
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
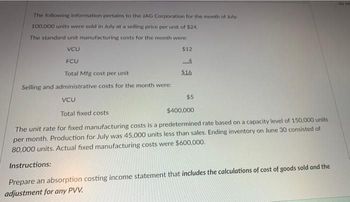
Transcribed Image Text:The following information pertains to the JAG Corporation for the month of July
100,000 units were sold in July at a selling price per unit of $24.
The standard unit manufacturing costs for the month were:
VCU
$12
FCU
4
Total Mfg cost per unit
$16
Selling and administrative costs for the month were:
$5
VCU
Total fixed costs
$400,000
The unit rate for fixed manufacturing costs is a predetermined rate based on a capacity level of 150,000 units
per month. Production for July was 45.000 units less than sales. Ending inventory on June 30 consisted of
80,000 units. Actual fixed manufacturing costs were $600,000.
Instructions:
Prepare an absorption costing income statement that includes the calculations of cost of goods sold and the
adjustment for any PVV.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Pattison Products, Inc., began operations in October and manufactured 40,000 units during themonth with the following unit costs: Direct materials $5.00Direct labor 3.00Variable overhead 1.50Fixed overhead* 7.00Variable marketing cost 1.20*Fixed overhead per unit 5 $280,000/40,000 units produced 5 $7. Total fixed factory overhead is $280,000 per month. During October, 38,400 units were sold at aprice of $24, and fixed marketing and administrative expenses were $130,500.Required:1. Calculate the cost of each unit using absorption costing.2. How many units remain in ending inventory? What is the cost of ending inventory usingabsorption costing?3. Prepare an absorption-costing income statement for Pattison Products, Inc., for the monthof October.4. What if November production was 40,000 units, costs were stable, and sales were 41,000units? What is the cost of ending inventory? What is operating income for November?arrow_forwardRasmussen Corporation expects to incur indirect overhead costs of $80,000 per month and direct manufacturing costs of $12 per unit. The expected production activity for the first four months of the year are as follows. January February March April Estimated production in units 6,000 7,000 3,000 4,000 Required Calculate a predetermined overhead rate based on the number of units of product expected to be made during the first four months of the year. Allocate overhead costs to each month using the overhead rate computed in Requirement a. Calculate the total cost per unit for each month using the overhead allocated in Requirement b.arrow_forwardSalem Company has the following costs information for June where production volume is 2,000 units: 7. The variable cost and fixed cost per unit respectively are: A) $8.75 and $1.50. B) $8.75 and $0.25. C) $4.25 and $3.00. D) $8.50 and $12.00. B) fixed cost per unit. C) total variable cost. D) total cost per unit. A) 1,000 B) 1,800 Direct materials Direct labor 8. If production changes to 2.200 units, which cost will remain the same? A) variable cost per unit. C) 3,200 D) 2,600 Straight-line depreciation Rent expenses other fixed costs 9.The production budget shows expected unit sales of 16,000. Beginning finished goods units are 1,800. Required production units are 16,800. What are the desired ending finished goods units? A) B) D) 10. The production budget shows expected unit sales are 50,000. The required production units are 52,000. What are the beginning and desired ending finished goods units, respectively? Ending Units 2,000 5,000 $8,500 $9,000 5800 Beginning Units 5,000 3.000…arrow_forward
- The following is a summary of costs related to a month of manufacturing products: Direct Materials and Direct Labor = $225,000.00 Indirect Materials, Indirect Labor, and other actual FOH costs = $30,000.00 FOH costs applied to WIP during the month = $17,000.00 From the following, select the journal entry used to record the FOH applied to production during the month. Group of answer choices a) Debit FOH 17,000 and Credit WIP 17,000 b) Debit WIP 30,000 and Credit FOH 30,000 c) Debit FOH 30,000 and Credit Accounts Payable 30,000 d) Debit WIP 17,000 and Credit FOH 17,000arrow_forwardSheridan Inc., which produces a single product, has prepared the following standard cost sheet for one unit of the product. Direct materials (8 pounds at $3.30 per pound) Direct labor (1 hours at $12.00 per hour) $26.40 $12.00 During the month of April, the company manufactures 240 units and incurs the following actual costs. Direct materials purchased and used (2,300 pounds) $8,050 Direct labor (280 hours) $3,304 Compute the total, price, and quantity variances for materials and labor. Total materials variance $ Materials price variance $ Searcharrow_forwardA department had the following information for the month: Total materials costs P45,000 Conversion cost per unit P3.00 Total manufacturing cost per unit P5.50 What are the equivalent units of production for materials?arrow_forward
- Alpesharrow_forwardThompson Company uses a standard cost system for its single product. The following data are available: Actual experience for the year: Purchases of raw materials (15,000 yards at $13): $ 195,000 Raw material used in production: 12,000 yards Direct labor costs (10,200 hours at $10): $ 102,000 Units produced: 12,600 Standards per unit of product: Raw materials: 1.1 yards at $15 per yard Direct labor: 8 hours at $9.50 per hour What is the materials price variance for the year? What is the materials quantity variance for the year?arrow_forwardElfalan Corporation produces a single product. The cost of producing and selling a single unit of this product at the company's normal activity level of 51,000 units per month is as follows: Per Unit Direct materials $ 48.10 Direct labor $ 9.20 Variable manufacturing overhead $ 2.20 Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 19.50 Variable selling & administrative expense $ 4.00 Fixed selling & administrative expense $ 19.00 The normal selling price of the product is $108.10 per unit. An order has been received from an overseas customer for 3,100 units to be delivered this month at a special discounted price. This order would not change the total amount of the company's fixed costs. The variable selling and administrative expense would be $2.30 less per unit on this order than on normal sales. Direct labor is a variable cost in this company. Suppose there is ample idle capacity to produce the units required by the overseas customer and the special discounted price on…arrow_forward
- Hutto Corp. has set the following standard direct materials and direct labor costs per unit for the product It manufactures. Direct materials (15 lbs. @ $4 per lb.) Direct labor (2 hrs. @ $15 per hr.) During May the company incurred the following actual costs to produce 8,100 units. Direct materials (125,300 lbs. @ $3.80 per lb.) Direct labor (20,400 hrs. @ $15.10 per hr.). AH = Actual Hours SH = Standard Hours AR = Actual Rate SR = Standard Rate AQ - Actual Quantity SQ - Standard Quantity = AP = Actual Price SP = Standard Price (1) Compute the direct materials price and quantity variances. (Indicate the effect of each varlance by selecting for favorable, unfavorable, and no varlance.) (2) Compute the direct labor rate variance and the direct labor efficiency variance. (Indicate the effect of each varlance by selecting for favorable, unfavorable, and no varlance. Round "Rate per hour" answers to 2 decimal places.) Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. 0 $60…arrow_forwardThe table below shows monthly data collected on production costs and on the number of units produced over a twelve month period. Month Total Production Costs Level of Activity (Units Produced) July $ 230,000 3,500 August 250,000 3,750 September 260,000 3,800 October 220,000 3,400 November 340,000 5,800 December 330,000 5,500 January 200,000 2,900 February 210,000 3,300 March 240,000 3,600 April 380,000 5,900 May 350,000 5,600 June 290,000 5,000 Required: Determine the variable cost per unit and the fixed cost using the high-low method. What is the equation of the total mixed cost function? Prepare the scatter diagram, clearly showing any outliers Using the line of best-fit, determine the company’s fixed cost per month and the variable cost per unit. (Use 0 & 5,000 units. In view of the department’s cost behaviour pattern, which of the two methods appear more appropriate?…arrow_forwardBramble Company produced 20, 300 units and sold 18, 060 during the current year. Under absorption costing, net income was $25,900. Fixed overhead was $162, 400. Determine the net income under variable costing. (Round per unit calculations to 2 decimal places, eg. 15.25 and final answer to O decimal places, eg. 125.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education