
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
consider the mass and pulley system in the attached file.
mass m1 = 29 kg and mass m2 = 12kg. the angle of the inclined plane is given and the coefficient of kinetic friction between mass m2 and the inclined plane is
uk = 0.12. assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless
when mass m2 moves a distance 4.94 m up the ramp, how far downward does mass m1 move?
d= ?
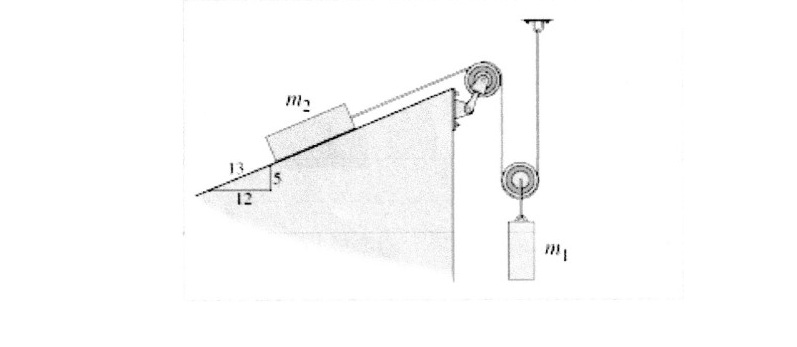
Transcribed Image Text:12
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In the figure, a climber with a weight of 390 N is held by a belay rope connected to her climbing harness and belay device; the force of the rope on her has a line of action through her center of mass. The indicated angles are 0 = 45° and p = 30°. If her feet are on the verge of sliding on the vertical wall, what is the coefficient of static friction between her climbing shoes and the wall? %3D %3D Hs =Number i Uarrow_forwardA uniform ladder of length 12 mand mass 30 kg rests with one ed on rough horizontal ground and the other end against a smooth vertical wall. The ladder is indined 65°. The coefficient of friction, H, between the ladder and the ground is 0.35. A woman of mass 65 kg is slowly dimbing up the ladder. She wants to know how far up the ladder she can dimb safely. Drawa diagramshowing all the force adting on the ladder when the woman is x metres fromthe foot of the ladder. (a) (b) Find the reaction of the ground on the ladder. (c) Show that the reaction of the wall on the ladder is less than 33.25g By taking moments about the base of the ladder, find how far up th ladder she an dimb safely. (d)arrow_forwardA carnival ride has people stand inside a vertical cylinder with their backs to the wall. The cylinder starts spinning and the riders find that they are “stuck” to the wall and don’t slide down, even if the floor is removed. The ride has a radius of r. The person has a mass of m and is moving with a constant speed of v. The coefficient of static friction between the person and the wall is μs , and kinetic friction μk. The person is only touching the wall, not touching the floor. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the person? In what direction does it point? The speed is constant. Why is the acceleration not zero? Briefly explain. No equations!arrow_forward
- I neee typing clear urjent i will give 5 upvotesarrow_forward2 Your answer is partially correct. Try again. In the figure, a slab of mass m, = 40 kg rests on a frictionless floor, and a block of mass m, = 9 kg rests on top of the slab. Between block and slab, the coefficient of static friction is 0.60, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40. A horizontal force F of magnitude 102 N begins to pull directly on the block, as shown. In unit-vector notation, what are the resulting accelerations of (a) the block and (b) the slab? u = 0- (a) Number T-7.4 -7.4 Units m/s^2 (b) Number i+ Units m/s^2 -0.88 Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: Open Show Work SHOW HINT LINK TO TEXT LINK TO SAMPLE PROBLEM LINK TO SAMPLE PROBLEM VIDEO MINI-LECTURE 10:50 PM search ENG 4/4/2021 ond 111Pgup) pri sc DOUSE insert dele home break 13) 23 bac 3 5. 4 R.arrow_forward2) After playing a game of pinball, you decide to do some calculations on the launching mechanism. The pinball and the plunger have a mass of 0.30 kg and 0.50 kg respectively. The spring coefficient in the pinball machine is 300 N/m. The original length of the spring is 100 mm and the compressed length is 35 mm. If the coefficient of friction between the ball and the surface is 0.15, calculate the velocity of the ball right before it loses contact with the plunger (in m/s). Note that the plunger is never in contact with the ground and assume the ball slides without rolling. [Ans. to check: 1.23 m/s] HO wwwarrow_forward
- A heavy cask (full of wine!) sits on an inclined plane. It is held in place by a rope that is attached to the cask and to a hook further up the inclined plane (at A). The rope comes off of the cask tangent to the cask. The mass of the cask is 40 kg, and the coefficient of static friction between the inclined plane and the cask is 0.25. What is the maximum value of 0 just before the cask begins to slip? Also, what is the tension in the rope when slipping is impending? Finally, if the inclined plane became icy, and the rope didn't break as the cask slipped, what would be remarkable about the lines of action of the W, N and T force vectors once equilibrium was re-established? 0.70 m 40arrow_forwardplease include fbdarrow_forwardFigure 2 В A Block A is hanging from a massless string which runs over a massless and frictionless pulley and connects to Block B. Block B slides over an inclined plane with ordinary kinetic friction. The plane under block B is inclined at an angle theta = 0 away from vertical. The other side of Block B is connected to another massless string which runs over another massless and frictionless pulley to connect to Cart C. Cart C rolls without friction over a plane which is inclined at an angle of phi = y away from vertical. Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY