
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
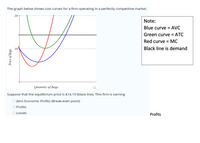
Transcribed Image Text:The graph below shows cost curves for a firm operating in a perfectly competitive market.
20
Note:
Blue curve = AVC
Green curve = ATC
Red curve = MC
Black line is demand
Quantity of Bags
Suppose that the equilibrium price is $14.19 (black line). This firm is earning
O Zero Economic Profits (Break-even point)
O Profits
O Losses
Profits
Price of Bags
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which describes the firms supply curve for the short run with perfect competition? O The section of MC that is above AVC O The section of MC that is above ATC There is no supply curve since it depends on the slope of demand O The section of ATC to the right of its intersection with MC Which describes the long run equilibrium situation for a firm in perfect competition? O Demand is sloping downward and tangent to ATC Demand is horizontal and tangent to the bottom of ATC O Demand is tangent to AVC O There are positive economic profits to motivate firms to keep producingarrow_forwardQuestion 21 please solvearrow_forwardA mattress company operates in a perfectly-competitive environment. If the firm can increase its profits by increasing output, O price is greater than marginal cost. O price is less than marginal cost. O price is equal to marginal cost. losses are minimized.arrow_forward
- 3arrow_forwardPrice (S) AB UD A) $(60-C) × 3 Quantity B) $(60-D) x 2 OC) $(60-B) × 5 OD) $(60-B) × 4 O E) $(60 - A) × 5 MC ATC Refer to the figure above, which indicates the short-run cost data for a typical firm in a perfectly competitive industry. If the price faced by a perfectly competitive firm is equal to $60, then this firm will earn profits of......if it maximizes profits. p = $60 AVCarrow_forwardSuppose the costs of a perfectly competitive firm are given by TC = 30 +3Q+0.5Q2 and MC= 3+Q. The supply equation of the firm is, therefore, Q = -3 + P. If the market price is $13, what is the total profit of the firm? O $20 $130 -$110 O $10arrow_forward
- Price (dollars) 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 80 O increase; increase; increase O remain same; remain same; decrease O decrease; remain same; decrease O decrease; decrease; decrease Short-run Short-run MC AC 100 110 The graph above shows the cost curves for a firm selling in a perfectly competitive market. If the market demand falls due to a recession, the long run equilibrium price will output will ., the firm's and industry output will Output (per day) Long-run ACarrow_forwardWhat is a price taker? A price taker is O A. a firm with a downward-sloping demand curve. O B. a firm that is unable to affect the market price. Oc. a firm with a perfectly inelastic demand curve. O D. a firm that has the ability to charge price greater than marginal cost. O E. a firm that does not seek to maximize profits. When are firms likely to be price takers? A firm is likely to be a price taker when O A. it sells a differentiated product. O B. barriers to entry are substantial. OC. it has market power. O D. it represents a small fraction of the total market,. O E. firms in the industry collude.arrow_forwardSuppose we have a firm in a perfectly competitive market. Assume that we have the usual shaped cost curves. At a market price of $15 the profit maximizing firm produces 53 units. Something changes that causes the firm to produce a quantity of zero at a price of $15 in the short-run. Which of the changes below can explain the change in the firm's behavior? O An increase in the fixed cost and a decrease in the marginal cost. O An increase in the fixed cost. O An increase in the marginal cost. O A decrease in the market price.arrow_forward
- 2. Suppose that the market for wind chimes is a competitive market. The following graph shows the daily cost curves of a particular firm operating in this PRICE (Dollars per wind chime) 40 b) 36 32 28 24 20 16 2 8 4 0 MC 0 2 4 + 10 12 14 16 18 20 QUANTITY (Thousands of wind chimes per day) 8 market: a) In short run, at a market price of $26 per wind chime how much will firm ATC AVC 6 the market price is $26 in th quantity you obtained in question (a), indicate the area that represents firm's profit or loss in short run on the graph. c) What is this firm's shutdown price, that is the price below which it is optimal for the firm to shut down in short run? d) In the long run, all firms can enter and exit the market, and all entrants have the same costs as above. As this market makes the transition to its long-run equilibrium, will the price rise or fall? Will the quantity demanded rise or fall? Will the quantity supplied by each firm rise or fall? Explain your answers. e) Graph the…arrow_forwardSuppose that marginal revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is $20. When the firm produces 10 units, its marginal cost is $20, its average total cost is $22, and its average variable cost is $17. Then to maximize its profit in the short run, the firm A) should stay open and incur an economic loss of $20. B) must decrease its output to increase its profit. C) must increase its output to increase its profit. O D) should not change its production because it is already maximizing its profit and is making an economic profit. E) should shut down.arrow_forwardFigure shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. at the market price $30, the break-even output is: Р. $30-- $25 $13 $5 O a. 1,000 O b. 450 O c. 30 O d. 800 450 MC 800 1,000 AT AVarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education