
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9781285165912
Author: N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please correct answer and don't use hand rating
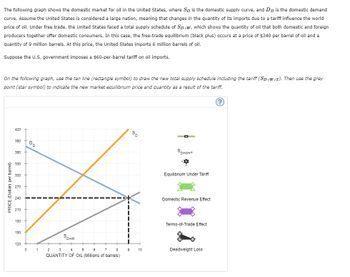
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the domestic market for oil in the United States, where Sp is the domestic supply curve, and DD is the domestic demand
curve. Assume the United States is considered a large nation, meaning that changes in the quantity of its imports due to a tariff influence the world
price of oil. Under free trade, the United States faced a total supply schedule of SD+w, which shows the quantity of oil that both domestic and foreign
producers together offer domestic consumers. In this case, the free-trade equilibrium (black plus) occurs at a price of $240 per barrel of oil and a
quantity of 9 million barrels. At this price, the United States imports 6 million barrels of oil.
Suppose the U.S. government imposes a $60-per-barrel tariff on oil imports.
On the following graph, use the tan line (rectangle symbol) to draw the new total supply schedule including the tariff (SD+W+T). Then use the grey
point (star symbol) to indicate the new market equilibrium price and quantity as a result of the tariff.
PRICE (Dollars per barrel)
420
390
360
330
300
270
240
210
180
So
SD+W+T
Equilibrium Under Tariff
Domestic Revenue Effect
Terms-of-Trade Effect
150
Sp+w
120
0 1 2 3 4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Deadweight Loss
QUANTITY OF OIL (Millions of barrels)
(?)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Assume two countries, Thailand (T) and Japan (J), have one good: cameras. The demand (d) and supply (s) for cameras In Thailand and Japan is described by the following functions: QsT=-5+14P QsJ=-10+14P QdT=60-P QdJ=80-P P is the price measured in a common currency used in both countries, such as the Thai Baht. Compute the equilibrium price (P) and quantities in each country without trade. Now assume that free trade occurs. The free-trade price goes to 56.36 Baht. Who exports and Imports cameras and in what quantities?arrow_forwardTrade has income distribution effects. For example, suppose that because of a government-negotiated reduction in trade barriers, trade between Germany and the Czech Republic increases. Germany sells house paint to the Czech Republic. The Czech Republic sells alarm clocks to Germany. Would you expect this pattern of trade to increase or decrease jobs and wages in the paint industry in Germany? The alarm clock industry in Germany? The paint industry in Czech Republic? The alarm clock industry in Czech Republic? What has to happen for there to be no increase in total unemployment in both countries?arrow_forwardFrom the Work It Out Effects of Trade Barriers, you can see that a tariff raises the price of imports. What is interesting is that the price rises by less than the amount of the tariff. Who pays the rest of the tariff amount? Can you show this graphically?arrow_forward
- The country of Pepperland exports steel to the Land of Submarines. Information for the quantity demanded (Qd) and quantity supplied (Qs) in each country, in a world without trade, are given in Table 34.6 and Table 34.7. What would be the equilibrium price and quantity in each country in a world without trade? How can you tell? What would be the equilibrium price and quantity in each country if trade is allowed to occur? How can you tell? Sketch two supply and demand diagrams, one for each country, in the situation before trade. On those diagrams, show the equilibrium price and the levels of exports and imports in the world after trade. If the Land of Submarines imposes an anti- dumping import quota of 30, explain in general terms whether it will benefit or injure consumers and producers in each country. Does your general answer change if the Land of Submarines imposes an import quota of 70?arrow_forwardExplain how a subsidy on agricultural goods like sugar adversely affects the income of foreign producers of imported sugar.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of MicroeconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781305156050Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781285165912
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Microeconomics
Economics
ISBN:9781305156050
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Exploring Economics
Economics
ISBN:9781544336329
Author:Robert L. Sexton
Publisher:SAGE Publications, Inc

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning