
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A student is asked to determine the chemical make-up of four different inks. She places four starting points made out of each ink sample on a sheet of chromatography paper and numbers the samples with a pencil as 1, 2, 3 and 4. She places the paper into a solution of chromatography solvent, allowing only the point to be submerged in the solvent. After about twenty minutes, she marks the end of the advancement of the mobile phase. Her chromatography paper is shown at the right. Which statement is correct based on the data?
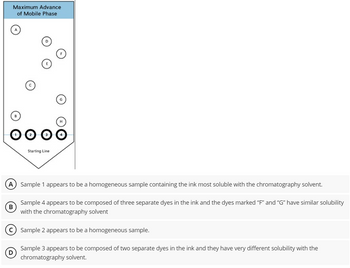
Transcribed Image Text:Maximum Advance
of Mobile Phase
OOOO
Starting Line
A) Sample 1 appears to be a homogeneous sample containing the ink most soluble with the chromatography solvent.
Sample 4 appears to be composed of three separate dyes in the ink and the dyes marked "F" and “G” have similar solubility
with the chromatography solvent
B
Sample 2 appears to be a homogeneous sample.
Sample 3 appears to be composed of two separate dyes in the ink and they have very different solubility with the
chromatography solvent.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Use a chemical dictionary, chemical text or encyclopedia to find a specific definition of "chromatography." List a few mobile and stationary phases.arrow_forwardDescribe how retention time of butanol on a poly (ethylene glycol) column will change with increasing temperature. Use the retention time for butanol in Figure 24-9b as the starting point.arrow_forward1. All chromatography involves a solid phase, and mobile phase. In thin layer chromatography the solid phase is the silica layer on a piece of glass, and the mobile phase is the organic solvent that will travel along the TLC plate. which direction will the mobile phase (the organic solvent) travel? A) UPWARD B) DOWNWARD C) HORIZONTALLY LEFT TO RIGHTarrow_forward
- What effect will the following have on plate height (H). Make sure to explain your full and complete reasoning. Increasing stationary phase thickness. Reducing the rate of sample injection. Increasing mobile phase flow rate. Decreasing temperature. Reducing stationary phase particle size.arrow_forwardThe following statements are true for any chromatographic analysis except: The analyte component interacting most strongly with the stationary phase elute faster than those with weaker interactions. On the other hand, those with least interaction with the mobile phase elute the slowest. Interactions between mobile phase-analyte - stationary phase can be both chemical and physical in nature. Chromatography is a separation technique. Electromagnetic radiation source for XPS. Gamma ray X-ray UV-Visible Infra red Radiowave The part of SEM that is responsible for the production of electrons. * Electron guns Condenser lens Secondary detector Electron beamarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY