
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Profit maximization Suppose that the market wage for blueberry pickers is $80 per worker per day, and the price of blueberries is $15 per pound.
On the following graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to plot Blewitt's labor demand curve when the output price is $15 per pound.
Note: Remember to plot each point between the two integers. For example, when the number of workers increases from 0 to 1 , the value of the
marginal product of for the first worker should be plotted with a horizontal coordinate of 0.5 , the value halfway between 0 and 1 . Line segments will
automatically connect the points.
At the given wage and price level, Blewitt's should hire At the given wage and price level, Blewitt's should hire
Suppose that the price of blueberries increases to $18 per pound, but the wage rate remains at $80.
On the previous graph, use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot Blewitt's labor demand curve when the output price is $18 per pound.
Now Blewitt's should hire
when the output price is $18 per pound.
Assuming that all blueberry-producing firms have similar production schedules, an increase in the price of blueberries will cause the
blueberry pickers to
Suppose that wages increase to $110 due to an increased demand for workers in this market. Assuming that the price of blueberries remains at $18
per pound, Blewitt's will now hire
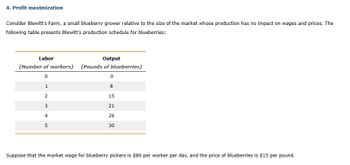
Consider Blewitt's Farm, a small blueberry grower relative to the size of the market whose production has no impact on wages and prices. The
following table presents Blewitt's production schedule for blueberries:
Suppose that the market wage for blueberry pickers is $80 per worker per day, and the price of blueberries is $15 per pound.
Transcribed Image Text:4. Profit maximization
Consider Blewitt's Farm, a small blueberry grower relative to the size of the market whose production has no impact on wages and prices. The
following table presents Blewitt's production schedule for blueberries:
Labor
Output
(Number of workers) (Pounds of blueberries)
0
1
2
345
0
8
15
21
26
30
Suppose that the market wage for blueberry pickers is $80 per worker per day, and the price of blueberries is $15 per pound.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4. A firm has a linear production function Q = 16L + 8K. The price of labor, w, is $6 per unit and the price of capital services, r, is $2 per unit. Find the optimal input combination given that the firm wishes to produce 320 units of output. Illustrate your answers with a diagram.arrow_forwardImagine you've been hired as the manager of a firm producing a certain product X. The following schedule shows the total production per week of product X Additionally, assume each unit of product X sells for $10 per unit, workers can be hired in a competitive labor market for $500 per week, and the rental price of a unit of capital is $R per week Capital (K) Quantity (Q) Labor (L) 0 5 0 1 5 40 2 5 105 3 5 170 4 5 245 5 5 325 6 5 410 7 5 500 8 5 595 9 5 695 10 5 760 11 5 810 12 5 855 13 5 890 14 5 915 15 5 930 a. How many workers should be hired? To answer this question, append to the above table three new columns similar to columns (3), (4) and (5) of Table 5-2 in your textbook. Explain your final answer!arrow_forwardUsing the information from the isoquant/isocost diagram to the right and assuming that PL = P = $2, complete the table below. (Enter your responses as integers.) Output Units 100 200 300 Total Cost of Output $100 $ $300 Units of Labor Demanded 25 50 Units of Capital Demanded 4 50 75 Units of capital (K) 200 175- 150- 125- 8100- 75- 50- 25+ 0+ 0 25 50 9=100 9 200 100 125 150 q=300 75 Units of labor (L) 175 200 Q Qarrow_forward
- Suppose that the price of labor (the wage rate) is $100 a day and that the rental price of capital is $50 a day. Currently the Jedie Weapons Corporation is using ten units of capital and five units of labor to produce 500 lightsabers a day. Each lightsaber sells for $2. At the current input use levels, the marginal product of capital is 40 lightsabers per day and the marginal product of labor is 60 lightsabers a day. Is the firm making an economic profit at its current levels of operation? 2. Could the firm increase its profits at the current level of output by adjusting its use of labor and capital? If so, how should input use be adjusted?arrow_forwardConsider a production process where flowers are grown (the output) using gardeners (labor) and greenhouses (capital). The quantity of flowers grown per day with various combinations of labor and capital are shown in the table. Fill in the marginal product of labor in the table below. (Enter your responses as integers).arrow_forwardQuantities Produced 225 220 215 210 205 200 195 190 185 180 175 170 165 160 155 150 145 140 135 130 125 120 115 110 105 100 95 90 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 0 1 2 3 Number of Workers units of output. productivity. The graph above shows the relationship between the daily quantities of a good produced by a small firm and the number of workers hired, given all the other resources available to the firm. For example, one worker can produce 30 units and two workers can produce 55 units. Such a relationship between a production factor (here labor) and the amount of output produced is called a production function. Currently the nominal wage rate is W = $200 per worker per day and the price of the product is P = $10 per unit. Of the amount of increase in production noted above, 4 Now suppose that the firm installs some new machines and offers the workers some rigorous training and as a result the productivity of the workers increases. In particular, the marginal product of each worker…arrow_forward
- Refer to the given data in the table below. Assume that labor is the only variable input. Please calculate the marginal product of labor for each level of labor input and and graph it using the diagram below. # Workers (L) 1 2 3 4 5 Total Output 7 12 15 16 16 Provide your answer below: 20 15 10 5- -2 -1 1 2 3 4 7 9 10 Labor -5- Marginal Productarrow_forward4. Ariel's T-shirt company hires labor at a rate of $8 per hour and rents capital (sewing machines) at a cost of $128 per machine per day. Throughout this question, you can think of Ariel renting fractions of sewing machines if necessary. Her production function is given by q = 6LK where q measures the number of T-shirts produced each day, L measures the total number of hours worked by all employees in a day and K measures the number of sewing machines. (a) Using the Lagrangian technique, find the cost-minimizing combination of labor and capital for the production of q T-shirts per day. (b) Write down an equation for Ariel's long-run expansion path. (c) Find Ariel's long-run total, average, and marginal cost as a function of the number of T-shirts she produces each day. (d) Sketch Ariel's long-run total expansion path in a diagram. Sketch at least two isoquants with the associated isocost lines. Using your diagram, determine how Ariel's long-run expansion path will shift if the cost of…arrow_forwardA custom motorcycle company can produce more motorcycles if it has more workers. The company has experimented with hiring workers in teams of four and has come up with the following table relating the number of workers to the companies annual production Part1. Using the straight line tool, graph the production function based on the information given. Construct the curve using four line segments joined end to end. Don it graph the individual points. Part 2. Give the numeric answers to tap decimals. A. The marginal product of each of the first four workers is ______ B. The marginal product of each of the second four workers is _______ C. Diminishing returns begin with the _______ worker.arrow_forward
- Graph the demand for labor as a function of the wage using this data. What happens to the number of workers when wage goes up? How many workers will be hired and how many cookies made at a wage of 40.50? Please give me the equations so I can understand how to create this graph.arrow_forwardThe table below shows data for the production of Avocados for an individual firm. Number of workers Number of Avocados 0 0 1 70 2 126 3 168 4 196 5 210 Given this data, what is the marginal product of labor when quantity increases from 1 by one unit?arrow_forwardAngela has been working at a real wage rate of $25 per hour. Illustrate in a diagram how Bruno’s decision to use more robots could affect Angela’s future levels of• real wage,• utility,• free time, and• consumption.Your diagram should have Angela’s daily free time on the horizontal axis and her daily consumption on the vertical axis. Briefly explain your diagram within 70 wordsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education