
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
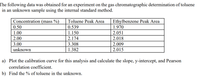
Transcribed Image Text:The following data was obtained for an experiment on the gas chromatographic determination of toluene
in an unknown sample using the internal standard method.
Concentration (mass %)
Toluene Peak Area
Ethylbenzene Peak Area
0.50
0.539
1.970
1.00
1.150
2.051
2.00
2.174
2.018
3.00
3.308
2.009
unknown
1.382
2.015
a) Plot the calibration curve for this analysis and calculate the slope, y-intercept, and Pearson
correlation coefficient.
b) Find the % of toluene in the unknown.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The identity of a volatile petroleum residue is determined by the (size, pattern) of its gas chromatogramarrow_forwardThin Layer Chromatography. All types of chromatography have mobile phaseand stationary phase. What is a stationary phase and a mobile phase? Elaborate your answer.arrow_forwardWhat is the relative average deviation in the following percent KHP values in ppt? (Enter your answer as a number without units.) 46.89 % 47.51 % 47.92 %arrow_forward
- The figure below shows a portion of a GC chromatogram for a mixture of two aromatic compounds labeled A and B. The separation employed a 2.50 meter packed column under isothermal conditions (90 °C) and a flow rate of 10 mL/min. Detector Signal 300.0 250.0 200.0 150.0 100.0 50.0 0.0 1.0 1.1 Unretained 1.5 time (min) Find the times that components A and B spend in the stationary phase. 2.0arrow_forwardwould column chromatography separate ketone and alcoholarrow_forwardA3arrow_forward
- 5arrow_forward1. From spinach, the chromatographic analysis will yield two major substances: (a) B-carotene (C40H56), which will separate from the spinach mixture to form a yellow band, and (b) chlorophyll A (CSSH72MGN4OS), which will separate from the mixture to form a green band. i. Describe the characteristics and draw structures of these molecules. ii. From the spectrophotometric analysis, what wavelength (Amax) would you expect ß-carotene (C40H56) to absorb? What wavelength would chlorophyll A (CssH72MgN4O5) absorb?arrow_forwardthe linear trendline equation y= 4.7033x + 0.0045arrow_forward
- The following data give the recovery of bromide from spiked samples of vegetable matter, measuredusing a gas–liquid chromatographic method. The same amount of bromide was added to each specimen(Roughan, J.A., Roughan, P.A. and Wilkins, J.P.G., 1983, Analyst, 108: 742).Tomato: 777 790 759 790 770 758 764 ug/gCucumber: 782 773 778 765 789 797 782 ug/g(a) Test whether the recoveries from the two vegetables have variances which differ significantly.(b) Test whether the mean recovery rates differ significantly.arrow_forwardWith the following information for a GC analysis using an internal standard, calculate the percentage of alcohol in the sample. The 1% ethanol standard sample has an ethanol peak area of 711 and a 1-propanol peak area of 9253; 3% is 3536 and 14432 for ethanol and 1-propanol respectively; 5% is 3506 and 10693; 7% is 5874 and 10847 and 9% is 5203 and 7522. The beer sample has an ethanol peak area of 5471 and 1-propanol of 14384. 4.95% 5.15% 5.05% 5.25%arrow_forwardA gas chromatogram of a mixture of toluene and ethyl (a) Measure w1/2 for each peak to the nearest 0.1 mm. When the thickness of the pen trace is significant relative to the length being measured, it is important to take the pen width into account. It is best to measure from the edge of one trace to the corresponding edge of the other trace, as shown at the bottom of the left column. (b) Find the number of theoretical plates and the plate height for each peak.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY