
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
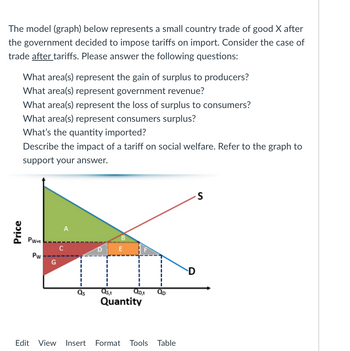
Transcribed Image Text:The model (graph) below represents a small country trade of good X after the government decided to impose tariffs on import. Consider the case of trade after tariffs. Please answer the following questions:
1. What area(s) represent the gain of surplus to producers?
2. What area(s) represent government revenue?
3. What area(s) represent the loss of surplus to consumers?
4. What area(s) represent consumers surplus?
5. What’s the quantity imported?
6. Describe the impact of a tariff on social welfare. Refer to the graph to support your answer.
### Graph Analysis
The graph provides a detailed view of supply and demand dynamics with the imposition of a tariff.
#### Key Elements of the Graph:
- **Axes**:
- The vertical axis is labeled `Price`.
- The horizontal axis is labeled `Quantity`.
- **Curves**:
- `S` represents the supply curve.
- `D` represents the demand curve.
- **Prices**:
- `P_W` is the world price.
- `P_W + t` is the world price plus the tariff.
- **Quantities**:
- `Q_S` is the quantity supplied domestically without tariff.
- `Q_S,t` is the quantity supplied domestically with tariff.
- `Q_D,t` is the quantity demanded domestically with tariff.
- `Q_D` is the quantity demanded domestically without tariff.
- **Areas**:
- `A, B, C, D, E, F, G`: Different regions on the graph representing various economic surpluses and losses.
From the graph:
- The area **A** represents producers' surplus gain due to the tariff.
- The area **B + D** represents government revenue collected from the tariff.
- The areas **B + D** represent the additional cost consumers incur due to the tariff, while **C + E** represent the deadweight loss.
- The area **A + B + C** represents the consumers' surplus without a tariff.
- The quantity imported after the tariff is the difference between `Q_D,t` and `Q_S,t`.
### Impact of a Tariff on Social Welfare:
The implementation of a tariff has multiple effects on the welfare of a country's economy. It increases producer surplus (Area A) as domestic producers benefit from higher prices. However, it also reduces consumer surplus by the sum of areas B, C, D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The United States and Canada have the production possibilities curves shown above. It is determined that the United States has the comparative advantage in peanuts. Will both nations gain from trade if the terms of trade that are offered are 1 Peanut= 3 Corn? Why or why not? Show your work.arrow_forwardDuring the last 20 to 30 years, there have been a number of countries whose economies have experienced important economic expansion and development. One group of countries has been labeled the BRIC countries and the other the VISTA countries. Identify each of the nine countries and provide some insights about their economies and economic importance. The theories of absolute and comparative advantage have been offered as an economic rationale for trade between and among regions and countries. Compare and contrast the two concepts. Which of the two do you think is more important for explaining the growth in global trade during the last 25 years? Why”arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT a common reason why tariffs are used despite being inefficient?arrow_forward
- Topic 3 Assignment The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for maize in Bangladesh. Bangladesh is open to international trade of maize without any restrictions. The world price (Pw) of maize is $245 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout this problem, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. Note: Once you enter a value in a white field, the graph and any corresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly. 470 Supply 420 305 X I I Demand I PRICE (Dollars perton) 445 245 720 D P W 40 80 120 150 200 240 280 320 350…arrow_forwardEconomics Questionarrow_forward(g) Explain how is the production structure (i.e. which goods are produced) affected in each country by opening up to trade. Is this consistent with the empirical evidence we observe in reality? How can this model be modified to produce a less stark result?arrow_forward
- help please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardIn South Korea's state-led industrialization, export subsidies allowed South Korean products (from Samsung, Hyundai) to be sold all over the world. Compare and contrast export subsidies to import tariffs. Which factor might lead a country to decide on one or the other?arrow_forwardThe United States imports a lot of cars, despite having its own auto industry. Each of the following statements are arguments some people could make for restricting imports of cars into the United States. For each statement, identify the threat to the U.S. industry that the argument is trying to counter, and identify the opportunities that would be given up if the argument wins. SELECT THE CORRECT ANSWER a. “Foreign manufacturers are offloading their cheap cars onto the U.S. market. We should stop this so that consumers have access to higher-quality U.S. cars.” -National security requires that strategically important goods be produced domestically. -Protection can help infant industries develop. -Foreign competition may lead to job losses. -Anti-dumping laws prevent unfair competition. -Trade should not enable foreign firms to skirt U.S. regulations. b. “We must foster the innovation of small car companies, like Tesla. Allowing foreign electric vehicle manufacturers…arrow_forward
- Suppose Kenya is open to free trade in the world market for wheat. Because of Kenya's small size, the demand for and supply of wheat in Kenya do not affect the world price. The following graph shows the domestic wheat market in Kenya. The world price of wheat is Pw =$250 per ton. On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing consumer surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producer surplus (PS). (? 490 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 460 CS 430 400 370 PS 340 310 280 Pw 250 220 190 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 QUANTITY (Thousands of tons of wheat) If Kenya allows international trade in the market for wheat, it will import tons of wheat. Now suppose the Kenyan government decides to impose a tariff of $60 on each imported ton of wheat. After the tariff, the price Kenyan consumers pay for a ton of wheat is s and Kenya will import tons of…arrow_forwardSuppose Guatemala is open to free trade in the world market for wheat. Since Guatemala is small relative to the international market, the demand for and supply of wheat in Guatemala have no impact on the world price. The following graph shows the domestic market for wheat in Guatemala. The world price of a ton of wheat is Pw = $400. On the following graph, use the green triangle (triangle symbols) to shade the area representing consumer surplus (CS) when the economy is at the free-trade equilibrium. Then, use the purple triangle (diamond symbols) to shade the area representing producer surplus (PS). (?) PRICE (Dollars per ton) 1200 1100 1000+ 900 800 700 600 500 400 300- 200 0 Domestic Demand 20 40 Domestic Supply 60 80 100 120 140 QUANTITY (Tons of wheat) PW 160 180 200 A CS T PS Because Guatemala participates in international trade in the market for wheat, it will import tons of wheat. Now suppose the Guatemalan government decides to impose a tariff of $200 on each imported ton of…arrow_forwardAnswer the question using 3 step approach 8. What happens to the domestic market when the government allows the importation of more units of rice but with a tariff?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education