
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
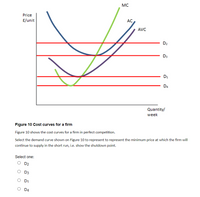
Transcribed Image Text:MC
Price
AC
£/unit
AVC
D2
D3
D1
D4
Quantity/
week
Figure 10 Cost curves for a firm
Figure 10 shows the cost curves for a firm in perfect competition.
the firm will
Select the demand curve shown on Figure 10 to represent to represent the minimum price at whic
continue to supply in the short run, i.e. show the shutdown point.
Select one:
O D2
O D3
O D1
O DA
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the figure below. If the industry is perfectly competitive and the market price is $15, what do we expect to happen in the long run? P $15 S₂ D₂ O O Supply will shift from $1 to $2 O Supply will shift from S2 to $1 000 Demand will shift from D1 to D2 O Demand will shift from D2 to D1 MC ATC MR-Parrow_forwardFigure 14-4 Suppose a firm operating in a competitive market has the following cost curves: Price MC ATC AVC P4 P3 P2 P1 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5 Quantity Refer to Figure 14-4. When price falls from P3 to P1, the firm finds that it should shut down immediately. should produce Q1 units of output. should produce Q3 units of output. decreases its fixed costs.arrow_forwardThe perfectly competitive firm in the market for blueberries is in long run equilibrium. Suddenly consumers expectations of future price changes. They believe that prices will be higher in the future. After this occurs, the long run comes and the market can adjust to long run equilibrium again. The adjustment to long run equilibrium means that the market supply curve will shift to the left. Select one: O True O Falsearrow_forward
- Consider a competitive firm with total costs given by T C(q) = 100 + 10q + q^2. The firm faces a market price p = 50. (a) Graph the AT C, AV C, MC, and MR curves in a single graph, and indicate the profit maximizing level of output. If there are profits, shade the region corresponding to profit and label it. (b) If fixed costs increase from 100 to 500, what happens to the profit maximizing level of output, T R, T C, and π? (c) If fixed costs increase from 100 to 500, should the firm continue to operate in the short-run? What about the long-run?arrow_forward1) The cost curves for a firm in a perfectly competitive industry are given below. Complete the table. If the firm operates in a perfectly competitive market, and the market price is $25 per unit, what Quantity should this firm produce at? TFC TC TVC AVC ATC MC TR S100 S100 1 S100 S130 2 S100 S150 S100 S160 S100 S172 5 S100 S185 6 S100 $210 S100 $240 S100 $280 S100 $330 10 S100 $390 Table 9.1arrow_forwardTotal Revenue $5,000 per Week $2,600 per Week $2,400 per Week Total Variable Cost Total Fixed Cost Let us suppose Harry's, a local supplier of chill and pizza, has the revenue and cost structure shown here. Multiple Choice Harry's should stay open in the short run. Harry's should shut down in the long run. Harry's should shut down in the short run. Harry's should stay open in the short run but shut down in the long run.arrow_forward
- Consider the perfectly competitive market for titanium. Assume that, regardless of how many firms are in the industry, every firm in the industry is identical and faces the marginal cost ( MCMC ), average total cost ( ATCATC ), and average variable cost ( AVCAVC ) curves shown on the following grapharrow_forward6. Deriving the short-run supply curve The following graph plots the marginal cost (MC) curve, average total cost (ATC) curve, and average variable cost (AVC) curve for a firm operating in the competitive market for sun lamps. COSTS (Dollars) 100 20 80 TO 0 □ 5 D MC-D Price (Dollars per lamp) 10 20 32 40 50 60 ATC AVC Quantity (Lamps) DO 15 QUANTITY (Thousands of lamps) 50 For every price level given in the following table, use the graph to determine the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps for the firm. Further, select whether the firm will choose to produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. (Assume that when price exactly equals average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero lamps and the profit-maximizing quantity of lamps.) Lastly, determine whether the firm will earn a profit, incur a loss, or break even at each price. ? Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss?arrow_forwardYou are given the following information for a producer of organic grommets in a perfectly competitive market. TFC = $7 Market price = $16 Quantity MC ($) 11 9 10 4 12 15 6 19 The marginal cost of production appears in the table above. What is the profit-maximizing output? Is the firm making a profit or loss? How much? Output: |(Click to select) v$arrow_forward
- The table below shows the weekly marginal cost (MC) and average total cost (ATC) for Buddies, a purely competitive firm that produces novelty ear buds. Assume the market for novelty ear buds is a competitive market and that the price of ear buds is $6.00 per pair. Buddies Production Costs Quantity MC ATC of Ear Buds ($) ($) 20 1.00 25 2.00 1.20 30 2.46 1.41 35 3.51 1.71 40 4.11 2.01 45 5.43 2.39 50 5.99 2.75 55 8.47 3.27 Instructions: In part a, enter your answer as the closest given whole number. In parts b-d, round your answers to two decimal places. a. If Buddies wants to maximize profits, how many pairs of ear buds should it produce each week? pairs b. At the profit-maximizing quantity, what is the total cost of producing ear buds? 2$ c. If the market price for ear buds is $6 per pair, and Buddies produces the profit-maximizing quantity of ear buds, what will Buddies profit or loss be per week? 2$arrow_forwardQuestion 16 Refer to Figure 5-1 The firm will earn positive economic profits if the price is P4 only O P4 or P3 only P4, P3, or P2 only O any of P4, P3, P2, or P1arrow_forwardThe table below shows the price and cost information for a firm that operates in a perfectly competitive market. Based on this information, what is the profit-maximizing output quantity? Price Quantity Total Cost $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $8 $6 $10 $15 $21 $28 $35 $45 1 2 3 4 5 6 Profit is maximized at a quantity of type your answer. units, where it is equal to $ type your answer. Is the long run price in this market likely to be higher or lower than the current price of $8? type your answer.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education