
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
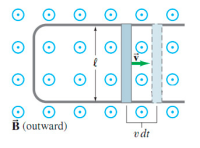
If the U-shaped conductor in the figure has resistivity ρ, whereas that of the moving rod is negligible, derive a formula for the current I as a function of time. Assume the rod starts at the bottom of the U at t=0 and moves with uniform speed v in the magnetic field B. The cross-sectional area of the rod and all parts of the U is A.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A cylindrical conductor with a radius R carries a current I. The current is uniformly distributed over the cross-sectional area of the conductor. Find the magnetic field as a function of the distance r from the conductor axis for both inside (rR) the conductor.arrow_forwardTwo very long parallel conductors are located at a distance of 2 · a from each other, perpendicular to the plane of the figure below. The left-side conductor is carrying a current of i = 11 A directed into the page. What current i, (magnitude and direction) must flow through right-side conductor to produce a zero magnetic field at point P,? Use out of the page as the positive direction and a = 5 cm and b = 13 cm. y P, a a b The current, i, = Units Select an answer What is the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point P,? The magnitude of the B-field, B, = Units Select an answer The field is directed Select an answer Select an answer Question Help: OUp Down P Post to forum To the Left Submit Question To the Rightarrow_forwardFour long, parallel conductors carry equal currents of I = 5.40 A. The figure below is an end view of the conductors. The current direction is into the page at points A and B and out of the page at C and D. (a) Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field at point P, located at the center of the square of edge length ℓ = 0.200 m. µT (b) Determine the direction of the magnetic field at point P, located at the center of the square of edge length ℓ = 0.200 m. (c) What If? What would be the magnitude and direction of the initial acceleration of an electron moving with velocity 2.88 ✕ 105 m/sinto the page at point P? magnitude m/s2directionarrow_forward
- A total current of 88 mA flows through an infinitely long cylinderical conductor of radius r = 6 cm which has an infinitely long cylindrical hole through it with a diameter equal to r centered at along the x-axis as shown. 2 y T. X What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance of 19 cm along the positive - axis? The permeability of free space is 4 π x 107T m/A. Assume the current density is constant throughout the conductor. Answer in units of T. Answer in units ofarrow_forwardPlease Help ASAP!!!!arrow_forwardAn electron moves in a circle of radius r = 6.19 × 10-11 m with a speed 2.47 x 106 m/s. Treat the circular path as a current loop with a constant current equal to the ratio of the electron's charge magnitude to the period of the motion. If the circle lies in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B = 6.04 mT, what is the maximum possible magnitude of the torque produced on the loop by the field? Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- A particle with charge 2.50 µC and mass 3.00x10-11 kg is initially traveling in the +y-direction with a speed vo = 1.60x105 m/s. It then enters a region containing a uniform magnetic field that is directed into, and perpendicular to, the page in the figure (Figure 1). The magnitude of the field is 0.450 T. The region extends a distance of 25.0 cm along the initial direction of travel; 75.0 cm from the point of entry into the magnetic field region is a wall. The length of the field- free region is thus 50.0 cm. When the charged particle enters the magnetic field, it follows a curved path whose radius of curvature is R. It then leaves the magnetic field after a time t1, having been deflected a distance Az1. The particle then travels in the field-free region and strikes the wall after undergoing a total deflection Ar. Part C Determine Az1, the horizontal deflection at the point of exit from the field. Express your answer in meters. Π ΑΣφ. ? Ar1 = Submit Previous Answers Request Answer…arrow_forwardloop. The magnetic field in this case is A vertically oriented square loop of copper wire falls from rest in a region in which the field B is horizontal, uniform, and perpendicular to the plane of the loop, into a field- free region, see (Figure 1). The side length of the loop is s and the wire diameter is d. The resistivity of copper is PR and the density of copper is pm. If the loop reaches its terminal speed while its upper segment is still in the magnetic-field region, find an expression for the terminal speed. Part I Find the emf. Express your answer in terms of the variables s, B, and v. ▸ View Available Hint(s) E = Ο ΑΣΦ Submit Figure Square loop of copper wire. Above this line: Buniform and horizontal Below this line: B=0 s = side length X X 1 of 1 X X X XBX X dwire diameter ↑ s = side length Part J Complete previous part(s) Part K Complete previous part(s) Part L Complete previous part(s) Part M Complete previous part(s) Part N Complete previous part(s) EVALUATE Uterminal Part…arrow_forwardFigure shows a cross section of a hollow cylindrical conductor of radii a and b, carrying a uniformly distributed current i. (a) What the equation of the magnetic field magnitude B(r) for the radial distance r in the range b < r < a (b) What is the magnetic field strength when r = a (c) What is the magnetic field strength when r = b (d) What is the magnetic field strength when b = 0arrow_forward
- A uniform magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of a circular loop of diameter 9.8 cm formed from wire of diameter 2.7 mm and resistivity of 2.41 × 10-8Ω·m. At what rate must the magnitude of the magnetic field change to induce a 11 A current in the loop?arrow_forwardThe accompanying figure shows a cross-section of a long, hollow, cylindrical conductor of inner radius r1=4 cm and outer radius r2=6.5 cm. A 35-A current distributed uniformly over the cross-section flows into the page. Calculate the magnetic field at r=2.5 cm, r=5.5 cm, and r=8 cm. Magnetic field at r=2.5 cm is_______T. Magnetic field at r=5.5 cm is__________T. Magnetic field at r=8 cm is____________T.arrow_forwardWe have a long wire with a circular cross section and radius a = 2.40 cm. The current density in this wire is uniform, with a total current of 4.00 A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at a distance of 0.72 cm from the center axis. Treat the wire as a cylinder. The picture is of a circular cross-section of that cylinder.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON