
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
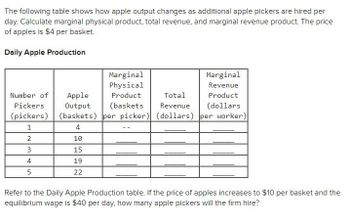
Transcribed Image Text:The following table shows how apple output changes as additional apple pickers are hired per
day. Calculate marginal physical product, total revenue, and marginal revenue product. The price
of apples is $4 per basket.
Daily Apple Production
Marginal
Physical
Product
(baskets
4
5
Marginal
Revenue
Number of Apple
Total
Pickers
Output
Revenue
(pickers) (baskets) per picker) (dollars) per worker)
1
4
2
10
3
15
19
22
Product
(dollars
Refer to the Daily Apple Production table. If the price of apples increases to $10 per basket and the
equilibrium wage is $40 per day, how many apple pickers will the firm hire?
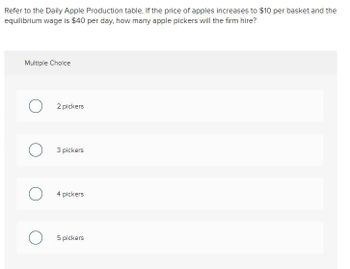
Transcribed Image Text:Refer to the Daily Apple Production table. If the price of apples increases to $10 per basket and the
equilibrium wage is $40 per day, how many apple pickers will the firm hire?
Multiple Choice
O2 pickers
о
3 pickers
4 pickers
5 pickers
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following graph plots daily cost curves for a firm operating in the competitive market for demin overalls. Hint: Once you have positioned the rectangle on the graph, select a point to observe its coordinates. PRICE (Dollars per overalls) 50 10 10 5 0 MC 2 ATC 8 18 QUANTITY (Thousands of overallises per day) AVC 10 20 Profit or Loss In the short run, given a market price equal to $15 per overalls, the firm should produce a daily quantity of On the preceding graph, use the blue rectangle (circle symbols) to fill in the area that represents profit or loss of the firm given the market price of $15 and the quantity of production from your previous answer. Note: In the following question, enter a positive number regardless of whether the firm earns a profit or incurs a loss. The rectangular area represents a short-run thousand per day for the firm. $ overallses.arrow_forwardPRICE (Dollars per pound) The following graph shows the long-run supply curve for plums. Place the orange line (square symbol) on the graph to show the most likely short-run supply curve for plums. (Note: Place the points of the line either on N and G or on N and Z.) 24 20 < G N 16 Long-Run Supply 12 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds of plums) Short-Run Supply ?arrow_forward100 90 90 00 80 COSTS (Dollars) 70 70 00 60 50 40 30 20 10 ATC AVC MC 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 QUANTITY (Thousands of snapbacks) 35 35 40 45 50 For every price level given in the following table, use the graph to determine the profit-maximizing quantity of snapbacks for the firm. Further, select whether the firm will choose to produce, shut down, or be indifferent between the two in the short run. (Assume that when price exactly equals average variable cost, the firm is indifferent between producing zero snapbacks and the profit-maximizing quantity of snapbacks.) Lastly, determine whether the firm will earn a profit, incur a loss, or break even at each price. Price (Dollars per snapback) 10 20 32 40 50 60 Quantity (Snapbacks) Produce or Shut Down? Profit or Loss?arrow_forward
- The graph shows the Cost curves for a profit maximizing firm in a competitive market. If the market price is $30 and the firm produces at the profit maximum quantity, what is the amount of the total fix costarrow_forwardPrinciples of Microeconomics Name: Homework #3 Prof. R. Harris DUE: Wednesday, April 17, 2019 at the beginning of class - NO EXCEPTIONS. Please remember to show all work and please be neat. Please staple this if you print it on your own. 1. Consider the following table of numbers, which represents demand and cost conditions for a com firm. petitive TR 600 0 1 2 $o $400 600 $400 $240 600 $430 $670 $960 $1,350 $1,840 $2,440 $3,120 $3,910 $4,800 600 600 600 600 600 600 5 6 7 600 600 9 10 (a) Fill in the missing values (b) Use the information in the chart to determine what level of output the firm should produce. Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardHow do you calculate whether your business has an economic profit using marginal approach to profit maximization? and what does an economic profit means?arrow_forward
- Assume coffee machine and labor are the only two inputs for a coffee shop. The labor demand elasticity will be larger if A. Coffee machine is the substitute for labor in the shop. in the short run. B. Coffee has a relative inelastic demand C. Labor cost is around 80% in the total cost of the shop. D. The supply of tea machine is quite elastic.arrow_forwardA kid wants to open a lemonade stand in their neighborhood. They would have elastic supply because O Lemonade takes a long time to produce O They can only produce one product O The product has to be sold from their house They have flexible inputsarrow_forwardWhen profit maximizing, the MRTS of two inputs is equal to a. The ratio of marginal products of the inputs, but not the ratio of the prices of the inputs b. The price of the good being produced c. The ratio of the prices of the inputs, but not the ratio of marginal products of the inputs d. Both the ratio of marginal products of the inputs and the ratio of the prices of the inputs Clear my choicearrow_forward
- Behind the Supply Curve: Inputs and Costs Work It Out: Question 2 of 5 The accompanying table shows a car manufacturer's total cost of producing cars. Calculate the variable cost (VC) for the following quantities. VC for a quantity of 0: $ VC for a quantity of 5: $ VC for a quantity of 9: $ 0 Quantity of cars Total Cost $500,000 540,000 560,000 570,000 590,000 620,000 660,000 720,000 800,000 920,000 1,100,00 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10arrow_forwardI need typing no chatgpt used please i will give 5 upvotesarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the image belowarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education