
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
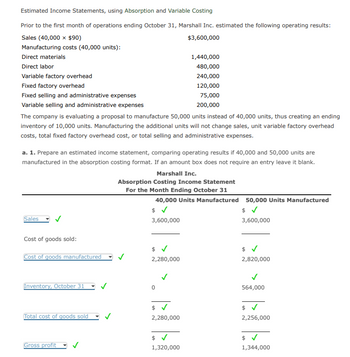
Transcribed Image Text:### Estimated Income Statements Using Absorption and Variable Costing
**Context:**
Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results for manufacturing 40,000 units:
- **Sales (40,000 units at $90 each):** $3,600,000
- **Manufacturing Costs (40,000 units):**
- Direct materials: $1,440,000
- Direct labor: $480,000
- Variable factory overhead: $240,000
- Fixed factory overhead: $120,000
- **Fixed Selling and Administrative Expenses:** $75,000
- **Variable Selling and Administrative Expenses:** $200,000
The proposal is to manufacture 50,000 units instead of 40,000, creating an inventory of 10,000 units. This change will not affect sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, or fixed costs.
#### Instruction:
Prepare an estimated income statement to compare operating results under absorption costing for manufacturing 40,000 and 50,000 units.
---
### Marshall Inc.
**Absorption Costing Income Statement for the Month Ending October 31**
| **Description** | **40,000 Units Manufactured** | **50,000 Units Manufactured** |
|-------------------------------|-------------------------------|-------------------------------|
| **Sales** | $3,600,000 | $3,600,000 |
| **Cost of Goods Sold:** | | |
| - Cost of goods manufactured | $2,280,000 | $2,820,000 |
| - Inventory, October 31 | 0 | 564,000 |
| **Total Cost of Goods Sold** | $2,280,000 | $2,256,000 |
| **Gross Profit** | $1,320,000 | $1,344,000 |
**Explanation:**
The table above illustrates the differences in cost and gross profit when comparing the manufacture of 40,000 units to 50,000 units. Key observations include:
- **Gross Profit Comparison:** The gross profit increases from $1,320,000 to $1,344,000 when additional inventory is created.
- **Inventory Impact:** There is an ending inventory value of $564,000 when manufacturing 50,000 units. This inventory reduces the total cost of goods sold, thus increasing
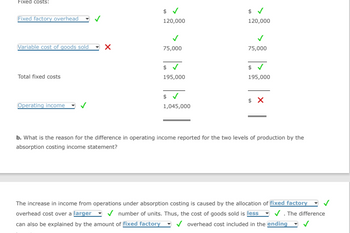
Transcribed Image Text:### Analysis of Costing and Operating Income
#### Fixed Costs:
- **Fixed factory overhead**:
- Amount: $120,000
- Status: Verified (✓)
- **Variable cost of goods sold**:
- Amount: $75,000
- Status: Unverified (✖)
- **Total fixed costs**:
- Total Amount: $195,000
- Status: Verified (✓)
#### Operating Income:
- **Operating income**:
- Amount: $1,045,000
- Status: Verified (✓)
#### Observations:
- **Variable Cost of Goods Sold**: There is a discrepancy noted here, indicated by the unverified status (✖).
#### Explanation:
**b. Reason for Difference in Operating Income:**
The increase in operating income under absorption costing is due to:
- **Allocation of fixed factory overhead** over a **larger** (✓) number of units. This results in a **lower** (✓) cost of goods sold.
- The variations can also be linked to the fixed factory overhead cost included in the **ending** (✓) inventory.
This information is crucial for understanding why different levels of production can lead to variations in reported operating income under absorption costing.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Absorption costing treat fixed manufacturing cost as product cost but variable costing includes only variable cost as product cost.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Variable Costing Income Statement On April 30, the end of the first month of operations, Joplin Company prepared the following income statement, based on the absorption costing concept: Joplin Company Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30 Sales (6, 100 units) $201, 300 Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured (7, 100 units) $163,300 Inventory, April 30 (1,000 units) (23,000) Total cost of goods sold (140, 300) Gross profit $61,000 Selling and administrative expenses (36,830) Operating income $24, 170 If the fixed manufacturing costs were $ 44,091 and the fixed selling and administrative expenses were $18, 040, prepare an income statement according to the variable costing concept. Round all final answers to whole dollars. Joplin Company Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30 $Sales Variable cost of goods sold: $- Select - - Select - - Select - $- Select - - Select - $ - Select - Fixed costs: $Variable cost of goods sold Fixed…arrow_forwardAt the end of the accounting period Tubman, Inc. reports operating income of $50,000, a contribution margin of $15, and a fixed overhead rate of $6 per unit. Under variable costing, if this company produces 100 more units of inventory, then operating income: a. will increase by $1,500 b. will decrease by $1,500 c. will increase by $900 d. will decrease by $900 e. will increase by $600 f. will decrease by $600 g. will not be affected h. Cannot be determinedarrow_forwardA manufacturing company that produces a single product has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price Units in beginning inventory Units produced Units sold Units in ending inventory Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense 154 2,560 2,230 330 51 24 $. 15 16 $92,160 $11,150 The tegross margin for the month under absorption costing is: Multiple Chotce $62.440 S15.610, K Prev 4: of 10 Next > ere to searcharrow_forward
- Preparing variable costing Income Statements, Production exceed sales ReVitalAde produced 13,000 cases of powdered drink mix and sold 12,009 Cases in April 2018. The Sales Price was $29, Variable costs were $12 Per case ($9 manufacturing and selling and administrative), and total fixed costs were $100,000 ($91,900 manufacturing overhead and $9,000 selling and administrative). The company had no beginning Finished Goods Inventory. Requirements Prepare the April income statement using variable costing. Determine the product cost per unit and the total cost of the 1,000 cases in the Finished Goods Inventory as of April 30.arrow_forwardneed helparrow_forwardVariable Costing Income Statement On April 30, the end of the first month of operations, Joplin Company prepared the following income statement, based on the absorption costing concept: Joplin Company Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30 Sales (5,600 units) Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured (6,600 units) Inventory, April 30 (900 units) Total cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling and administrative expenses Operating income Variable cost of goods sold: $138,600 (18,900) Fixed costs: $162,400 If the fixed manufacturing costs were $30,492 and the fixed selling and administrative expenses were $12,600, prepare an income statement according to the variable costing concept. Round all final answers to whole dollars. Joplin Company Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30 (119,700) $42,700 (25,720) $16,980arrow_forward
- At the end of the first year of operations, 5,600 units remained in the finished goods inventory. The unit manufacturing costs during the year were as follows: Direct materials $29.10 Direct labor 13.20 Fixed factory overhead 4.80 Variable factory overhead 4.20 Determine the cost of the finished goods inventory reported on the balance sheet under (a) the absorption costing concept and (b) the variable costing concept. Absorption costing $ Variable costing $arrow_forwardAaron Corporation, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price Units in beginning inventory Units produced Units sold Units in ending inventory Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead. Variable selling and administrative expense Multiple Choice Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense What is the unit product cost for the month under variable costing? $110 per unit $137 per unit $143 0 $120 per unit 6,850 6,550 300 $93 per unit $23 $53 $17 $17 $184,950 $ 27,300arrow_forwardKeyser Corporation, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations Selling price $113 Units in beginning inventory 3700 Units produced 8,600 Units sold 8,700 Units in ending inventory 600 Variable costs per unit: Direct materials: Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense $ 24 $ 41 $5 $ 15 $68,800 $ 162,700 The company produces the same number of units every month, although the sales in units very from month to month. The company's variable costs per unit and total fixed costs have been constant from month to month What is the net operating income for the month under absorption costing?arrow_forward
- On October 31, the end of the first month of operations, Maryville Equipment Company pre- pared the following income statement, based on the variable costing concept: Maryville Equipment Company Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended October 31 Sales (220,000 units).... $ 7,920,000 Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods manufactured . Inventory, October 31 (45,000 units) .. Total variable cost of goods sold... Manufacturing margin....... Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 6,360,000 (1,080,000) (5,280,000) $ 2,640,000 (330,000) $ 2,310,000 Contribution margin... Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs ... Fixed selling and administrative expenses.. $ 530,000 100,000 Total fixed costs.... (630,000) $ 1,680,000 Operating income... Prepare an income statement under absorption costing.arrow_forwardGrace Corporation, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price Units in beginning inventory Units produced Units sold Units in ending inventory Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative expense Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense $6,400 $18,600 $5,600 SS $(20,400) $ $ $ 95 0 3,500 3,100 400 22 What is the net operating income for the month under absorption costing? 2975 39 55,900 3,000arrow_forwardVariable Costing Income Statement On April 30, the end of the first month of operations, Joplin Company prepared the following income statement, based on the absorption costing concept: Joplin Company Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30 Sales (3,700 units) $74,000 Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured (4,300 units) $60,200 Inventory, April 30 (600 units) (8,400) Total cost of goods sold (51,800) Gross profit $22,200 Selling and administrative expenses (13,480) Operating income $8,720 If the fixed manufacturing costs were $16,254 and the fixed selling and administrative expenses were $6,600, prepare an income statement according to the variable costing concept. Round all final answers to whole dollars.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education