
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:How is laminated glass produced?
a) Glass is immersed in potassium salt to replace Na ions with larger K ions
b) Glass surface is quenched in air causing compressive stresses on the surface
c) A polymer is sandwiched between two annealed glass pieces
d) Molten glass is allowed to solidify over a bath of liquid tin
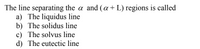
Transcribed Image Text:The line separating the a and (a+ L) regions is called
a) The liquidus line
b) The solidus line
c) The solvus line
d) The eutectic line
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- of iron Steel and cast iron represent different a) Crystal structures b) Alloys c) Allotropes d) Compositesarrow_forwardConsider Cu - Ag Phase diagram below: 1200 A -Liquidus 1000 Liquid -Solidus 779°C (TE) 800 Temperature (°C) 600 400 a C 200 0 B 8.0 (Cag) Solvus a +L a + ß E 71.9 (CE) B+L 91.2 (CBE) B H 1 1 1 1 1 { ( L 20 40 60 80 100 (Cu) Composition (wt% Ag) (Ag) Consider 71.9% Ag-28.1% Cu, which is cooled below 779°C. What is the composition of the phases present just below 779°C and give the amount of beta phase presentarrow_forwardDraw the iron-Fe3C phase diagram. Consider 0.4 and 1.1 wt% C steel alloy. It is cooled slowly from a temperature within austenite phase to room temperature. Show a) microstructure at 1000 °C b) microstructure at 730°C c) microstructure at 715°C and d) microstructure at room temperature e) determine the phase present, the phase compositions at 715 and 730 °C f) What do you say about mechanical properties of these alloys, depending on their microstructure at room temperature?arrow_forward
- question j620 Find the Miller indices of each crystallographic planearrow_forwardCalculate the invariant reactions for Cu-Zn Reaction (eutectic eutectoid peritectic peritectoide) Temperature Transformationarrow_forwardMeasured vs. Theoretical Density A rectangular piece of molybdenum with dimensions 1cm x 2cm x 4cm is placed on a mass balance and is found to have a mass of 81.857 g. a) Use this data to calculate the density of the sample. b) Use atomic and crystal structure data obtained from Wikipedia to calculate the theoretical density of molybdenum. c) Offer a brief explanation as to why these two values might be different.arrow_forward
- 1. four processes. 2. Fill out the blanks by labeling the phase regions. 3. Identify the Indicate an in- termediate compound, if any. 3. Temperature (°C) 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 1538°C 0 (Fe) -1493°C 1394°C 912°C y, Austenite 1 2 0.16 5 0,022 a, Ferrite A N 2.14 Composition (at% C) 15 10 3 1147°C L4 3 4 Composition (wt% C) 4.30 727°C Sketch the microstructure at A, label phases, figure out compositions. 20 Cementite (Fe3C). 5 6 25 6.70arrow_forwardA Pb-30% Sn alloy is cooled from 300°C to 50°C. a) What phases are present for this alloy at 50°C? b) How much of each phase is present at 50°C? c) What is the primary phase and its amount for this alloy at 50°C? Composition (at% Sn) 20 40 60 80 100 327°C 600 300 Liquid 500 232°C a + L 200 ß + L 400 183°C 18.3 61.9 97.8 300 100 a + B 200 100 40 60 80 100 (Pb) Composition (wt% Sn) (Sn) Temperature (°C) 20 Temperature (°F)arrow_forwardA NIO-20 mol % Mgo ceramic is allowed to solidify. (See the figure below.) Temperature (°C) 2800 2600 2400- 2200 2000 L (Ni, Mg)0 40 60 80 MgO Mole percent MgO NIO 20 (a) Determine the composition (in mol% MgO) of the first solid to form. 80 x (b) Determine the composition (in mol% MgO) of the last liquid to solidify under equilibrium conditions. 35 X%arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY