
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
The following information was taken from the records of Tinker Enterprises: Year 1 Year 2 Beginning Inventory $60,000 $72,000 Cost of goods purchased 480,000 504,000 Cost of goods available for sale 540,000 576,000 Ending inventory 72,000 66,000 Cost of goods sold $468,000 $510,000 The following two errors were made in the physical inventory counts: 1. Year 1 ending inventory was understated by $9,600 2. Year 2 ending inventory was overstated by $4,800 Compute the correct cost of goods sold for both years. Year 1 Year 2 Cost of goods sold $ tA $.
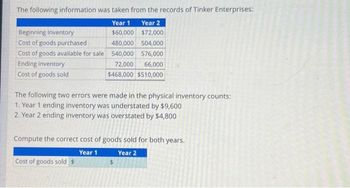
Transcribed Image Text:The following information was taken from the records of Tinker Enterprises:
Year 1 Year 2
Beginning Inventory
$60,000
$72,000
Cost of goods purchased
480,000 504,000
Cost of goods available for sale 540,000
576,000
72,000
66,000
$468,000 $510,000
Ending inventory
Cost of goods sold
The following two errors were made in the physical inventory counts:
1. Year 1 ending inventory was understated by $9,600
2. Year 2 ending inventory was overstated by $4,800
Compute the correct cost of goods sold for both years.
Year 1
Year 2
Cost of goods sold $
$
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Give the answer of 4.(a) and 4.(b).arrow_forwardShanrock Company uses the periodic inventory method and had the following inventory information available: 1/1 1/20 7/25 10/20 1. 2. 3. Beginning Inventory 4. (a) Purchase 4. (b) Purchase Purchase Units Unit Cost 100 400 Answer the following independent questions. 200 300 1,000 $4 $6 $7 $8 Total Cost A physical count of inventory on December 31 revealed that there were 400 units on hand. $400 2,400 1,400 2,400 $6,600 Assume that the company uses the FIFO method. The value of the ending inventory at December 31 is Assume that the company uses the Average-Cost method. The value of the ending inventory on December 31 is Assume that the company uses the LIFO method. The value of the ending inventory on December 31 is Determine the difference in the amount of income that the company would have reported if it had used the FIFO method instead of the LIFO method. Would income have been greater or less? $ $ $ $arrow_forwardAce Company reported the following information for the current year: Sales Cost of goods sold: Beginning inventory Cost of goods purchased Cost of goods available for sale Ending inventory Cost of goods sold Gross profit $ 417,000 $ 142,500 280,000 422,500 151,000 271,500 $ 145,500 The beginning inventory balance is correct. However, the ending inventory figure was overstated by $27,000. Given this information, the correct gross profit would be: Multiple Choice $118,500. $145,500. $172,500. $131.500arrow_forward
- I have answer for a and b Solve carrow_forwardLower-of-cost-or-market inventory Data on the physical inventory of Ashwood Products Company as of December 31 follow: Description InventoryQuantity Market Value per Unit(Net Realizable Value) B12 38 $57 E41 18 180 G19 33 126 L88 18 550 N94 400 7 P24 90 18 R66 8 250 T33 140 20 Z16 15 752 Quantity and cost data from the last purchases invoice of the year and the next-to-the-last purchases invoice are summarized as follows: Description LastPurchasesInvoiceQuantityPurchased LastPurchasesInvoiceUnit Cost Next-to-the-LastPurchasesInvoiceQuantityPurchased Next-to-the-LastPurchasesInvoiceUnit Cost B12 30 $60 30 $59 E41 35 178 20 180 G19 20 128 25 129 L88 10 563 10 560 N94 500 8 500 7 P24 80 22 50 21 R66 5 248 4 260 T33 100 21 100 19 Z16 10 750 9 745 Required: Determine the inventory at cost and also at the lower of cost or market applied on an item-by-item basis, using the first-in, first-out method. Record the appropriate unit costs on the…arrow_forwardIf Wakowski Company's ending inventory was actually $86,000 but was adjusted at year end to a balance of $68,000 in error, what would be the impact on the presentation of the balance sheet and income statement for the year that the error occurred, if any? If no entry is required, select "None" and leave the amount boxes blank. Balance Sheet: Merchandise Inventory $4 Current Assets Total Assets Retained Earnings Income Statement: Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit/Gross Margin Net Incomearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education