
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%

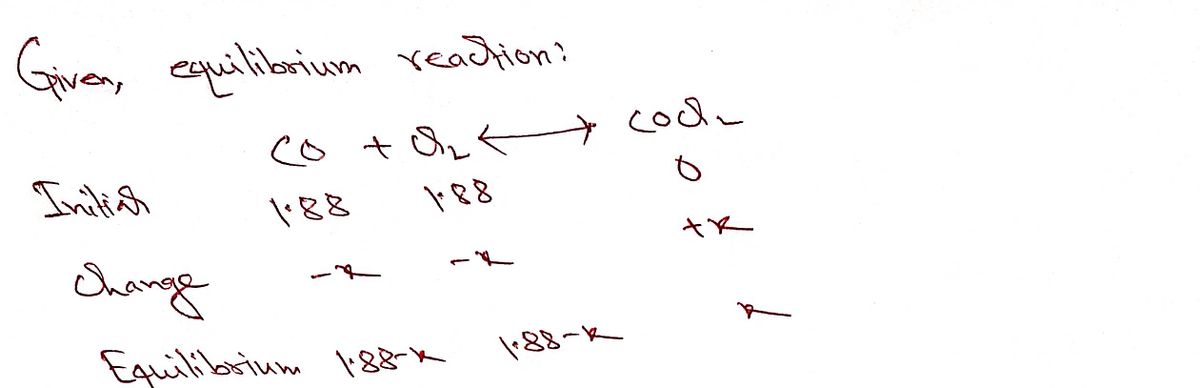
Transcribed Image Text:The equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following reaction is 1.57 at 600 K:
?
Co(g) + Cl2(g)
coCI2(g)
Calculate the equilibrium partial pressures of all species when CO and Cl2,
each at an intitial partial pressure of 1.88 atm, are introduced into an
evacuated vessel at 600 K.
Pco
atm
PCl2
atm
Pcocl2 =
atm
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A student ran the following reaction in the laboratory at 295 K:2NO(g) + Br2(g) 2NOBr(g)When she introduced NO(g) and Br2(g) into a 1.00 L evacuated container, so that the initial partial pressure of NO was 1.26 atm and the initial partial pressure of Br2 was 0.587 atm, she found that the equilibrium partial pressure of NOBr was 0.701 atm.Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, she obtained for this reaction.Kp =arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 83.3 at 500 K.PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) PCl5(g)Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.264 moles of PCl3 and 0.264 moles of Cl2 are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 500 K. [PCl3] = M [Cl2] = M [PCl5] = Marrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, K,, for the following reaction is 0.636 at 600 K: COCl,(E) CO(g) + Cl(g) Calculate the equilibrium partial pressures of all species when COC1,(g) is introduced into an evacuated flask at a pressure of 1.33 atm at 600 K. Рсос, - atm Рсо atm atmarrow_forward
- A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: N₂(g) + 3H₂(g) → 2 NH3(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.00014. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with nitrogen and hydrogen, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction vessel A B C compound N₂ H₂ NH3 N₂ H₂ NH₂ N₂ H₂ NH₂ pressure 32.70 atm 49.38 atm 23.45 atm 33.09 atm 50.55 atm 22.67 atm 33.10 atm 50.59 atm 22.64 atm expected change in pressure ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase O ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease ↓ decrease decrease ↓ decrease decrease decrease (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) (no change) O (no change) (no…arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kp, for the following reaction is 5.40 at 346 K:COBr2(g) CO(g) + Br2(g)Calculate the equilibrium partial pressures of all species when COBr2(g) is introduced into an evacuated flask at a pressure of 0.767 atm at 346 K. PCOBr2 = atm PCO = atm PBr2 = atmarrow_forwardAt 1560 oC the equilibrium constant for the reaction: 2 IBr(g) I2(g) + Br2(g) is KP = 0.846. If the initial pressure of IBr is 0.00674 atm, what are the equilibrium partial pressures of IBr, I2, and Br2?p(IBr) = p(I2) = p(Br2) =arrow_forward
- A student ran the following reaction in the laboratory at 303 K:2NO(g) + Br2(g) 2NOBr(g)When she introduced NO(g) and Br2(g) into a 1.00 L evacuated container, so that the initial partial pressure of NO was 1.15 atm and the initial partial pressure of Br2 was 0.408 atm, she found that the equilibrium partial pressure of Br2 was 0.138 atm.Calculate the equilibrium constant, Kp, she obtained for this reaction. Kp =arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 55.6 at 698 K.H2 (g) + I2 (g) 2 HI (g)Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and product when 0.228 moles of H2 and 0.228 moles of I2 are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 698 K. [ H2 ] = M [ I2 ] = M [ HI ] = Marrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant (Kc ) for the reaction: PCl3 + Cl2 <=> PCl5 equals 51 at 235°C. If 0.648 mol of phosphorus trichloride and 0.748 mol chlorine (Cl2) are added to a 9.00 L reaction vessel, what is the amount of moles of Cl2 at equilibrium in the mixture at 235°C?arrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant Kp for the reaction PC15(g) = PC13(g) + Cl₂(g) is 1.05 at 250°C. The reaction starts with a mixture of PC15, PC13, and Cl₂ at pressures 0.177 atm, 0.233 atm, and 0.161 atm, respectively, at 250°C. When the mixture comes to equilibrium at that temperature, which pressure(s) will have decreased? Cl₂ PC13 PC15arrow_forwardA chemical engineer is studying the following reaction: H2(9)+Cl2(g) → 2 HCl(g) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction is 1.1. The engineer charges ("fills") three reaction vessels with hydrogen and chlorine, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. reaction vessel compound pressure expected change in pressure H, 2.75 atm t increase I decrease (no change) Cl, 4.00 atm t increase O I decrease O (no change) A HCI 2.10 atm O f increase OI decrease O (no change) H, 2.78 atm t increase I decrease O (no change) Cl, 4.03 atm t increase I decrease (no change) 2.06 atm t increase I decrease (no change) HCl H2 3.22 atm O f increase I decrease (no change) t increase I decrease (no change) Cl, 4.98 atm OI decrease O (no change) H CI 4.26 atm…arrow_forwardWrite the expression for the equilibrium constant Kp for the following reaction.Enclose pressures in parentheses and do NOT write the chemical formula as a subscript. For example, enter (PNH3)2 as (P NH3)2 . If either the numerator or denominator is 1, please enter 1 2 Co3O4(s) ↔ 6 CoO(s) + O2(g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY