Question
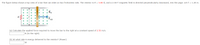
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows a top view of a bar that can slide on two frictionless rails. The resistor is R = 5.80 N, and a 2.50-T magnetic field is directed perpendicularly downward, into the page. Let l = 1.20 m.
Bin
R
app
(a) Calculate the applied force required to move the bar to the right at a constant speed of 2.50 m/s.
N (to the right)
(b) At what rate is energy delivered to the resistor? (Power)
W
x x x x
x x x
X x x X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A metal strip 5.00 cm long, 0.800 cm wide, and 0.700 mm thick moves with constant velocity through a uniform magnetic field B = 1.00 T directed perpendicular to the strip, as shown in the figure. A potential difference of 4.70 mV is measured between points x and y across the width of the strip. Calculate the speed v (in m/s). Hint: How fast are the electrons moving through the magnetic field? Give your answer as only the numerical value in the SI units specified. e is interpreted as x10^ for use with large or small values; 1.01e2 is interpreted as 1.01 x 102. Barrow_forwardA proton moves perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B at a speed of 1.10 x 10' m/s and experiences an acceleration of 1.60 x 1013 m/s2 in the positive x direction when its velocity is in the positive z direction. Determine the magnitude and direction of the field. 0.7952e-2 magnitude Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. Tarrow_forwardThe rectangular loop shown below, carrying the current I, is located in a uniform magnetic field of 0.50 T pointing in the positive y direction. Ꮎ What is the magnitude of the magnetic dipole moment of the loop? Use the following data: h = 5.5 cm, w = 5.5 cm, 0 = 37.00, I = 9.0 A. Submit Answer Incompatible units. No conversion found between "m^2" and the required units. Tries 0/12 Previous Tries Calculate the magnitude of the torque about the z-axis on the loop. Submit Answer Tries 0/12arrow_forward
- A rectangular conducting loop has sides a = 0.065 m, sides b = 0.15 m, and resistance R = 55 Ω. It moves into a magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.81 T with speed v = 5.5 m/s. Refer to the diagram. A) Find the current, Ii, in amperes, flowing in the loop as it enters the magnetic field. B) Find the current, If, in amperes, in the loop as it leaves the magnetic field. It leaves at the same speed it enters.arrow_forwardA thin conducting wire is bent into the shape shown in the figure. The circular portion of the wire has radius R. The wire is in the plane of the screen and carries a current I. (a) What is the direction of the magnetic field at the center of the loop? O to the left O to the right O upward Odownward into the screen O out of the screen. R B = Q (b) Find an expression for the magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the loop. (Use the following as necessary: R, I, and μo. Do not substitute numerical values; use variables only.) 10² 1 + π 2πr X Think of the total magnetic field as the superposition of the field due to the long straight wire that due to the circular loop. Find the sum of these contributions.arrow_forwardTwo very long parallel conductors are located at a distance of 2 · a from each other, perpendicular to the plane of the figure below. The left-side conductor is carrying a current of i = 11 A directed into the page. What current i, (magnitude and direction) must flow through right-side conductor to produce a zero magnetic field at point P,? Use out of the page as the positive direction and a = 5 cm and b = 13 cm. y P, a a b The current, i, = Units Select an answer What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P,? The magnitude of the B-field, B, = Units Select an answer The field is directed Select an answer Select an answer Question Help: OUp Down P Post to forum To the Left Submit Question To the Rightarrow_forward
- A rod of mass 0.720 kg and radius 6.00 cm rests on two parallel rails (see figure below) that are d = 12.0 cm apart and L = 45.0 cm long. The rod carries a current of I = 70.0 A in the direction shown and rolls along the rails without slipping. A uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.260 T is directed perpendicular to the rod and the rails. If it starts from rest, what is the speed of the rod as it leaves the rails? (Assume that the rod is of uniform density.) m/s L teaarrow_forwardA square loop 2.20 m on a side is placed in a magnetic field of magnitude 0.500 T. If the field makes an angle of 50.0° with the normal to the plane of the loop, find the magnetic flux through the loop. T·m2arrow_forwardA conducting rod slides over two horizontal metal bars with a constant speed v to the left. The entire set up is in a region of uniform magnetic field that is perpendicular to the plane of the rod and bars. If the induced current through the resistor is as indicated, what is the direction of the magnetic field? R out of the page into the page I Carrow_forward
- Q.04 A rigid coil has a 4.00 cm radius and contains 500 turns. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field that varies with time according to the following equation: 5T/54)t4 B = (0.0120 T/s)t + (3.00 × 10-5 T The coil is connected to a 600 2 resistor and its plane is perpendicular to the magnetic field. You can ignore the internal resistance of the coil. Find: (a.) The magnitude of the induced emf in the coil as a function of time. Hint: put together an equation. (b.) What is the current in the resistor at a time t = 5.00 s?arrow_forwardA loop of wire has the shape shown in the drawing. The top part of the wire is bent into a semicircle of radius r = 0.19 m. The normal to the plane of the loop is parallel to a constant magnetic field (p = 0°) of magnitude 0.60 T. What is the change AO in the magnetic flux that passes through the loop when, starting with the position shown in the drawing, the semicircle is rotated through half a revolution? B (into paper) ΔΦ = i x X میرا www Iarrow_forwardA straight conductor of length I moves with an acceleration a = 0.1 ms2 at right angles to a magnetic field of uniform strength B = 10 T. The e.m.f. between the ends of the conductor increased from 0 to 5 V during the first 20 s after the beginning of motion. Calculate I and give your answer in SI units.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios