
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three month period ending March 31 are as follows. Complete the instructions.
| Instructions | |
| 1. | Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. |
| 2. | Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize the entries in the sales and cost of goods sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on account and date your |
| 3. | Determine the gross profit from sales for the period. |
| 4. | Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31. |
| 5. | Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the ending inventory using the last-in, first-out method to be higher or lower? |
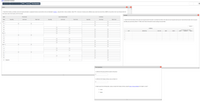
Transcribed Image Text:FIFO perpetual inventory
Instructions
Chart of Accounts
FIFO
Journal
Final Questions
FIFO
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the first-in, first-out method. Under FIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the LOWER unit cost first in the Cost of Goods Sold Unit
Cost column and in the Inventory Unit Cost column.
Journal
Date
Purchases
Cost of Goods Sold
Inventory
Date
Quantity
Unit Cost
Total Cost
Quantity
Unit Cost
Total Cost
Quantity
Unit Cost
Total Cost
2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize the entries in the sales and cost of goods sold accounts. Assume that all sales were on account
Jan. 1
$
$
and date your journal entry March 31. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles.
10
$
2$
$
$
10
$
$
PAGE 10
28
JOURNAL
28
$
$
$
ACCOUNTING FOUATION
30
$
$
$
$
DATE
DESCRIPTION
POST. REF.
DEBIT
CREDIT
ASSETS
LIABILITIES
EQUITY
1
Feb. 5
$
$
$
$
10
$
$
2
10
$
3
16
2$
4
16
$
2$
$
$
28
$
$
$
Mar. 5
2$
2$
$
$
$
$
14
$
2$
14
$
$
$
$
25
2$
2$
$
25
$
$
30
$
$
$
$
30
$
$
31
Balances
$
Final Questions
3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period.
24
4. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31.
5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the ending inventory using the last-in, first-out method to be higher or lower?
O Lower
O Higher
%24

Transcribed Image Text:Instructions
Chart of Accounts
General Ledger
The beginning inventory at Midnight Supplies and data on purchases and sales for a three month period ending March 31 are as follows:
ASSETS
REVENUE
Date
Transaction Number of Units
Per Unit
Total
110 Cash
410 Sales
1 Inventory
$130,000
Jan.
2,500
$52.00
111 Petty Cash
610 Interest Revenue
10
Purchase
7,800
60.00
468,000
120 Accounts Receivable
28
Sale
3,750
104.00
390,000
131 Notes Receivable
EXPENSES
30
Sale
1,200
104.00
124,800
132 Interest Receivable
510 Cost of Goods Sold
Feb.
Sale
500
104.00
52,000
141 Inventory
515 Credit Card Expense
10
Purchase
17,500
62.00
1,085,000
145 Office Supplies
516 Cash Short and Over
16
Sale
8,600
109.00
937,400
146 Store Supplies
520 Salaries Expense
28
Sale
8,900
109.00
970,100
151 Prepaid Insurance
531 Advertising Expense
Mar.
5
Purchase
14,200
63.60
903,120
181 Land
532 Delivery Expense
14
Sale
10,200
109.00
1,111,800
191 Office Equipment
533 Insurance Expense
25
Purchase
3,400
64.00
217,600
192 Accumulated Depreciation-Office Equipment
534 Office Supplies Expense
30
Sale
7,900
109.00
861,100
193 Store Equipment
535 Rent Expense
194 Accumulated Depreciation-Store Equipment
536 Repairs Expense
Instructions
537 Selling Expenses
1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of goods sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 3, using the
LIABILITIES
538 Store Supplies Expense
first-in, first-out method.
2. Determine the total sales and the total cost of goods sold for the period. Journalize the entries in the sales and cost of goods sold accounts.
210 Accounts Payable
561 Depreciation Expense-Office Equipment
Assume that all sales were on account and date your journal entry March 31. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles.
221 Notes Payable
562 Depreciation Expense-Store Equipment
3. Determine the gross profit from sales for the period.
222 Interest Payable
590 Miscellaneous Expense
4. Determine the ending inventory cost as of March 31.
231 Salaries Payable
710 Interest Expense
5. Based upon the preceding data, would you expect the ending inventory using the last-in, first-out method to be higher or lower?
241 Sales Tax Payable
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Date Line Item Description Value Jan. 1 Inventory 2,900 units at $5 Feb. 17 Purchase 2,800 units at $7 Jul. 21 Purchase 3,200 units at $9 Nov. 23 Purchase 1,100 units at $11 There are 1,400 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. This information has been collected in the Microsoft Excel Online file. Open the spreadsheet, perform the required analysis, and input your answers in the questions below. a. Determine the inventory cost by the first-in, first-out method. b. Determine the inventory cost by the last-in, first-out method. c. Determine the inventory cost by the weighted average cost method. Round your answer to the nearest dollararrow_forwardBased upon the following data for a business with a periodic inventory system, determine the cost of goods sold for August. Inventory, August 1 Inventory, August 31 Purchases Purchases returns and allowances Purchases discounts Freight in Schedule of the Cost of Goods Sold For the Month Ended August 31 Line Item Description Cost of merchandise purchased: Net purchases Total cost of merchandise purchased $ 71,130 90,820 368,870 16,360 12,190 3,540 Amount Amount 1000 $arrow_forwardThe following are the transactions for the month of July. Units Unit Cost Unit Selling Price July 1 Beginning Inventory 55 $ 10 July 13 Purchase 275 11 July 25 Sold (100 ) $ 14 July 31 Ending Inventory 230 Calculate cost of goods available for sale and ending inventory, then sales, cost of goods sold, and gross profit, under FIFO. Assume a periodic inventory system is used. How would i creat a FIFO periodic table?arrow_forward
- A company reports the following beginning inventory and two purchases for the month of January. On January 26, the company sells 280 units. Ending inventory at January 31 totals 130 units. Beginning inventory on January 1 Purchase on January 9 Purchase on January 25 Perpetual FIFO: Required: Assume the perpetual inventory system is used. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the FIFO method. Date January 1 January 9 January 25 January 26 Totals Goods purchased # of units Cost per unit Units Unit Cost 250 60 100 # of units sold $2.30 2.50 2.64 Cost of Goods Sold Cost per Cost of Goods unit Sold Inventory Balance Cost per unit # of units Inventory Balancearrow_forwardThe units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan 1 Inventory 15 units at 122 April 15 Purchase 140 units at 116 September 9 Purchase 26 units at 122 There are 31 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using the last-in, first-out (LIFO)arrow_forwardPlease help me make a perpetual FIFO, perpetual LIFO, Weighted Average, and Specific ID chart. Thank youarrow_forward
- Sant Summa is a retailer that purchases merchandise inventory from Lee Co. Sant Summa record inventory purchases using the gross method and the perpetual inventory system. Sant Summa started the month of July with $2,000 in inventory. Required: Record the journal entries for the following transactions Calculate Sant Summa's Cost of Goods Available for Sale based on the above information. Calculate Sant Summa's Ending Inventory based on the above information. 2-Jul Purchased $5,200 of merchandise inventory from Lee Co. with credit terms 2/15, n60 and FOB shipping point. (Inventory cost Lee $4,000) 3-Jul Paid $350 for shipping charges for the May 2 purchase. 4-Jul Sant Summa returned $200 of damaged merchandise inventory to Lee Co. (inventory cost to Lee of $170) 13-Jul Paid the appropriate amount for the Lee Co. purchases of July 2, taking all discounts. (Lee…arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forwardThe following purchase transactions occurred during the last few days of Whilczel Company's business year, which ends October 31, or in the first few days after that date. A periodic inventory system is used. · An invoice for P6,000, terms FOB shipping point, was received and entered November 1. The invoice shows that the material was shipped October 29, but the receiving report indicates receipt of goods on November 3. · An invoice for P2,700, terms FOB destination, was received and entered November 2. The receiving report indicates that the goods were received October 29. · An invoice for P3,150, terms, FOB shipping point, was received October 15, but never entered. Attached to it is a receiving report indicating that the goods were received October 18. Across the face of the receiving report is the following notation: "Merchandise not of the same quality as ordered - returned for credit October 19". · An invoice for P3,600 terms FOB shipping…arrow_forward
- PLEASE HELP MEarrow_forwardScoresby Incorporated tracks the number of units purchased and sold throughout each year but applies its inventory costing method at the end of the year, as if it uses a periodic inventory system. Assume its accounting records provided the following information at the end of the annual accounting period, December 31. Transactions a. Inventory, Beginning For the year: b. Purchase, March 5 c. Purchase, September 19 d. Sale, April 15 (sold for $75 per unit) 00 8 e. Sale, October 31 (sold for $78 per unit) f. Operating expenses (excluding income tax expense), $607,000 Required: 1. Calculate the number and cost of goods available for sale. 2. Calculate the number of units in ending inventory. Units 4,000 Unit Cost $ 30 10,000 31 6,000 4,400 9,000 33 3. Compute the cost of ending inventory and cost of goods sold under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, and (c) weighted average cost. 4. Prepare an income statement that shows the FIFO method, LIFO method and weighted average method. 6. Which inventory…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education