
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
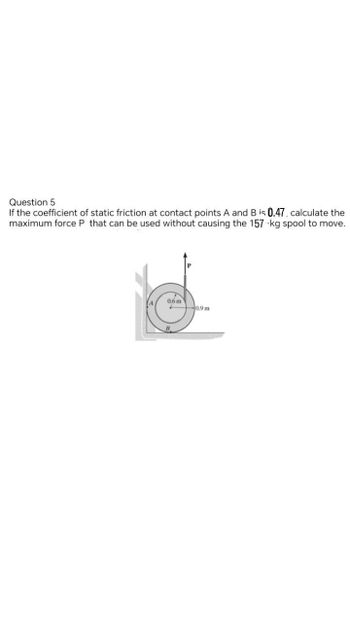
Transcribed Image Text:Question 5
If the coefficient of static friction at contact points A and B is 0.47, calculate the
maximum force P that can be used without causing the 157-kg spool to move.
0.6 m
0.9 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- AI The block D weighs 200 lbs and is connected to the block B by a cable. Block B has a weight of 160 lb acting at its center of gravity, CG,8, and Block B has a weight of 100 lb acting at its center of gravity, CG,A. The coefficient of friction between blocks A and B is uAB = 0.85. 1,15m 1.15m The coefficient of friction between block A and the ground is HAG = 0.4. a) Determine if slipping will occur between block B and block A. b) Determine if blocks A and B will tip on the ground (assume no slipping at A-B for this scenario).arrow_forwardCalculate the maximum force P that can be applied without causing any motion for the given coefficients of static friction. The weight of block A is 20 lb. and that of B is 10 lb. MB = 0.4 2 ft. B A 3 ft. MA=0.5 P MD=0.3 D Pc=0.35 Carrow_forwardThe uniform 14-ft pole weighs 150 lb. and is supported as shown. Calculate the magnitude of the force P required to move the pole if the coefficient of static friction for each contact location is 0.40. Express your answer in units of lb. 6' A 14' - יך B - Parrow_forward
- Force P is applied to the end of a rope being used to hold the 50-lb block on the 20° incline. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the incline is u. = 0.30. Determine the largest value of P for which the block is in equilibrium and will not begin to move up the incline when 0 = 15°. Hs = 0.30 20° The solution to this problem requires a free-body diagram of the block, and a sketch of the coordinate system used. Use the components of the forces with EF = 0 and EF, = 0 to y apply ΣF=0.arrow_forwardPlease be neat with steps show free body diagramarrow_forwardSix 5 N blocks are stacked vertically. The coefficient of static friction between the blocks is µs = 0.20. Determine the horizontal force that must be applied to the fifth block from the top of the stack, in order to slide it out without moving the other blocks.arrow_forward
- Part B Determine the maximum force P that can be applied without causing movement of the 110-kg crate that has a center of gravity at G. The coefficient of static friction at the floor is Us = 0.38. Assume that tipping occurs. Figure 1 of 1 Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 0.5 m, 0.5 m µA ? P = 110 0.8 m Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1.5 m 1.2 m X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Provide Feedback Next >arrow_forwardQuestion 5 If the coefficient of static friction at contact points A and B is 0.46 calculate the maximum force P that can be used without causing the 196 kg spool to move. (X,XX,XXX represents the last digits number pf your IC) 0.6 m 0.9marrow_forwardIf the coefficient of static friction at the contact points A and B is μs = 0.4, determine the following if the girl is 75-lb and the plank is 20-lb:1. Reaction at A (in lb) (ANSWER: 90.4) and Reaction at B (in lb) (ANSWER: 60.2). 2. The minimum distance d (in ft) can a girl stand on the plank without causing it to slip. (ANSWER: 2.23).arrow_forward
- The pickup truck pulls the wooden crate, as shown in Figure 2. The truck has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center of mass at G. The coefficient of static friction between the truck's wheel and the ground is µ = 0.5, and between the wooden crate and the ground is µs' = 0.4. Determine the greatest weight of the wooden crate the pickup truck can pull if: a) the truck has rear-wheel drive while the front wheels are free to roll, and b) the truck has four-wheel drive.arrow_forwardTwo blocks A and B, each having a mass of 7kg, are connected by the linkage shown in (Figure 1). If the coefficient of static friction at the contacting surfaces is Us = 0.5, determine the largest vertical force P that can be applied to pin C without causing the blocks to move. Neglect the weight of the links. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units.arrow_forwardThe man is pedaling his bicycle at a constant speed up a slippery slope of 5%. The man and the bicycle have a total mass of 82 kg centered at G. If the rear wheel is about to slip, find the coefficient of friction u between the tire and the road. If the coefficient of friction were doubled, what friction force would act on the rear wheel? (Why can we neglect the friction under the front wheel?)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY