
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The above table shows the payoffs that either Darrin or Rob receive depending on whether they choose a high or a low
A. Darrin - Low Price; Rob - Low Price.
B. Darrin - Low Price; Rob - High Price.
C. Darrin - High Price; Rob - Low Price.
D. Darrin - High Price; Rob - High Price.
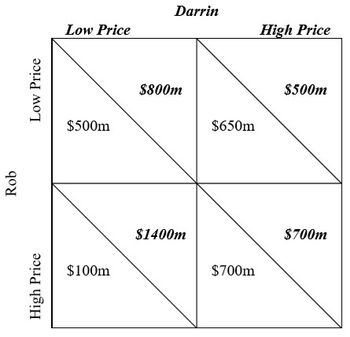
Transcribed Image Text:Rob
Low Price
High Price
Low Price
$500m
$100m
Darrin
$800m
$1400m
$650m
$700m
High Price
$500m
$700m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question one is for information only, I need question 4arrow_forwardQ3. Two ice cream trucks operate on a beach and play a simultaneous pricing game. If one of them prices low and the other high it gets all the customers and a pay off of 12 while the other gets zero. If both price high each gets 6, and if both price low each get 5. The best strategy is for both to price high. True/False/Uncertain. Explain.arrow_forwardWhich of the following gambles is “unfair”? a. A game that promises to pay you $1 if a coin comes up head and cost you $1 if a coin comes up tail, with no entry fee. b. A game that promises to pay you $10 if a coin comes up head and cost you $1 if a coin comes up tail, with no entry fee. c. A game that promises to pay you $10 if a coin comes up head and cost you $1 if a coin comes up tail, with an entry fee of $4.50 for the right to play. d. All of the above.arrow_forward
- Which one of the following statements is incorrect? A. Nash equilibrium analysis can be applied to both the Cournot and Bertrand models. B. In both the Cournot and Bertrand games the players' payoff functions are profit functions. C. In both the Cournot and Bertrand games the consumers are not explicitly modelled as players. D. One of the above is incorrect.arrow_forward1. Use the following one-shot, normal form game to answer the questions below. Strategy A 100, 125 300, 250 200, 100 250, 0 500, 500 750, 400 400, 300 -100, 350 0, -100 (a) Find each player's dominant strategy, if it exists. (b) Find the Nash equilibrium.arrow_forwardrituo? A. Identify the pure-strategy Nash equilibrium/a in the game below, and identify the Pareto efficient strategy combinations. (You may simply state these, you do not need to show how you derived your answer.) B. Identify the mixed-strategy equilibrium to the game. Show your work. You may use the equations from the "generic" 2X2 game if you wish. Doing it the long way is fine, however. C. State the payoff for each player in the mixed-strategy equilibrium. Is the mixed-strategy combination Pareto efficient? Player 1 U D 20 Player 2 L (10,15) (1,5) R (0,6) (1,6)arrow_forward
- Asaaaparrow_forwardIt's a game theory bargaining game problem. I'm not familiar with cursive writing.arrow_forwardBeta's Price Policy High Low A B $20 $30 High Alpha's Price Policy $20 $10 C D $10 $15 Low $30 $15 Refer to the diagram, where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars. Beta's profits are shown in the northeast corner and Alpha's profits in the southwest corner of each cell. If both firms follow a high-price policy. Multiple Choice Beta will realize a $10 million profit and Alpha a $30 million profit. each will realize a $15 million profit Alpha will realize a $10 million profit and Beta a $30 million profitarrow_forward
- Refer to the following payoff table: Firm A's Advertising Budget Low Multiple Choice Medium High A D G $900, $900 Low $1,000, $800 Firm A High; Firm B Low Firm A Low; Firm B Low Firm B's Advertising Budget Medium B E H $820, $1,220 $950, $1,025 с F 1 High $875, $920 $800, $875 $1,025, $1,175 Using the method of successive elimination of dominated strategies, which strategies, if any, are eliminated after the first round? $1,060, $1,100 $1,040, $1,000arrow_forwardGame Theoryarrow_forwardGame theory - please help. Thanks!arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education