
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
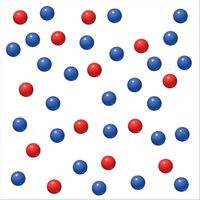
The following figure represents an equilibrium mixture of reactant A (red spheres) and product B (blue). The associated
Assume the volume of the box is 1.0 L and that each sphere represents 1 mole of A or B.
What is the value of the equilibrium constant Kc?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 125 L tank with 47. mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 22. mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 16. mol of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. ||mol x10arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.6 mol of H₂ and 0.30 mol of HI. This reaction becomes possible: H₂(g) + 12₂(g) → 2HI(g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of I2. You can leave out the M symbol for molarity. initial change equilibrium H₂ 0 1₂ x 0 HI 0 X Sarrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium: N₂O4(g) = 2NO2(g) A 1.00 L container is initially filled with 0.200 mol N₂O4At equilibrium, 0.160 mol NO₂are present. What is the equilibrium concentration of N₂O4? 0.120 mol/L 0. 040 mol/L O.0.160 mol/L 0.080 mol/L 0.100 mol/Larrow_forward
- For the reaction 2 NO2 (g) <-=> N2O4 (g) , Kp =_____ Kc(RT) Kc/RT (RT)/Kc Kcarrow_forward"Synthesis gas" is a mixture of carbon monoxide and water vapor. At high temperature synthesis gas will form carbon dioxide and hydrogen, and in fact this reaction is one of the ways hydrogen is made industrially. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 25 L tank with 11. mol of carbon monoxide gas and 12. mol of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 6.9 mol of carbon monoxide gas, 7.9 mol of water vapor and 4.1 mol of hydrogen gas. The engineer then adds another 3.0 mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of carbon dioxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. molarrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.3 mol of Cl₂ and 0.80 mol of HC1. The following reaction becomes possible: H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl (g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 9.14 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H₂. Round your answer to two decimal places. M X Ś E A olo 18arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is a true statement concerning a reaction that has reached a state of equilibrium? A system has reached equilibrium when the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. A system has reached equilibrium when the reaction has stopped and no more products are formed. A system has reached equilibrium when the rate constant for the forward reaction equals the rate constant of the reverse reaction. A system has reached equilibrium when the concentrations of reactants and products correspond to the stoichiometric ratios determined by the balanced equation.arrow_forwardWhile ethanol (CH,CH,OH) is produced naturally by fermentation, e.g. in beer- and wine-making, industrially it is synthesized by reacting ethylene (CH,CH,) with water vapor at elevated temperatures. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 100 L tank with 45. mol of ethylene gas and 35. mol of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 34. mol of ethylene gas and 24. mol of water vapor. The engineer then adds another 18. mol of water, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of ethanol after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. | molarrow_forwardSuppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.7 mol of NO2, 0.80 mol of CO and 0.70 mol of CO2. The following reaction becomes possible: NO2(g) + CO(g) = NO(g) + CO2(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 2.90 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forward
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 0.80 mol of I, and 1.7 mol of HI. The following reaction becomes possible: H₂(g) +1₂(g) → 2HI(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.600 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of I2. Round your answer to two decimal places. M Xarrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.5 mol of H₂ and 1.2 mol of Cl₂. The following reaction becomes possible: H₂(g) + Cl₂(g) → 2HCl(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 3.45 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H₂. Round your answer to two decimal places. M Śarrow_forwardNitrogen dioxide is one of the many oxides of nitrogen (often collectively called "NOx") that are of interest to atmospheric chemistry. It can react with itself to form another form of NOx, dinitrogen tetroxide. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 100L tank with 27. mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 9.0 mol of nitrogen dioxide gas. The engineer then adds another 6.8 mol of nitrogen dioxide, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the moles of dinitrogen tetroxide after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY