
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
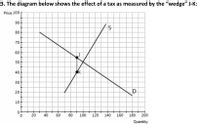
Transcribed Image Text:3. The diagram below shows the effect of a tax as measured by the "wedge" J-K:
Price 100
90
80
70
60
50+
40-
K
30
20
D
10
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
180
200
Quantity
20
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is producer and consumer surplus AFTET tax?arrow_forwardPrice 20 18 16 14 12 10 х $1.200 0 300 400 500 $2.000 S1 SO Quantity Assume that the market in the graph above is at an initial equilibrium price of $10 and an equilibrium quantity of 500 units. If the government decides to add a $4 per-unit tax on this good, it will be able to collect the following amount of tax revenue: Demand 1000arrow_forwardThe vertical distance between points A and B represents a tax in the market. 22- Price 222 20 18- 16 14 12- 22 10 8 9 Supply Demand 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Quantity Refer to Figure 8-6. Total surplus with the tax in place isarrow_forward
- The following is a Table that contains the demand and supply schedules of chocolate ice-creams. Price (cents per ice-cream) $0.90 0.80 0.70 0.60 0.50 0.40 Quantity Demanded (millions per day) 1 asifWNH 2 3 4 5 6 Quantity Supplied (millions per day) 7 6 10 10 5 4 3 2 a) If there is no tax on ice-creams, what is their price and how many are produced and consumed? b) If a tax of $0.20 cents is imposed on every ice-cream consumed, what happens to the price of an ice-cream and the number produced and consumed? Illustrate the effects of this policy on the market for chocolate ice-creams. c) How much tax does the government collect and who pays it?arrow_forwardThe current market price of bananas is $1 per pound. Use a graph and words to show the effect of a ten cent tax on each pound of bananas. Insert your own numbers into your graph. Be sure to indicate the new price paid by consumers, the new price received by sellers, and the new quantity sold.arrow_forwardWhat is an indirect tax give two examples in economicsarrow_forward
- Price (dollars per hour) 7.00 6.60 6.00 5.60 5.00 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Quantity (thousands of frisbees) Figure 6.3.1 OB) $5.60. S + tax Refer to Figure 6.3.1 showing the market for frisbees before and after a tax is imposed. On each frisbee, the sellers' burden of the tax is OA) $0.60. OC) $0.40. S OD) $6.60.arrow_forwardUse Exhibit to answer question a. A. b. C. c. B. d. B + C + E + F. Price e. C + F. 22 PB Po Ps I FIBI U O Size of tax per unit 'm/ F If a tax is placed on the product in this market, tax revenue paid by the sellers is the area Qo Supply Demand Quantityarrow_forwardUrgently needarrow_forward
- The table shows the market for chocolate bars Quantity demanded Quantity supplied (thousands per day) Price (dollars per chocolate bar) 1.10 1.20 1.30 1.40 1.50 50 5 40 10 30 15 20 20 10 25 A tax of $0.30 per chocolate bar is imposed on sellers What is the new price of a chocolate bar? Who pays the tax? The new price of a chocolate bar following the tax is $ The tax is A. paid totally by the buyer B. paid totally by the seller C. split between the buyer and the sellerarrow_forwardWhat is the price elasticity of demand(Using the Midpoint method) when the price changes from $10 to $13? If the Government imposes a tax of $6 per burrito, how many burritos will be sold in the market?arrow_forward1. Use the following graph, calculate the costs and benefits of a subsidy. 20 200 165 108 80 23 60 88 S S-Sub SMBarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education