
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
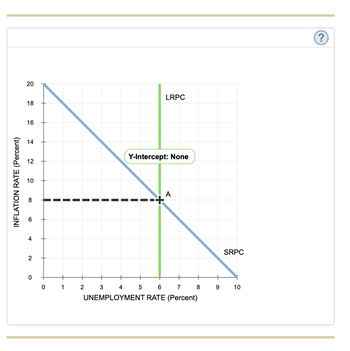
The following graph plots the short-run and long-run
Suppose that the central bank for this economy has decided that inflation is too high and thus wants to decrease the inflation rate by 6 percentage points per year. A reduction in the rate of inflation is known as (deflation/disinflation) . To reduce inflation from 8% to 2% in the short run, the central bank would have to accept an unemployment rate of____%
True or False: If people have rational expectations, the economy may not have to endure an unemployment rate as high as predicted by the short-run Phillips curve.
-True
-False
.
Transcribed Image Text:INFLATION RATE (Percent)
20
18
16
14
12
9
∞
4
2
0
0
1
+
2
+ +
3
4
LRPC
Y-Intercept: None
5
A
6
7
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)
8
9
SRPC
10
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In 2013, Prussia's aggregate demand curve was determined by the equation M + 0 = 4%. A change in aggregate demand means that in 2014, Prussia's aggregate demand curve was determined by the equation M + U = 7%. Using this information, draw Prussia's old and new dynamic aggregate demand curves on the graph. Inflation rate 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 4 3 2 1 0 -4 -3 2-1 0 1 2 3 4 5 Real GDP growth rate AD 2013 AD 2014 6 7 8 9 10 Which of the factors could have resulted in the change in aggregate demand seen between 2013 and 2014? higher consumer confidence an improvement in technology O a decrease in oil prices an increase in importsarrow_forwardSuppose that the level of unemployment in the economy is determined by the follow equation: U = 7.55 1.88*(i - ie) Where U is the unemployment rate, i is the actual inflation rate, and it is the expected inflation rate. All variables are entered in percentage form (e.g. if inflation is 30.57%, you plug in 30.57 for i, not 0.3057). Last year, the inflation rate was 7.87%, and people have adaptive expectations. What does the inflation rate need to be this year in order for the unemployment rate to be 2.81%? Note: Everything is already in percentage form. You do not need to multiply or divide by 100 at any point. Enter in your answer as it is calculated in the equation. Round your final answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardIn a certain economy, the Dynamic Aggregate Supply (DAS) line is represented by the function = - π₁ = Ę ₁ = ₁ π + α ( Y₁ − Ÿ) + D and the inflation expectations formation mechanism is adaptive, that is, E₁+1 Absent a supply shock (v₁ = 0), in a figure representing period t inflation rate, π, on the vertical axis, and period t output, Y₁, on the horizontal axis, the period t DAS line will pass through the pair of points, : OA. (-1) B. (α, Y) ○ C. (Y) D. (πt, Yt)arrow_forward
- If the current inflation rate is 10% and you are asked to predict the cost of decreasing it to 3% next year. 1)Will it result deflation policy or a disinflation policy? Why? 2) Give an estimate of the cost in terms of output assuming the sacrifice ratio is 4 and explain the economic cost of reducing inflation by drawing the Phillips curve. 3) If an economist says computing the cost of this policy using the sacrifice ratio is not totally correct because people are rational and they will take the new policy into account when forming expectations about the future. Explain this statement and the reason behind it by showing what happens the Phillips curve 4)if people update their expectations about the future instantaneously. How costly would it be to reduce inflation if the adjustment in expectations occurs instantaneously?arrow_forwardMA4. 13. If the equation for a country's Phillips curve is π = 0.05 – 0.8(u – 0.05), where π is the rate of inflation and u is the unemployment rate, what is the short-run inflation rate when unemployment is 3 percent (0.03)? A) .066 B) -.056 C) -.066 D) .056 11. The aggregate supply equation is Y = Y + α(P – EP). Assume that Y is 2,000, α = 200, P = 1.12 and EP = 1.00. What is the value of Y? A) 2,232 B) 2,024 C) 2,400 D) 2,012 9. If policymakers announce in advance how policy will respond to various situations but then renege on their announcements, this a problem of: A) policy by rule. B) policy by discretion. C) time inconsistency of policy. D) monetary policy. 10. According to the sticky-price model, output will be above the natural level if: A) firms expect a high price level and the demand for goods is high. B) the proportion of firms with flexible prices equals the proportion of firms with sticky prices. C) the price level is above the…arrow_forwardSuppose gold (G) and silver (S) are substitutes for each other because both serve as hedges against inflation. Suppose also that the supplies of both are fixed in the short run and \{(:Q_{C}=300)\} and that the demands for gold and silver are given by the following equations: P_{G}=960-Q_{G}+0.50P_{S} and P_{S}=600-Q_{S}+0.50P_{G} What the the equilibrium prices of gold and silver? The equilibrium price of gold is S and the equilibrium price of silver is S Please explain and show work.arrow_forward
- true or false Suppose that the central bank lost credibility in the sense that people no longer believe its inflation target (that is, inflation expectations are not `anchored’). In this case, both short-run output and long-run output do not increase in response to a permanently higher inflation target.arrow_forwardConsider an economy with a natural unemployment rate, u, of 7%. The expectations-augmented Phillips curve is: 1= - 0.5(u -ū) Assume that Okun's Law holds so that a 1 percentage point increase in the unemployment rate maintained for one year reduces GDP by 2% of full employment output. Note: Okun's Law can be expressed as: *--2(u-ü) What is the long-run Phillips curve: OA. Inflation rate 8- OB. OC. O D. none of the answers is correct Inflation rate Inflation rate 6- 6- 6-arrow_forwardAs with demand and supply analysis, changes in the economy can cause both shifts of and movements along the short-run Phillips curve. Which of the following would cause a shift of the short-run Phillips curve? Check all that apply. An increase in government spending A decrease in short-run aggregate supply An increase in the expected inflation ratearrow_forward
- 2. The inflation-unemployment relationship The following graph shows the combinations of unemployment and inflation that existed in the United States for selected years between 1961 and 1969. Click on any blue point (circle symbol) on the graph to get its exact coordinates. You can also use the black point (cross symbol) to find the coordinates of other points along the curve. (Note: You will not be graded for any adjustments made to the graph.) INFLATION RATE (Percent) 1969 5.2 4.5 1988 85 1967 20 1.5 10 0.5 1960 1984 1963 1981 0 2.0 3.5 40 4.5 5.0 5.5 GO 4.5 7.0 UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)arrow_forwardKk.132.arrow_forwardSuppose the Phillips curve in Country A is estimated to be ??=???−0.25(??−?∗?)πt=πte−0.25(ut−ut∗)(supplied in picture) The natural rate of unemployment in the year 2020 equals 3%. Inflation in the year 2020 is expected to be around 1%. The Okun’s coefficient in Country A equals 2. The central bank of Country A is considering three possible monetary policy scenarios for the year 2020. Scenario 1: the central bank performs a monetary contraction, and the inflation rate becomes 0.5%. Scenario 2: the central bank performs a monetary expansion, and the inflation rate becomes 1.5%. Scenario 3: the central bank keeps monetary policy unchanged, and the inflation rate matches expected inflation and equals 1%. For each of these policy scenarios, 1) Determine the corresponding rate of cyclical unemployment in 2020 2) Determine the actual unemployment ??ut that would result in 2020 3) Use Okun’s law to determine the corresponding…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education