forwardThe rectangular plate is subjected to force P that causes elongation in the horizontal direction and shrinking in the vertical direction as shown with the dashed line in the figure. Assume a = 550 mm, Δx = 2 mm, and Δy = 1.1 mm. Determine the shear strain γxy at point A?in micro rad Determine the shear strain γnt at point A?in micro rad What is the normal strain in the x-direction?micro£arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning