
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
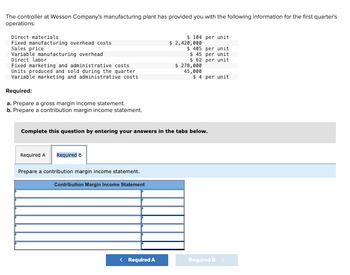
Transcribed Image Text:The controller at Wesson Company's manufacturing plant has provided you with the following information for the first quarter's
operations:
Direct materials
Fixed manufacturing overhead costs
Sales price
Variable manufacturing overhead
Direct labor
Fixed marketing and administrative costs
Units produced and sold during the quarter
Variable marketing and administrative costs
Required:
a. Prepare a gross margin income statement.
b. Prepare a contribution margin income statement.
Complete this question by entering your answers
Required A Required B
Prepare a contribution margin income statement.
Contribution Margin Income Statement
< Required A
$ 104 per unit
$ 2,420,000
$ 485 per unit
$ 45 per unit
$ 62
per unit
$ 278,000
45,000
the tabs
$ 4 per unit
low.
Required B >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please see image file for complete problemarrow_forward! Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Preble Company manufactures one product. Its variable manufacturing overhead is applied to production based on direct labor-hours and its standard cost card per unit is as follows: Direct materials: 5 pounds at $10 per pound Direct labor: 4 hours at $16 per hour Variable overhead: 4 hours at $7 per hour Total standard cost per unit $ 50 64 28 $ 142 The planning budget for March was based on producing and selling 20,000 units. However, during March the company actually produced and sold 24,600 units and incurred the following costs: a. Purchased 164,000 pounds of raw materials at a cost of $7.50 per pound. All of this material was used in production. b. Direct laborers worked 57,000 hours at a rate of $17 per hour. c. Total variable manufacturing overhead for the month was $653,220. 8. What direct labor cost would be included in the company's flexible budget for March? Direct labor costarrow_forwardBenson Manufacturing Company established the following standard price and cost data. Sales price Variable manufacturing cost $ 8.00 per unit $3.40 per unit $ 2,400 total $900 total Fixed manufacturing cost Fixed selling and administrative cost Bertson planned to produce and sell 2,700 units. Actual production and sales amounted to 3,000 units. Required a. Prepare the pro forma income statement in contribution format that would appear in a master budget. b. Prepare the pro forma income statement in contribution format that would appear in a flexible budget Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required Prepare the pro forma income statement in contribution format that would appear in a master budget. BENSON MANUFACTURING COMPANY Pro Forma Income Statement Master Budget 2,700 Units oarrow_forward
- Nevada Corporation makes a product with the following standard costs: Standard Quantity or Hours Standard Price or Rate 3.00 per ounce 6.4 ounces 0.4 hours 0.4 hours $ $ 13.00 per hour S 5.00 per hour The company reported the following results concerning this product in March. Originally budgeted output Actual output Raw materials used in production Actual direct labor-hours Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Purchases of raw materials Actual price of raw materials Actual direct labor rate Actual variable overhead rate O $3,136 F O $3,260 F S S S O $3,136 U O $3,260 U Standard Cost Per Unit S S S 4,800 units 4,900 units 30,230 ounces 1,910 hours. 32,600 ounces 2.90 per ounce 12.40 per hour 4.90 per hour The company applies variable overhead on the basis of direct labor-hours. The direct materials purchases variance is computed when the materials are purchased. The materials price variance for March is: 19.20 5.20 2.00arrow_forwardThe management of Hartman Company is trying to determine the amount of each of two products to produce over the coming planning period. The following information concerns labor availability, labor utilization, and product profitability: Labor-Hours Required(hours/unit) Department Product 1 Product 2 Hours Available A 1.00 0.35 95 B 0.30 0.20 36 C 0.20 0.50 50 Profit contribution/unit $30.00 $15.00 (a) Develop a linear programming model of the Hartman Company problem. Solve the model to determine the optimal production quantities of products 1 and 2. If required, round your answer to two decimal places. Product 1 Product 2 Production (b) In computing the profit contribution per unit, management does not deduct labor costs because they are considered fixed for the upcoming planning period. However, suppose that overtime can be scheduled in some of the departments. Which departments would you recommend scheduling for…arrow_forwardMission Company is preparing its annual profit plan. As part of its analysis of the profitability of individual products, the controller estimates the amount of overhead that should be allocated to the individual product lines from the information provided below (CMA adapted) Units produced Material moves per product line. Direct labor-hours per product line Budgeted material handling costs: $644,000 Wall Mirrors Specialty Windows 220 20 5 1,100 60 1,200 Under a traditional costing system that allocates overhead on the basis of direct labor-hours, the materials handling costs allocated to one unit of Specialty Windows would be Multiple Choice O $16.800 $54,900 $14,000 $22.700arrow_forward
- Please assist!arrow_forwardA company has two products A and B. The budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is $10,000. It is expected to work in full capacity. It plans to use cost-based pricing by using the absorption method. Assume the company can produce and sell 1,000 units Product A and 1,000 units Product B. Product A Product B Direct Labor $1 $3 Direct Materials $3 $2 Variable Manufacturing Overhead $2 $1 Budgeted labor hours used for each unit product 1 4 Budgeted machine hours used for each unit product 3 1 Sale Demand 1000units 1000units Required ROI Rate 10% 5% Required Investment $5000 $30000 Fixed Selling Expenses $2000 $4000 Unit Variable Selling Expenses $1 $2 If allocating fixed manufacturing overhead based on machine hour basis, calculate the sale price of products A and B and budgeted profit of products A and B.arrow_forwardLindquist Company has the following information for February: Line Item Description Amount Sales $370,000 Variable cost of goods sold 173,900 Fixed manufacturing costs 55,500 Variable selling and administrative expenses 40,700 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 22,200 Determine the following for Lindquist Company for the month of February: Line Item Description Amount a. Manufacturing margin $fill in the blank 1 b. Contribution margin $fill in the blank 2 c. Operating income $fill in the blank 3arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education