
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
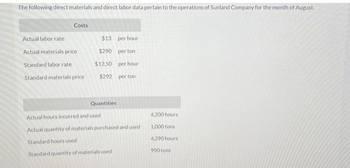
Transcribed Image Text:The following direct materials and direct labor data pertain to the operations of Sunland Company for the month of August.
Costs
Actual labor rate
Actual materials price
Standard labor rate
Standard materials price
$13
$290
$12.50
per hour
per ton
per hour
$292 per ton
Quantities.
Actual hours incurred and used
Actual quantity of materials purchased and used
Standard hours used
Standard quantity of materials used.
4,200 hours
1,000 tons
4,290 hours
990 tons
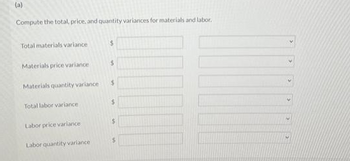
Transcribed Image Text:(a)
Compute the total, price, and quantity variances for materials and labor.
Total materials variance
Materials price variance
Materials quantity variance
Total labor variance
Labor price variance
Labor quantity variance
$
$
$
$
$
$
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured for a Manufacturing Company Cost data for Sandusky Manufacturing Company for the month ended January 31 are as follows: Inventories January 1 January 31 Materials $151,500 $128,780 Work in process 101,510 86,280 Finished goods 77,270 86,280 Direct labor $272,700 Materials purchased during January 290,880 Factory overhead incurred during January: Indirect labor 29,090 Machinery depreciation 17,570 Heat, light, and power 6,060 Supplies 4,850 Property taxes 4,240 Miscellaneous costs 7,880 a. Prepare a cost of goods manufactured statement for January. Sandusky Manufacturing Company Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured For the Month Ended January 31 $fill in the blank 9dc536060f91fdb_2 Direct materials: $fill in the blank 9dc536060f91fdb_4 fill in the blank 9dc536060f91fdb_6 $fill in the blank 9dc536060f91fdb_8 fill in the blank…arrow_forwardKaranarrow_forwardThe debits to Work in Process-Assembly Department for May, together with data concerning production, are as follows: May 1, work in process: Materials cost, 3,000 units Conversion costs, 3,000 units, 66.7% completed Materials added during May, 10,000 units Conversion costs during May Goods finished during May, 11,500 units May 31 work in process, 1,500 units, 50% completed $7,600 5,100 26,700 30,700 a. $2.32 Ob. $2.67 C. $3.83 Od. $3.07 0 All direct materials are placed in process at the beginning of the process and the first-in, first-out method is used to cost inventories. The materials cost per equivalent unit for May isarrow_forward
- Direct Materials Used, Cost of Goods Manufactured In September, Lauren Ashley Company purchased materials costing $200,000 and incurred direct labor cost of $150,000. Overhead totaled $375,000 for the month. Information on inventories was as follows: September 1 September 30 Materials $110,000 $120,000 Work in process $60,000 $90,000 Finished goods $75,000 $75,000 Required: 1. What was the cost of direct materials used in September ?$ 2. What was the total manufacturing cost in September ?$ 3. What was the cost of goods manufactured for September ?$ Check My Workarrow_forwardPrimare Corporation has provided the following data concerning last month's manufacturing operations. Purchases of raw materials Indirect materials used in production Direct labor Manufacturing overhead applied to work in process Underapplied overhead Inventories Raw materials Work in process Finished goods Beginning $ 11, 200 $ 55,700 $ 33,700 Ending $ 19,900 $ 65,800 $ 42,800 $ 31,000 $ 4,940 $ 59,300 $ 87,600 $ 4,080 Required: 1. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods manufactured for the month. 2. Prepare a schedule of cost of goods sold for the month. Assume the underapplied or overapplied overhead is closed to Cost of Goods Sold.arrow_forwardEquivalent Units of Materials Cost The Rolling Department of Kraus Steel Company had 3,800 tons in beginning work in process inventory (20% complete) on October 1. During October, 63,400 tons were completed. The ending work in process inventory on October 31 was 3,200 tons (80% complete).arrow_forward
- EXERCISE NO. 1 The following direct materials and direct labour data are for the operations of Batista Manufacturing Company for the month of August: Costs Actual labour rate $13.00 per hour Actual materials price Standard labour rate Standard materials price $89.00 per tonne $12.00 per hour $90.00 per tonne Quantities Actual hours incurred and used Actual quantity of materials purchased and used Standard hours used Standard quantity of materials used 3,200 hours 910 tonnes 3,240 tonnes 900 tonnes 1. Calculate the total, price, and quantity variances for materials and labour. 2. Provide two possible explanations for each of the unfavourable variances calculated in part (a), and suggest which department might be responsible for the unfavourable result.arrow_forwardStatement of Cost of Goods Manufactured for a Manufacturing Company Cost data for Johnstone Manufacturing Company for the month ended March 31 are as f Inventories March 1 March 31 Materials Work in process Finished goods $193,500 129,650 98,690 $166,410 111,490 113,160 Direct labor Materials purchased during March Factory overhead incurred during March: Indirect labor Machinery depreciation Heat, light, and power Supplies Property taxes Miscellaneous costs Direct materials: $348,300 371,520 37,150 22,450 7,740 6,190 5,420 10,060 a. Prepare a cost of goods manufactured statement for March. Johnstone Manufacturing Company Statement of Cost of Goods Manufactured For the Month Ended March 31arrow_forwardThe following information is available for Department C for the month of August: Units Cost Work in process, August 1 (70% complete) 10,000 Direct materials $36,000 Direct labor 18,000 Manufacturing overhead 24,000 Total work in process, August 1 $78,000 Started in production during August 40,000 Costs added: Direct materials $108,000 Direct labor 48,000 Manufacturing overhead 61,040 Total costs added during August $217,040 Work in process, August 31 (80% complete) 4,000 Units completed and transferred out 42,000 Materials are added at the beginning of the process. Inspection takes place at the 50% point in the conversion process to determine spoiled units. (Round unit costs to two decimal places.) The company uses the weighted average cost flow assumption. Department C's equivalent units of production for conversion using the weighted average costing method are a. 50,000. b. 54,000. c. 44,800. d. 47,200.arrow_forward
- Direct Materials Used, Cost of Goods Manufactured In September, Lauren Ashley Company purchased materials costing $210,000 and incurred direct labor cost of $140,000. Overhead totaled $320,000 for the month. Information on inventories was as follows: Materials Work in process Finished goods Required: X September 1 September 30 X $130,000 1. What was the cost of direct materials used in September ? $70,000 $75,000 X $140,000 $70,000 $70,000 2. What was the total manufacturing cost in September ? 3. What was the cost of goods manufactured for September?arrow_forwardThe standards for one case of Springfever Tonic are as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead (based on direct labor hours) 5.70 pound @ $4.70 per pound = $26.79 4.70 hour @ $11.70 per hour = $54.99 4.70 hour @ $5.70 per hour = $26.79 During the week ended March 13, the following activity took place: 19,500 pound of raw materials were purchased for inventory at a cost of $4.65 per pound. 2,900 cases of finished product were produced. 18,000 pound of raw materials were used. 13,500 direct labor hours were worked at a total cost of $178,200. $75,600 of actual variable overhead costs were incurred. ed: Calculate each of the following variances. Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). a. Price variance for raw materials purchased. b. Raw materials usage variance. c. Direct labor rate variance. d. Direct labor efficiency variance.…arrow_forwardEquivalent units of materials cost The Rolling Department of Fortress Steel Company had 200 tons in beginning work in process inventory (60% complete) on July 1. During July, 3,900 tons were completed. The ending work in process inventory on July 31 was 300 tons (25% complete). What are the total equivalent units for direct materials for July if materials are added at the beginning of the process?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education