
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
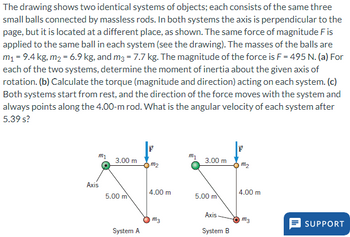
Transcribed Image Text:The drawing shows two identical systems of objects; each consists of the same three
small balls connected by massless rods. In both systems the axis is perpendicular to the
page, but it is located at a different place, as shown. The same force of magnitude F is
applied to the same ball in each system (see the drawing). The masses of the balls are
m₁ = 9.4 kg, m₂ = 6.9 kg, and m3 = 7.7 kg. The magnitude of the force is F = 495 N. (a) For
each of the two systems, determine the moment of inertia about the given axis of
rotation. (b) Calculate the torque (magnitude and direction) acting on each system. (c)
Both systems start from rest, and the direction of the force moves with the system and
always points along the 4.00-m rod. What is the angular velocity of each system after
5.39 s?
m₂
Axis
3.00 m
5.00 m
System A
m₂
4.00 m
m3
m₂
3.00 m
5.00 m
Axis
System B
m₂
4.00 m
m3
SUPPORT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A system comprised blocks, a light frictionless pulley, and connecting ropes is shown in the figure. The B block has a mass of 9.3 kg and is on a perfectly smooth horizontal table. The surfaces of the A block, which has a mass of 8.2 kg, are rough, with μk=μk= 0.25 between the block and the table. If the C block with mass 9.9 kg accelerates downward when it is released, find its acceleration.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a claw hammer being used to pull a nail out of a horizontal board where ? = 27.3°. The mass of the hammer is 1.00 kg. A force of 165 N is exerted horizontally as shown, and the nail does not yet move relative to the board. Assume the force the hammer exerts on the nail is parallel to the nail. A hand uses a hammer to pull a nail out of the ground. The head of the hammer is curved and touches the ground at a single point of contact at the center of the head. The nail in the ground makes an acute angle ? clockwise from the vertical. The nail is hooked in the hammer claw 5.00 cm horizontally to the left of the hammer head's point of contact to the ground. The hand pulls the hammer handle horizontally to the right 30.0 cm above the ground with a force vector F.(a) Find the force exerted by the hammer claws on the nail.magnitude kNdirection ° above the horizontal (b) Find the force exerted by the surface on the point of contact with the hammer head.( î + ĵ)…arrow_forwardA tightrope walker is walking between two buildings holding a pole with length L = 16.5 m, and mass mp 17.5 kg. The daredevil grips the pole with each hand a distance d = 0.530 m from the center of the pole. A bird of mass - 525 g lands on the very end of the left-hand side of the pole. Assuming the daredevil applies upward forces with the left X4 and right hands in a direction perpendicular to the pole, what magnitude of force Fjeft and Fright must the left and right hand exert to counteract the torque of the bird? Fieft Fright Narrow_forward
- A Block A with mass mĄ rests on a horizontal tabletop, while block B with mass mg hangs from a string of negligible mass that passes over a pulley and attaches to block A, as shown above. The pulley has negligible mass and rotates with negligible friction about its axle. The blocks are at rest due to friction between block A and the tabletop. The coefficient of static friction between block A and the tabletop is u (mu), where u < 1.arrow_forwardMasses m₂, m₂, m3 and om are connected together as shown in the figure below. All the surfaces are smooth. If m₁ = 3.2kg, m₂ = 2.8kg, m3 = 3.8kg, om = 1.3kg and = 55°, calculate a) the acceleration of the system. b) the normal force between m3 and ōm. 7²1 7122 In+one 183arrow_forwardWhen a person stands on tiptoe (a strenuous position), the position of the foot is as shown in Figure a. The total gravitational force on the body, F, is supported by the force n exerted by the floor on the toes of one foot. A mechanical model of the situation is shown in Figure b, where T is the force exerted by the Achilles tendon on the foot and R is the force exerted by the tibia on the foot. Find the values of T, R, and e when F, = n = 675 N. (For e, enter the smaller of the two possible values between 0° and 90°.) Achilles tendon Tibia 15.0° 18.0 cm 25.0 cm T = N R = N Need Help? Read Itarrow_forward
- For a meter stick of mass 147.89 g, it is found that its weight can be balanced by hanging a 183.99 g mass at the 95.00 cm mark. Where does the center of the weight of the meter stick locate on the meter stick? Enter the number in cm unit.arrow_forwardIn the very Dutch sport of Fierljeppen, athletes run up to a long pole and then use it to vault across a canal as shown in (Figure 1). At the very top of his arc, a 70 kg vaulter is moving at 2.9 m/s and is 5.5 m from the bottom end of the pole. What is the magnitude of the vertical force that the pole exerts on the vaulter? Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardTwo masses with mass mA = 3.220 kg and mB = 22.81 kg, respectively, hang with a massless line over an inhomogeneous pulley with mass mC = 41.81 kg. The mass center of the pulley is located in the middle of the pulley. The pulley is attached with a frictionless bearing in the middle. g = 9,806 m / s². If mass A accelerates upwards by 5.75 m/s², what force then acts on the suspension of the inhomogeneous pulley?arrow_forward
- In the figure, a man is trying to get his car out of mud on the shoulder of a road. He ties one end of a rope tightly around the front bumper and the other end tightly around a utility pole 29 m away. He then pushes sideways on the rope at its midpoint with a force of 550 N, displacing the center of the rope 0.28 m from its previous position, and the car barely moves. What is the magnitude of the force on the car from the rope? (The rope stretches somewhat.)arrow_forwardplease include free body diagrams, thank you!arrow_forwardIn the figure, a man is trying to get his car out of mud on the shoulder of a road. He ties one end of a rope tightly around the front bumper and the other end tightly around a utility pole 13 m away. He then pushes sideways on the rope at its midpoint with a force of 620 N, displacing the center of the rope 0.24 m from its previous position, and the car barely moves. What is the magnitude of the force on the car from the rope? (The rope stretches somewhat.) Number i 5.3e3 Units Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON