
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
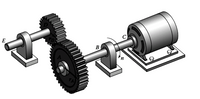
The input shaft to a gearbox, shown in Figure 3, operates at a speed of n1 and
transmits a power of 30 hp. The output power is 27 hp at a speed of n2. (a) What
is the torque of each shaft (in kip · in.) and (b) the efficiency of the gearbox?
Use n1 = 1800 rpm, n2 = 425 rpm. (c) Also compute for the torsional stress on
the 1.5” diameter solid shaft C, and on the hollow shaft at E whose D =2”
and d = 1.5”.
Transcribed Image Text:B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Like will be given :)arrow_forwardA motor supplies 173 hp at 650 rpm to flange A of the shaft. Gear B transfers 75 hp of power to operating machinery in the factory, and the remaining power in the shaft is transferred by gear D. Shafts (1) and (2) are solid aluminum [G = 4400 ksi] shafts that have the same diameter and an allowable shear stress of T = 5.8 ksi. Shaft (3) is a solid steel [G=9100 ksi] shaft with an allowable shear stress of T = 10.2 ksi. Assume that L₁=2.3 ft, L₂=1.2 ft, L3-2.9 ft. Determine: (a) the minimum permissible diameter d₁=d₂ for aluminum shafts (1) and (2). (b) the minimum permissible diameter d3 for steel shaft (3). (c) the rotation angle D/A of gear D with respect to flange A if the shafts have the minimum permissible diameters as determined in (a) and (b). Answers: (a) d₁=d₂ = i (b) d3= i (c) & DIA = i (1) L₁ TB. B (2) L2 in. in. o' (3) L3 Tp Mommu Darrow_forwardSpur gear train is used to transmit the power of 2kW from input gear A rotating at 120 rpm to output gear D through a compound gear BC. The number of teeth on the gear A, B, C and D are 16, 32, 12 and 18 respectively. Given: Module = 4mm, pressure angle=20° The tangential force acting on the gear B is N A D Вarrow_forward
- Parvinbhaiarrow_forwardThe shaft shown in the figure is machined from AISI 1040 CD steel. The shaft rotates at 1600 rpm and is supported in rolling bearings at A and B. The applied forces are F₁ = 1600 lbf and F2 = 640 lbf. A steady torque of 1600 lbf-in is being transmitted through the shaft between the points of application of the forces. 1 / in ] A in [lin -10 in- F₁ in F₂ -10 in- All fillets in R. 12in] 3 in The value of the notch sensitivity is The value of the fatigue stress concentration factor is in NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. What is the value of the theoretical stress concentration factor for torsion, the notch sensitivity, and the fatigue stress concentration factor? (You must provide an answer before moving to the next part.) The value of the theoretical stress concentration factor for torsion isarrow_forwardGear shaft ABCDE is subjected to the torques shown in the figure. Find the internal torque in each seg- ment, and then plot the torsional moment diagram. Assume that the spacing between gears is constant, i.e., 10 in. T1 = T2 = 1000 lb-in. 500 lb-in. A B T3 = 800 Ib-in. C Ta = 500 lb-in. d = 1.0 in. D T; = 800 lb-in. Earrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY