
Please answer b1, b2, b3. Thanks
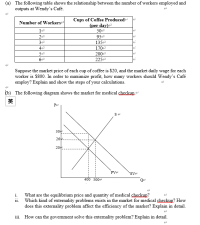
- The following table shows the relationship between the number of workers employed and outputs at Wendy’s Café.
|
Number of Workers |
Cups of Coffee Produced (per day) |
|
1 |
50 |
|
2 |
95 |
|
3 |
135 |
|
4 |
170 |
|
5 |
200 |
|
6 |
225 |
Suppose the market
(b) The following diagram shows the market for medical checkup.
As per enclosed file
1. What are the
2. Which kind of externality problems exists in the market for medical checkup? How does this externality problem affect the
3. How can the government solve this externality problem? Explain in detail.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- The marginal product of labor for a firm is given by: MPL = 112 - 4H, where H is the number of hours they hire workers to work. For example, the marginal product of the first hour of labor would be 112 - 4*1, and the marginal product of the second hour of labor would be 112 - 4*2. If the market wage is $16 per hour, how many hours of labor will this firm hire? Round your final answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardRead the "Clear it Up: Do Profit Maximizing Employers Exploit Labor" Do Profit Maximizing Employers Exploit Labor? (Source: OER) If you look back at the labor dynamics of supply and demand, you will see that only the firm pays the last worker it hires what they’re worth to the firm. Every other worker brings in more revenue than the firm pays him or her. This has sometimes led to the claim that employers exploit workers because they do not pay workers what they are worth. Let’s think about this claim. The first worker is worth $x to the firm, and the second worker is worth $y, but why are they worth that much? It is because of the capital and technology with which they work. The difference between workers’ worth and their compensation goes to pay for the capital, technology, without which the workers wouldn’t have a job. The difference also goes to the employer’s profit, without which the firm would close and workers wouldn’t have a job. The firm may be earning excessive profits,…arrow_forwardWAGE RATE Assume that the accounting and actuarial industries employ people with similar skills. Suppose an increase in the demand for actuaries leads to a rise in their wages, while the demand for accountants remains the same. The following graph shows the labor market for accountants in the United States. Show the effect of the rise in demand for actuaries on the U.S. labor market for accountants by shifting the labor demand curve, the labor supply curve, or both. Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. QUANTITY OF LABOR о Supply Demand Demand Supply As a result, the wage rate for U.S. accountants and the level of employment ?arrow_forward
- The human resource manager of the Culinary Chameleon makes the following claim: “Our workers make an average of $400 per week. We produce $4500 worth of output each week using only 10 workers. That averages out to $450 per worker per week. We should therefore hire more people as long as the wage is $400 per week." Assess this claim - is the reasoning solid or do you disagree? 2.arrow_forwardWould the owner of a profit-maximizing clothing store hire another worker for $85 per day if that worker added faster service, increasing sales and revenue by $80 per day? Why or why not? Explain your answer. BI UV A/ Paragraph 영 + X 11.arrow_forwardWhy might a labor supply curve be backward bending? Explain your answer using the concepts of the income effect and the substitution effect. (You can explain your answer using words or you can draw a graph accompanied with a brief explanation)arrow_forward
- Consider the fast food industry in the United States. Research existing estimates of the demand for fast food, the labor share for fast food, and the elasticity of substitution between capital and labor in the fast food industry. Based on the estimates in the literature, what is a plausible range of values for the elasticity of labor demand for the fast food industry? Thanks!arrow_forwardWAGES (Dollars perteacher) Suppose that the states pass a law that prohibits home schooling and requires that all children attend public schools. Assume home- schooled children were being taught by parents who would not become public school teachers as a result of the new legislation. The following graph depicts the labor market for public school teachers. The market for public school teachers is perfectly competitive. Adjust the graph to show the effect of this legislation on the market for public school teachers. Note: Select and drag one of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. The wages for teachers will QUANTITY (Teachers) Supply Demand Demand Supply ? and the quantity of teachers in the classroom willarrow_forwardConsider the Labor Economics Question. This will provide insight into the idea of the optimal number of workers and the value of the marginal product of labor. If wages in the restaurant is $20.00 per hour and the price of a Hamburger is $8.00 and the production function for the workers is: Q = 11L – 0.25L^2 a. How many workers should Your Restaurant employ during the lunch hour to maximize profits? 1 Point (note—the value of the marginal product of labor and the marginal revenue product are the same) We maximize profits which are total revenues less total costs: b. Compute the maximum profit at Your Restaurant. (note—consider that profit involves Total Revenue and Total Costs). 1 Point c. Compute the profit created if You hire an additional worker. Explain why it is or is not profit maximizing to hire an additional worker. The idea of this question is to recognize that we can find the profit maximizing quantity of labor– after that point, profit begins to…arrow_forward
- 1. Suppose a short-run production function is described as Q40L 0.04L2 where L is the number of labors used each hour.arrow_forward5. In Chapter 9 of your text, complete Exercise #3 found on page 321. Suppose that you observe that the wages for accountants in your town have gone up and that the number of accountants employed has also gone up. Which one of the following conditions could explain this? Illustrate your answer with a graph and explain in a brief paragraph. a) Businesses are failing, reducing the need for accountants. b) Many accountants are leaving the field in order to train to become financial analysts instead. c) A rash of business scandals has increased the demand for auditing services performed by accountants. d) The local university has just graduated an unusually large group of accountants.arrow_forwardConsider the Labor Economics Question. This will provide insight into the idea of the optimal number of workers and the value of the marginal product of labor. If wages in the restaurant is $16.80 per hour and the price of a Hamburger is $8.30 and the production function for the workers is: Q = 11L – 0.25L2 How many workers should Your Restaurant employ during the lunch hour to maximize profits? 1 Point (note—the value of the marginal product of labor and the marginal revenue product are the same) We maximize profits which are total revenues less total costs:arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





