Question
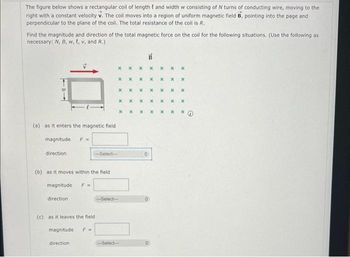
Transcribed Image Text:The figure below shows a rectangular coil of length and width w consisting of N turns of conducting wire, moving to the
right with a constant velocity v. The coil moves into a region of uniform magnetic field B, pointing into the page and
perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The total resistance of the coll is R.
Find the magnitude and direction of the total magnetic force on the coil for the following situations. (Use the following as
necessary: N, B, w, t, v, and R.)
(a) as it enters the magnetic field
magnitude F=
direction
(b) as it moves within the field i
magnitude F=
direction
(c) as it leaves the field
magnitude
direction
-Select--
F =
x
X
x
X
-Select--
x
-Select--
X
X
x
x
x
x
x
x x
O
B
X X
x
x
x
x
X x
X X
X X
X x
X
X
X x *
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A rectangular conducting loop has sides a = 0.065 m, sides b = 0.15 m, and resistance R = 55 Ω. It moves into a magnetic field of magnitude B = 0.81 T with speed v = 5.5 m/s. Refer to the diagram. A) Find the current, Ii, in amperes, flowing in the loop as it enters the magnetic field. B) Find the current, If, in amperes, in the loop as it leaves the magnetic field. It leaves at the same speed it enters.arrow_forwardSuppose you have a long straight wire AB, carrying a current in the direction shown in the figure. Below this wire is a rectangular loop 20 cm long and 5 cm wide, carrying a current of equal magnitude to the wire, where the long sides are parallel to the wire. The wire and the loop both have a linear density equal to 0.0125 kg/m. The separation between the upper long side of the loop and the wire is 1 cm. Find the magnitude of the current ? flowing through both the wire and the loop.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a rectangular coil of length f and width w consisting of N turns of conducting wire, moving to the right with a constant velocity v. The coil moves into a region of uniform magnetic field B, pointing into the page and perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The total resistance of the coil is R. Find the magnitude and direction of the total magnetic force on the coil for the following situations. (Use the following as necessary: N, B, w, e, v, and R.) х х * х х х х х х х * x x x x x x G (a) as it enters the magnetic field magnitude F = direction - Select-- (b) as it moves within the field magnitude F = direction Select--- (c) as it leaves the field magnitude direction --Select---arrow_forward
- The figure shows two closed paths wrapped around two conducting loops carrying currents i = 5.0 A and iz = 2.2 A. What is the value of the integral ¢B. ds for (a) path 1 and (b) path 2? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA 9.00-uC charge is moving with a speed of 7.50 x 10^6 m/s parallel to a long, straight wire. The wire carries a current of 77.0 A in the same direction as the moving charge, and is 5.00 x 10-2m away from the charge.Find the magnitude (in Newtons) on the charge. Use 4 decimal placesarrow_forwardDesign a current loop that, when rotated in a uniform magnetic field of strength 0.52 T, will produce an emf E = E, sin(@t), where En = 110 V and o = 120x rad/s. First, choose the number of turns the loop should have. (Enter a positive integer less than 100.) 0.1 turns Then calculate the needed area of the loop (in m2). (Use the number of turns you entered above.) m2arrow_forward
- The long straight wire in the figure has current I = 1 A flowing in it. A square loop which has 10-cm sides is positioned 10 cm away from the wire as shown. The loop is then moved in the positive x-direction with a speed v = 10 cm/s. If the loop has a resistance of 0.02 ohms, calculate the direction and the magnitude of the net force acting on the loop the instant the loop is made to move.arrow_forwardA square coil of wire of side 2.95 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 2.50 T directed into the page as in the figure shown below. The coil has 38.0 turns and a resistance of 0.780 S If the coil is rotated through an angle of 90.0° about the horizontal axis shown in 0.335 s, find the following. Rotation axis x x x x x x x x x x (a) the magnitude of the average emf induced in the coil during this rotation mV (b) the average current induced in the coil during this rotation MAarrow_forwardA coil with the radius of 20 cm has 10 turns and carries a current of 4 A. A charged particle whose charge equals 60 µ C moves at 1500 m/s through the center of the coil at an angle of 300 to the axis. Compute the magnitude of the force exerted on the particle.arrow_forward
- Two identical conducting bars of length 56.6 cm can be moved across two parallel conducting wires. The bars can be moved either to the left or right with the speeds v₁ and v₂. The top wire has a resistor with a resistance of 3.2 and the bottom wire has an ammeter (a device used to measure the current). The ammeter has neglibible resistance and reports a positive current if the current flows through it to the right. A uniform magnetic field exists everywhere with strength B either pointing into or out of the page. B or O R L V₁ A V2 1) Scenerio 1: The right bar is held at rest and the left bar is moved to the right at a constant speed of v₁ = 4.1 m/s. The magnetic field is into the page with a strength of 6.2 T. What is the EMF induced in the left bar? A positive value means the top of the bar is at a higher potential than the bottom of the bar. V Submit You currently have 0 submissions for this question. Only 10 submission are allowed. You can make 10 more submissions for this…arrow_forwardThe slide generator in the figure below is in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.0500 T. The bar of length 0.340 m is pulled at a constant speed of 0.500 m/s. The U-shaped conductor and the bar have a resistivity of 2.75 ✕ 10−8 Ω · m and a cross-sectional area of 9.00 ✕ 10−4 m2. Find the current in the generator when x = 0.680 m. (Note that the A in the image below is the area of the loop, not the cross-sectional area of the conductor and bar.)arrow_forwardA circuit is made with a resistor of resistance 25 ohms and a movable bar with length 15 cm moving to the left with speed 8 m/s. The whole circuit is in a magnetic field B = 1.5 T (into page). Use this set up to answer the following questions. Select the direction of the current in the circuit.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios