
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
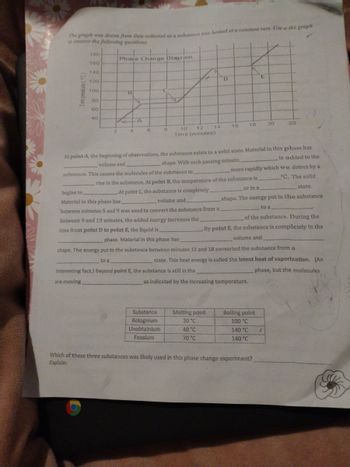
Transcribed Image Text:The graph was drawn from data collected as a substance was heated at a constant rate. Use the graph
an answer the following questions.
180
140
120
100
60
40
Phase Change Diagram
B
T LA
4
8
14
12
10
Time (minutes)
D
to a
interesting fact.) Beyond point E, the substance is still in the
are moving
Substance
Bolognium
Unobtainium
Foosium
16
At point A, the beginning of observations, the substance exists in a solid state. Material in this phase has
is added to the
volume and.
shape. With each passing minute,.
more rapidly which we detect by a
substance. This causes the molecules of the substance to
°C. The solid
rise in the substance. At point B, the temperature of the substance is
begins to
At point C, the substance is completely.
Material in this phase has.
volume and
between minutes 5 and 9 was used to convert the substance from a
Between 9 and 13 minutes, the added energy increases the.
or in a
state.
shape. The energy put to the substance
to a
time from point D to point E, the liquid is
phase. Material in this phase has
shape. The energy put to the substance between minutes 13 and 18 converted the substance from a
state. This heat energy is called the latent heat of vaporization. (An
phase, but the molecules
as indicated by the increasing temperature.
Melting point
20 °C
40 °C
70 °C
of the substance. During the
By point E, the substance is completely in the
volume and
18 20
E
Boiling point
100 °C
140 °C
140 °C
Which of these three substances was likely used in this phase change experiment?
Explain:
)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gmail FC www-awu.aleks.com/ YouTube = O STATES OF MATTER Using a phase diagram to predict phase at a given temperature... Maps Study the following phase diagram of Substance X. 0.8- 19 solid liquid pressure (atm) 100 gas F 200 temperature (K) Use this diagram to answer the following questions. Suppose a small sample of pure X is held at -243. °C and 0.4 atm. What will be the state of the sample? Suppose the temperature is held constant at -243. °C but the nreccure is decreased hv 03 atm What will hannen to the cample? Explanation Check ✓ (choose one) solid liquid gas (choose one) tv Search or type URL Ⓒ2022 McGraw Harrow_forwardThe pressure above a pure sample of solid Substance X at - 72. °C is raised. At what pressure will the sample melt? Use the phase diagram of X below to find your answer. 0.8- Hiquid 0.4- solid gas 0. 200 400 600 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 0.05 atm of the exact answer to be graded correct. atm pressure (atm)arrow_forwardThis is not a graded assigment, is just a practice problem.arrow_forward
- Please helparrow_forwardCreate a model of the atoms of a substance moving through the solid, liquid, and gas states. Be sure to include and label the following items in your model:-the three states of matter -movement and spacing of molecules -loss or gain of kinetic energy and temperature -transfer of heat breaking or building of intermolecular bonds. Include one paragraph (5 to 8 sentences) to explain the movement of energy during phase transitions.arrow_forward140 120 100 80 P 60 40 20 20 a 26 40 80 100 120 Time (min) Answer the following questions for the heating curve of a substance, given above. a) Melting point of the substance is °C. b) The letter represents the temperature range where the solid is being heated is C) In which part of the curve, substance is available in both solid and liquid state simultaneously? d) Which letter represents the state of the substance having definite shape and definite volume? e) The letter represents process of boiling is °C. ) Freezing point of the substance is Temperature ("C)arrow_forward
- A pure solid sample of Substance X is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is heated at a steady rate and the temperature recorded as time passes. Here is a graph of the results: temperature (°C) 180.- 160.- 140.- 120- 100. 80.- 60.- 40. 10. What is the melting point of X? heat added (kJ/mol) Use this graph to answer the following questions: What phase (physical state) of X would you expect to find in the flask after 13 kJ/mol of heat has been added? °C 30. (check all that apply) Osolid O liquid Ogas X 40arrow_forwardAnswer number 4 onlyarrow_forwardIdentify each of the labeled points (indicated with letters) or changes (indicated with two letters separated by an arrow) shown on the phase diagram. 1.00 Y Pressure (atm) 0.50 F 0.10- -150 -75 0 75 150 Temperature ("C) Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. • View Available Hint(s) Reset Help sublimation freezing melting triple point critical point deposition Q ist IG pu. boiling condensation 7. The transition shown by the line from D to C is 8. The transition shown by the line from C to E isarrow_forward
- A student carries out an investigation of the viscosity of various compounds. The data is listed below. Sample Time to flow to the bottom of container A 14.5 seconds 2.1 seconds C 0.9 seconds D 8.3 seconds Which of the following statements below is correct based on the data? A has the weakest intermolecular forces because it has the highest viscosity. A has the strongest intermolecular forces because it has the highest viscosity. C has the strongest intermolecular forces because it has the highest viscosity. C has the weakest intermolecular forces because it has the highest viscosity.arrow_forward4. Match the following phase change description to the phase change name. Freezing Melting Sublimination Deposition 1. Frozen laundry becomes dry on the clothesline 2. Water becomes ice 3. Frost becomes water 4. Ice crystals form on a window panearrow_forwardIt is snowing outside! This process is described by which of the following? Ocondensation O evaporation O sublimation O deposition Freezingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY