
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
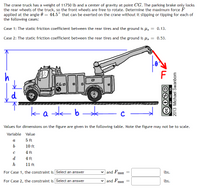
Transcribed Image Text:The crane truck has a weight of 11750 lb and a center of gravity at point CG. The parking brake only locks
the rear wheels of the truck, so the front wheels are free to rotate. Determine the maximum force F
applied at the angle 0 = 44.5° that can be exerted on the crane without it slipping or tipping for each of
the following cases:
Case 1: The static friction coefficient between the rear tires and the ground is us
= 0.13.
Case 2: The static friction coefficient between the rear tires and the ground is us
= 0.53.
d
k a sk
b.
Values for dimensions on the figure are given in the following table. Note the figure may not be to scale.
Variable Value
a
5 ft
10 ft
4 ft
d
4 ft
h
11 ft
For Case 1, the constraint is Select an answer
v and Fmax
lbs.
For Case 2, the constraint is Select an answer
and Fmax
lbs.
||
NC
2013 Michael Swanbom
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Data given -
F = 11750 lb
Theta = 44.5°
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the minimum coefficient of static friction between the uniform 78.5-kg spool and the wall so that the spool does not slip. 60° B 0.6 m 0.3 marrow_forward5. Using the definition of the static friction and the first condition of equilibrium, show or prove that the coefficient of static friction in Table B is the ratio of the “rise” to the “run”. Note: Show the free body diagram. Please refer to my experimental Dataarrow_forwardPLLLSS ANSWER WITHIN AN HOUR The spool in the given figure weighs 25 N, and its center of gravity is located at the geometric center. The weight of block C is 50 N. The coefficients of static friction at the two points of contact are as shown. Determine the largest horizontal force P that can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium of the system.arrow_forward
- PROBLEM 1: Two blocks A and B, each having a mass of 5 kg, are connected by the linkage shown in the figure. If the coefficient of static friction at the contacting surfaces is μ = 0.50, determine the largest force P, in N, that can be applied to pin C of the linkage: (a) without causing movement of block A; (b) without causing movement of block B; and (c) without causing movement to both blocks A and B. P 30° C 30° A 30°arrow_forwardProblem 1 The downhill racer team is testing a new design. There are 4 wheels each with a diameter of 0.4 m and a mass of 2.0 kg. The rest of the cart has a mass of 20 kg. A spring-loaded brake applies a constant force of 50 N on the two rear wheels. The coefficient of friction between a brake pad and a wheel is 0.7. The cart is traveling down a slope of 0 = 10° at 13.5 km/hr when the brake is applied. Determine how far the racer will travel down the slope until it stops. Model the wheels as uniform thin discs. Garrow_forwardA screw of the type indicated below is used to apply a force to the wedge, which then moves the 500-kg block. If the coefficient of static friction between all contacting surfaces is 0.2, what is the minimum torque T that must be applied to the screw? Neglect the weight of the wedge.arrow_forward
- Find Frictional Force as wellarrow_forwardCalculate the horizontal force P on the light 14° wedge necessary to initiate movement of the 49-kg cylinder. The coefficient of static friction for both pairs of contacting surfaces is 0.40. Also determine the friction force FB at point B. (Caution: Check carefully your assumption of where slipping occurs.) P Answers: P= FB = i i 49 kg B N N Aarrow_forwardThe man pushes on the roller with force P through a handle that connects to the central axle of the roller. If the coefficient of static friction between the 49-lb roller and the floor is s = 0.22, determine the maximum force Pthat can be applied to the handle, so that roller rolls on the ground without slipping. Assume the roller to be a uniform cylinder. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. Take g = 32.2 ft/s2. 1.5 ft 30° Your Answer: Answer unitsarrow_forward
- Subject: Statics of Rigid Bodiesarrow_forwardThe two 200-lb blocks are pushed apart by the 15° wedges of negligible weight.The angle of static friction is 12° at all contact surfaces.Determine the force P required to start the blocks moving.arrow_forwardconsider the mass and pulley system in the attached file. mass m1 = 29 kg and mass m2 = 12kg. the angle of the inclined plane is given and the coefficient of kinetic friction between mass m2 and the inclined plane is uk = 0.12. assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless when mass m2 moves a distance 4.94 m up the ramp, how far downward does mass m1 move? d= ?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY