
Principles of Economics 2e
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9781947172364
Author: Steven A. Greenlaw; David Shapiro
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 34, Problem 57P
The country of Pepperland exports steel to the Land of Submarines. Information for the quantity demanded (Qd) and quantity supplied (Qs) in each country, in a world without trade, are given in Table 34.6 and Table 34.7.
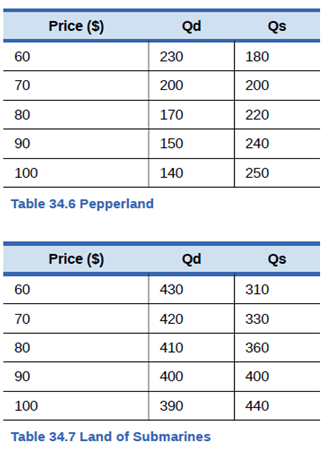
- What would be the
equilibrium price and quantity in each country in a world without trade? How can you tell? - What would be the equilibrium price and quantity in each country if trade is allowed to occur? How can you tell?
- Sketch two
supply and demand diagrams, one for each country, in the situation before trade. - On those diagrams, show the equilibrium price and the levels of exports and imports in the world after trade.
- If the Land of Submarines imposes an anti- dumping import quota of 30, explain in general terms whether it will benefit or injure consumers and producers in each country.
- Does your general answer change if the Land of Submarines imposes an import quota of 70?
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
If Bangladesh is open to international trade of wheat without any restrictions, it will import
the full value for your answer, accounting for the horizontal axis units.)
Suppose the Bangladeshi government wants to reduce imports to exactly 200,000 bushels of wheat to help domestic producers. A tariff of S
per bushel will achieve this.
A tariff set at this level would raise $
bushels of wheat. (Note: Be sure to enter
in revenue for the Bangladeshi government.
The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for maize in Bangladesh. The world price (Pw) of maize is $255 per ton and is
represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world
price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic
suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place.
455
Domestic Demand
Domestic Supply
430
405
380
355
330
305
280
Pw
255
230
205
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
QUANTITY (Tons of maize)
If Bangladesh is open to international trade in maize without any restrictions, it will import
300 tons of maize.
Suppose the Bangladeshi government wants to reduce imports to exactly 100 tons of maize to help domestic producers. A tariff of $
per ton
will achieve this.
A tariff set at this level would raise $
in revenue for the…
The world price of wine is below the price that would prevail in Canada in the absence of trade. Assume that Canadian imports of wine are a small part of
total world wine production.
The following graph shows the Canadian market for wine under free trade.
Use the green triangle (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus when Canada is open to trade. Then use the purple triangle (diamond symbol) to
shade producer surplus in this case.
Price of Wine
Domestic Demand
Quantity of Wine
Domestic Supply
World Price
Consumer Surplus
Producer Surplus
(?)
Chapter 34 Solutions
Principles of Economics 2e
Ch. 34 - Explain how a tariff reduction causes an Increase...Ch. 34 - Explain how a subsidy on agricultural goods like...Ch. 34 - Explain how trade barriers save jobs in protected...Ch. 34 - Explain how trade barriers raise wages in...Ch. 34 - How does international trade affect working...Ch. 34 - Do the jobs for workers in low-income countries...Ch. 34 - How do trade barriers affect the average Income...Ch. 34 - How does the cost of saving jobs in protected...Ch. 34 - Explain how predatory pricing could be a...Ch. 34 - Why do low-income countries like Brazil, Egypt, or...
Ch. 34 - Explain the logic behind the race to the bottom...Ch. 34 - What are the conditions under which a country may...Ch. 34 - Why is the national security argument not...Ch. 34 - Assume a perfectly competitive market and the...Ch. 34 - What is the difference between a free trade...Ch. 34 - Why would countries promote protectionist laws,...Ch. 34 - What might account for the dramatic increase in...Ch. 34 - How does competition, whether domestic or foreign,...Ch. 34 - What are the gains from competition?Ch. 34 - Who does protectionism protect? From what does it...Ch. 34 - Name and define three policy tools for enacting...Ch. 34 - How does protectionism affect the price of the...Ch. 34 - Does international trade, taken as a whole,...Ch. 34 - Is international trade likely to have roughly the...Ch. 34 - How is international trade, taken as a whole,...Ch. 34 - Is international trade likely to have about the...Ch. 34 - What are main reasons for protecting infant...Ch. 34 - What is dumping? Why does prohibiting it often...Ch. 34 - What is the race to the bottom scenario?Ch. 34 - Do the rules of international trade require that...Ch. 34 - What is the national interest argument for...Ch. 34 - Name several of the international treaties where...Ch. 34 - What is the general trend of trade barriers over...Ch. 34 - If opening up to free trade would benefit a...Ch. 34 - Who gains and who loses from trade?Ch. 34 - Why is trade a good thing if some people lose?Ch. 34 - What are some ways that governments can help...Ch. 34 - Show graphically that for any tariff, there is an...Ch. 34 - From the Work It Out Effects of Trade Barriers,...Ch. 34 - If trade barriers hurt the average worker in an...Ch. 34 - Why do you think labor standards and working...Ch. 34 - How would direct subsidies to key industries be...Ch. 34 - How can governments identify good candidates for...Ch. 34 - Microeconomic theory argues that it is...Ch. 34 - How do you think Americans would feel if other...Ch. 34 - Is it legitimate to impose higher safety standards...Ch. 34 - Why might the unsafe consumer products argument be...Ch. 34 - Why might a tax on domestic consumption of...Ch. 34 - Why do you think that the GAIT rounds and, more...Ch. 34 - An economic union requires giving up some...Ch. 34 - What are some examples of innovative products that...Ch. 34 - In principle, the benefits of international trade...Ch. 34 - Economists sometimes say that protectionism is the...Ch. 34 - Trade has income distribution effects. For...Ch. 34 - Assume two countries, Thailand (T) and Japan (J),...Ch. 34 - You have just been put in charge of trade policy...Ch. 34 - The country of Pepperland exports steel to the...
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Ravenna Candles recently purchased candleholders for resale in its shops. Which of the following costs would be...
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
S4–14 Calculating the current ratio
Learning Objective 6
End of Line Montana Registration has these account b...
Horngren's Accounting (12th Edition)
E2-13 Identifying increases and decreases in accounts and normal balances
Learning Objective 2
Insert the mis...
Horngren's Accounting (11th Edition)
Define cost object and give three examples.
Cost Accounting (15th Edition)
Discussion Questions 1. What characteristics of the product or manufacturing process would lead a company to us...
Managerial Accounting (4th Edition)
Prepare a production cost report and journal entries (Learning Objectives 4 5) Vintage Accessories manufacture...
Managerial Accounting (5th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- From the Work It Out Effects of Trade Barriers, you can see that a tariff raises the price of imports. What is interesting is that the price rises by less than the amount of the tariff. Who pays the rest of the tariff amount? Can you show this graphically?arrow_forwardConsider two countries: South Korea and Taiwan. Taiwan can produce one million mobile phones per day at the cost of 10 per phone and South Korea can produce 50 million mobile phones at 5 per phone. Assume these phones are the same type and quality and there is only one price. What is the minimum price at which both countries will engage in trade?arrow_forwardPlease answer only question 3.4 and 3.5arrow_forward
- The following graph shows the same domestic demand and supply curves for tangerines in Guatemala. Suppose that the Guatemalan government changes its international trade policy to allow free trade in tangerines. The horizontal black line (Pw) represents the world price of tangerines at $500 per ton. Assume that Guatemala's entry into the world market for tangerines has no effect on the world price and there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in tangerines. Also assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand s much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. Use the green triangle (triangle symbol) to shade consumer surplus, and then use the purple triangle (diamond symbol) to shade producer surplus. o sha (? Domestic Supply 620 Domestic Demand 590 Consumer Surplus 560 530 Producer Surplus 500 P. 470 ш 440 410 380 350 320 100 125 150 175 QUANTITY (Tons of tangerines) 25 50 75 200 225 250 When Guatemala allows free…arrow_forwardThe nation of textilia Does not allow imports of clothing. In it’s equilibrium Without trade, a T-shirt cost $24, and the equilibrium quantity is 4 million T-shirts. One day, after reading Adam Smith’s ‘The wealth of Nations’ While on vacation, the president decides to open the textilian market to international trade. The market price of a T-shirt falls to the world price of $16. The number of T-shirts consumed in textilia arises to 8 million, while the number of T-shirts produced declines to 2 million.arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for maize in Burundi. The world price (Pw) of maize is $260 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 530 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 500 470 440 410 380 350 320 270, 260 290 260 230 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 QUANTITY (Tons of maize) PRICE (Dollars per ton)arrow_forward
- The nation of Textilia does not allow imports of clothing. In its equilibrium without trade, a T-shirt costs $20, and the equilibrium quantity is 3 million T-shirts. After reading Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations while on vacation, the president decides to open the Textilian market to international trade. The market prices of a T-shirt falls to the world price of $16. The number of T-shirts consumed in Textilia rises to 4 million, while the number of T-shirts produced declines to 1 million. Illustrate the situation just described in a graph. Your graph should show all the numbers. Calculate the change in consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus that results from opening trade. (Hint: Recall that the area of a triangle is ½ x base x height.)arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for maize in Burundi. The world price (Pw) of maize is $270 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 450 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 430 410 390 370 350 330 310 290 P 270 250 40 80 120 180 200 240 280 320 360 400 QUANTITY (Tons of maize) If Burundi is open to international trade in maize without any restrictions, it will import tons of maize. Suppose the Burundian government wants to reduce imports to exactly 160 tons of maize to help domestic producers. A tariff of per ton will achieve this. A tariff set at this level would raise $ in revenue for the…arrow_forwardThe nation of Textilia does not allow imports of clothing. In its equilibrium without trade, a T-shirt costs $20 and the equilibrium quantity is 3 million T-shirts. One day, after reading Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations while on vacation, the president decides to open the Textilian market to international trade. The market price of a T-shirt falls to the world price of $16. The number of T-shirts consumed in Textilia rises to 4 million, while the number of T-shirts produced declines to 1 million. If the domestic demand curve and domestic supply are both linear, the resulting increase in the total surplus in the Textilian T-shirt market is about Zero dollars $6 million $14 million) $4 million $12 million $8 millionarrow_forward
- The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for wheat in New Zealand. The world price (PWPW) of wheat is $255 per bushel and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of wheat and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in wheat. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place.arrow_forwardAlthough both tariffs and quotas are tools used to restrict or reduce trade, which of the statements best describes their differences? which sentence is true? Tariffs are a subsidy for exported goods, and quotas act as a minimum limit of exports. Tariffs are a tax on imported goods, and quotas are limits on the number of imported goods. Tariffs are a tax on exported goods, and quotas are limits on the number of exported goods. Tariffs are a tax on imported goods, and quotas are limits on the number of exported goods. Quotas are a tax on imported goods, and tariffs are a tax on imported goods.arrow_forwardThe following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for maize in Guatemala. The world price (Pr) of maize is $255 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of maize and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in maize. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 435 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 415 305 375 355 X 335 315 295 275 Pu W 255 235 0 40 80 300 400 120 100 200 240 280 320 QUANTITY (Tons of maize) If Guatemala is open to international trade in maize without any restrictions, it will import. tons of maize. per ton will Suppose the Guatemalan government wants to reduce imports to exactly 80 tons of maize to help domestic producers. A tariff of S achieve this. A tariff set at this level would raise $ in revenue…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781285165912
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337617383
Author:Roger A. Arnold
Publisher:Cengage Learning


