
Financial And Managerial Accounting
15th Edition
ISBN: 9781337902663
Author: WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher: Cengage Learning,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:வடி
Shilow Company
Income Statement
For the Quarter Ended June 30
Cost of goods sold:
בן
Selling and administrative expenses:
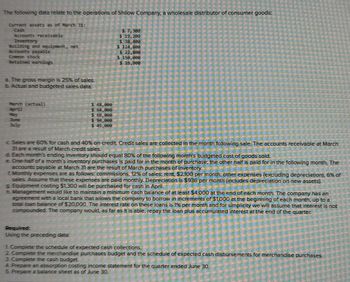
Transcribed Image Text:The following data relate to the operations of Shilow Company, a wholesale distributor of consumer goods:
Current assets as of March 31e
Cash
Accounts receivable
Inventory
E
Building and equipment, net
Accounts payable
Retained earnings
$7.300
$38,400
$ 124,898
$22,800
$ 150,000
316-999
a. The gross margin is 25% of sales.
b. Actual and budgeted sales data
March (actual)
May
July
בוה
21
11
$ 48,498
$69-898
94,000
$45,898
c. Sales are 60% for cash and 40% on credit. Credit sales are collected in the month following sale. The accounts receivable at March
31 are a result of March credit sales.
d. Each month's ending inventory should equal 80% of the following month's budgeted cost of goods sold.
e. One-half of a month's inventory purchases is paid for in the month of purchase, the other half is paid for in the following month. The
accounts payable at March 31 are the result of March purchases of inventory.
f. Monthly expenses are as follows: commissions, 12% of sales, rent, $2,100 per month; other expenses (excluding depreciation), 6% of
sales. Assume that these expenses are paid monthly. Depreciation is $936 per month (includes depreciation on new assets).
g. Equipment costing $1,300 will be purchased for cash in April.
h. Management would like to maintain a minimum cash balance of at least $4,000 at the end of each month. The company has an
agreement with a local bank that allows the company to borrow in increments of $1,000 at the beginning of each month, up to a
total loan balance of $20,000. The interest rate on these loans is 1% per month and for simplicity we will assume that interest is not
compounded. The company would, as far as it is able, repay the loan plus accumulated interest at the end of the quarter
Required:
Using the preceding data:
1. Complete the schedule of expected cash collections.
2 Complete the merchandise purchases budget and the schedule of expected cash disbursements for merchandise purchases.
3. Complete the cash budget.
4. Prepare an absorption costing income statement for the quarter ended June 30
5. Prepare a balance sheet as of June 30.
ווה
וו
STILE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Cost of goods sold and related items The following data were extracted from the accounting records of Harkins Company for the year ended April 30, 20Y8: Estimated returns of current year sales 11,600 Inventory, May 1, 20Y7 380,000 Inventory, April 30, 20Y8 415,000 Purchases 3,800,000 Purchases returns and allowances 150,000 Purchases discounts 80,000 Sales 5,850,000 Freight in 16,600 a. Prepare the Cost of goods sold section of the income statement for the year ended April 30, 20Y8, using the periodic inventory system. b. Determine the gross profit to be reported on the income statement for the year ended April 30, 20Y8. c. Would gross profit be different if the perpetual inventory system was used instead of the periodic inventory system?arrow_forwardThe following information is available for Cooke Company for the current year: The gross margin is 40% of net sales. What is the cost of goods available for sale? a. 5840,000 b. 960,000 c. 1,200,000 d. 1,220,000arrow_forwardThe following is select account information for August Sundries. Sales: $850,360; Sales Returns and Allowances: $148,550; COGS: $300,840; Operating Expenses: $45,770; Sales Discounts: $231,820. If August Sundries uses a multi-step income statement format, what is their gross margin?arrow_forward
- The following is select account information for Sunrise Motors. Sales: $256,400; Sales Returns and Allowances: $34,890; COGS: $120,470; Sales Discounts: $44,760. Given this information, what is the Gross Profit Margin Ratio for Sunrise Motors? (Round to the nearest whole percentage.)arrow_forwardThe following selected information is taken from the financial statements of Arnn Company for its most recent year of operations: During the year, Arnn had net sales of 2.45 million. The cost of goods sold was 1.3 million. Required: Note: Round all answers to two decimal places. 1. Compute the current ratio. 2. Compute the quick or acid-test ratio. 3. Compute the accounts receivable turnover ratio. 4. Compute the accounts receivable turnover in days. 5. Compute the inventory turnover ratio. 6. Compute the inventory turnover in days.arrow_forwardANALYSIS OF ACTIVITY MEASURES Based on the financial statement data in Exercise 24-1B, compute the following activity measures for 20-2 (round all calculations to two decimal places): (a) Accounts receivable turnover (b) Merchandise inventory turnover (c) Asset turnoverarrow_forward
- The following data relate to the operations of Shilow Company, a wholesale distributor of consumer goods: Current assets as of March 31: Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Building and equipment, net Accounts payable Common stock Retained earnings a. The gross margin is 25% of sales. b. Actual and budgeted sales data: March (actual) April May $ 7,600 $ 20,400 $ 40,200 $128,400 $ 23,925 $ 150,000 $ 22,675 $51,000 $ 67,000 $ 72,000 June July $ 97,000 $ 48,000 c. Sales are 60% for cash and 40% on credit. Credit sales are collected in the month following sale. The accounts receivable at March 31 are a result of March credit sales. d. Each month's ending inventory should equal 80% of the following month's budgeted cost of goods sold. e. One-half of a month's inventory purchases is paid for in the month of purchase; the other half is paid for in the following month. The accounts payable at March 31 are the result of March purchases of Inventory. £ Monthly expenses are as follows:…arrow_forwardThe following data relate to the operations of Shilow Company, a wholesale distributor of consumer goods: Current assets as of March 31: Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Building and equipment, net Accounts payable Common stock Retained earnings a. The gross margin is 25% of sales. b. Actual and budgeted sales data: March (actual) April May June July $ 51,000 $ 67,000 $ 72,000 $ 97,000 $ 48,000 $ 7,600 $ 20,400 $ 40,200 $ 128,400 $ 23,925 $ 150,000 $ 22,675 c. Sales are 60% for cash and 40% on credit. Credit sales are collected in the month following sale. The accounts receivable at March 31 are a result of March credit sales. d. Each month's ending inventory should equal 80% of the following month's budgeted cost of goods sold. e. One-half of a month's inventory purchases is paid for in the month of purchase; the other half is paid for in the following month. The accounts payable at March 31 are the result of March purchases of inventory. f. Monthly expenses are as follows:…arrow_forwardAshvinnbhaiarrow_forward
- Assume Cooper Company has the following reported amounts: Sales revenue $7,533 Sales returns and allowances $579 Cost of goods sold $1,501 Operating expenses $1,237 Compute Income from Operations.arrow_forwardSellall Department Stores reported the following amounts as of its December 31 year-end: Administrative Expenses, $1,800; Cost of Goods Sold, $19,440; Income Tax Expense, $2,790; Interest Expense, $1,400; Interest Revenue, $160; General Expenses, $2,000; Net Sales, $32,580; and Delivery (freight-out) Expense, $240.Prepare a multistep income statement for distribution to external financial statement users.arrow_forwardView Policies Current Attempt in Progress Assume Sunland Company has the following reported amounts: Sales revenue $1,000,000, Sales returns and allowances $29,000, Cost of goods sold $649.599, and Operating expenses $215,600. (a) Compute net sales. Net sales $ (b) Compute gross profit. Gross profit S (c) Compute income from operations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning

Financial And Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337902663
Author:WARREN, Carl S.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And Analysis
Accounting
ISBN:9781337788281
Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald Pagach
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Accounting Volume 1
Accounting
ISBN:9781947172685
Author:OpenStax
Publisher:OpenStax College

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27
Accounting
ISBN:9781337794756
Author:HEINTZ, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...
Accounting
ISBN:9781337115773
Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. Heitger
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...
Accounting
ISBN:9781305666160
Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. Parry
Publisher:Cengage Learning