
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Search
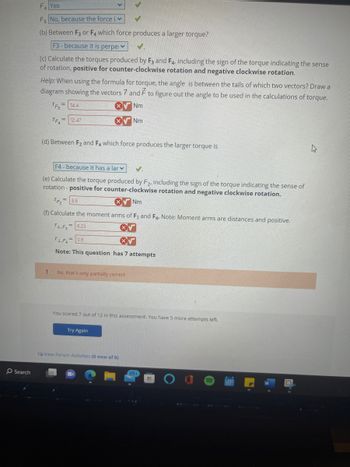
F₁ Yes
F5 No, because the force i
(b) Between F3 or F4 which force produces a larger torque?
F3- because it is perpe
(c) Calculate the torques produced by F3 and F4, including the sign of the torque indicating the sense
of rotation, positive for counter-clockwise rotation and negative clockwise rotation.
Help: When using the formula for torque, the angle is between the tails of which two vectors? Draw a
diagram showing the vectors 7 and F to figure out the angle to be used in the calculations of torque.
TF3
14.4
Nm
TF 12.47
(d) Between F₂ and F4 which force produces the larger torque is
F4- because it has a lar
✓.
(e) Calculate the torque produced by F2, including the sign of the torque indicating the sense of
rotation - positive for counter-clockwise rotation and negative clockwise rotation.
XNm
TF₂
(f) Calculate the moment arms of F3 and F4. Note: Moment arms are distances and positive.
F1,F₂= 6.23
!
= 3.6
Nm
1.F= 0.6
Note: This question has 7 attempts
No, that's only partially correct
You scored 7 out of 12 in this assessment. You have 5 more attempts left.
Try Again
View Forum Activities (0 new of 0)
99+
h
Transcribed Image Text:tivityBranding&COURSEID=5110&SECTIONID=293095
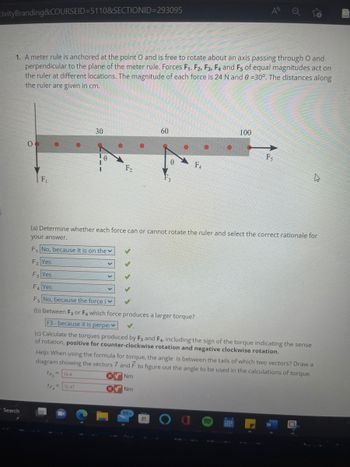
1. A meter rule is anchored at the point O and is free to rotate about an axis passing through O and
perpendicular to the plane of the meter rule. Forces F₁, F2, F3, F4 and F5 of equal magnitudes act on
the ruler at different locations. The magnitude of each force is 24 N and 0 =30°. The distances along
the ruler are given in cm.
Search
F₁
30
0
12.47
F₂
60
0
99-
F4
A
100
Fs
(a) Determine whether each force can or cannot rotate the ruler and select the correct rationale for
your answer.
F₁ No, because it is on the
F₂ Yes
F3 Yes
F₁ Yes
Fs No, because the force iv
(b) Between F3 or F4 which force produces a larger torque?
F3-because it is perpe
(c) Calculate the torques produced by F3 and F4, including the sign of the torque indicating the sense
of rotation, positive for counter-clockwise rotation and negative clockwise rotation.
h
Help: When using the formula for torque, the angle is between the tails of which two vectors? Draw a
diagram showing the vectors 7 and F to figure out the angle to be used in the calculations of torque.
TF3
=144
Nm
TF₁ =
Nm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The force F has a magnitude of 480 Ib and acts along the diagonal of the parallelepiped as shown. Express Fin terms of its magnitude times the appropriate unit vector and determine its x-, y-, and z-components. A 6' F = 480 b 8' 3' B Answers: i+ i j+ i F= ( i Ib)( i Fx Ib i Fy Ib F2 Ib iarrow_forwardTwo hockey players check an opponent into boards simultaneously. Player 1 hits from the left at an angle of 37 degrees to horizontal and a force of 400N. Player 2 hits from the left at an angle of 41 degrees to horizontal and a force of 600N. What is the magnitude and direction of total force applied to opposing playerarrow_forwardWrite the solution on a paper and round to 4 decimal placesarrow_forward
- Resolve the force F2 into components acting along the u and v axes and determine the magnitudes of the components.arrow_forwardF1 F2 Given that F1 825 N, F2 = 630 N, and a = 32° , determine the magnitude of the resultant force and its direction measured counterclockwise from the positive x axis. . The magnitude of the resultant force in N is (round to two decimal places) : N The direction of the resultant force in degrees is (round to two decimal places) : degreesarrow_forwardA heavier mass m, and a lighter mass m, are 17.5 cm apart and experience a gravitational force of attraction that is 9.00 x 10-9 N in magnitude. The two masses have a combined value of 6.00 kg. Determine the value of each individual mass. m1 Consider the product and sum of the two masses to solve for the two unknown variables. kg m2 = |kg Additional Materials еВookarrow_forward
- Vvarrow_forwardIn (Figure 1), F = {500i - 300j +400k} N. Figure 6 2m 2 -1m D 6 m 3m 1 of 1 Part A Determine the magnitude of the projection of the force F acting along the cable C'A. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FoncA= Submit Provide Feedback Di HÅ Value Request Answer F Units ?arrow_forward9.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON