
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The double pulley shown in the figure is formed by two wheels that are coupled to each other. The complete pulley (formed by the two wheels) has a mass of 15 kg and a turning radius of 110mm.
Block A has a mass of 40 kg. If a force of 2 kN is applied to the tied rope of the inner pulley wheel, determine the speed of block A after 3 seconds. At the beginning, the whole system was at rest. Disregard the mass of the string and consider that the moment of inertia (kg.m²) of the complete pulley is given by IP = mko²
where m is the mass of the pulley and Ko is the radius
spinning
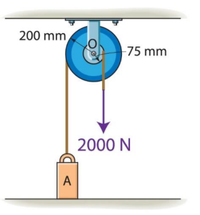
Transcribed Image Text:200 mm
-75 mm
2000 N
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- PLEASE URGENTarrow_forwardThe collar C with mass m slides on the smooth horizontal bar when the bar AB rotates with constant angular velocity @o in the counter-clockwise direction. If m = 1 kg and wo = 2 rad/sec, calculate the magnitude of the normal force on the collar at the instant, by neglecting the size of the collar. Present your answer in Newtons using 3 significant figures. = 2 m 2 marrow_forwardBlock A weighs 200 lb and rides in a frictionless vertical guide as shown. Uniform cylinder B weighs 300 lb and is connected to block A by member AB which weighs 180 lb. Cylinder B starts directly below block A with negligible velocity. Calculate the velocity of block A when the system has achieved the position show.arrow_forward
- The 1 kg sleeve is pulled to the configuration shown and released from rest. The spring has an unstretched length of 4 m. Determine the speed of the sleeve when it gets to point A. Also determine the power of the applied force. Neglect friction. Determine: The sleeve speed at A, VA = The power, P, of the applied Force = F = 2Narrow_forwardTwo identical 16-kg spheres are attached to the light rigid rod, which rotates in the horizontal plane centered at pin Part A: If the spheres are subjected to tangential forces of P = 10 N, and the rod is subjected to a couple moment M=(8t)N⋅mM=(8t)N⋅m, where t is in seconds, determine the speed of the spheres at the instant t = 4 s. The system starts from rest. Neglect the size of the spheres. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardMember AB is uniform and has a mass of 150 kg. It is released from rest in the position shown, and the spring has an initial tension of 500 N. When member AB is horizontal it has a clockwise angular velocity of 2.00 rad/s. Calculate the force constant of the spring if the guide blocks A and B are massless.arrow_forward
- 5. Cart A had a mass of 250g, and it rolled down an incline before it caught up to cart B which had a mass of 350g. Cart A started from rest, 1.00m vertically above the level of cart B. Cart B was moving at 1.50m/s [right] before cart A collided with it. Cart B has a compression-spring connected to its rear side so that Cart A compresses the spring as it collides with Cart B. The spring constant of the compression spring was 200.0N/m. a. Determine the maximum compression of the spring as the carts collide b. Determine the velocities of each of the carts once the spring has completely recoiledarrow_forwardsolve, answer is provided, show all steps.arrow_forwardPart A. what is the acceleration of the collar after it has moved 6.25 m?Part B. what is the speed of the collar after it has moved 6.25 m?arrow_forward
- The 190-kg lunar lander is descending onto the moon's surface with a velocity of 6.0 m/s when its retro-engine is fired. If the engine produces a thrust T for 3.8 s which varies with the time as shown and then cuts off, calculate the velocity of the lander when t 4.7s assuming that it has not yet landed. Gravitational acceleration at the moon's surface is 1.62 m/s?. The velocity is positive if moving downward, negative if up. 6.0 m/s T.N 756 1.9 3.8 Answe: v m/sarrow_forwardPlease help with the attached problem.arrow_forward2. The spheres have a mass of 7.50 kg each and are moving at v = 3.50 m/s at time t = 0 as shown. The shaft and frame have negligible mass. A time dependent driving moment M=4-t² is applied. Calculate the speed of the spheres at time t = 6.00 s. M 0.5 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY