
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
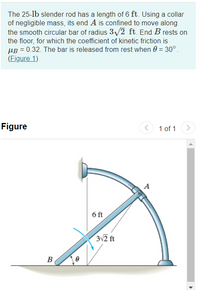
Transcribed Image Text:The 25-lb slender rod has a length of 6 ft. Using a collar
of negligible mass, its end A is confined to move along
the smooth circular bar of radius 3/2 ft. End B rests on
the floor, for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is
µB = 0.32. The bar is released from rest when 0 = 30°.
(Figure 1)
Figure
1 of 1
A
6 ft
3v2 ft
B
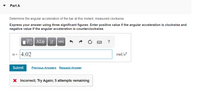
Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Determine the angular acceleration of the bar at this instant, measured clockwise.
Express your answer using three significant figures. Enter positive value if the angular acceleration is clockwise and
negative value if the angular acceleration is counterclockwise.
vec
a = 4.02
rad/s?
Submit
Previous Answers Request Answer
X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remaining
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Part B and Carrow_forward4. A uniform disc of mass m = 3 kg and radius R= 0.5 may roll without slip on the 30 degree incline shown. An elastic spring of stiffness k= 100 newtons/meter is connected to the center C of the disc. Initially, the disc is held in place in the position shown, with the spring neither stretched nor compressed and with the disc at rest. At t = 0 the disc is released and is subjected to a constant force of Fo = 30 newtons along the incline. Determine the maximum speed achieved by the disc center C as the disc moves up the incline. For gravity use g = 10 m/sec². (note: initially the constant force Fo will be greater than the forces exerted by the spring and by gravity, and the disc will accelerate up the incline; but there will come a distance x along the incline after which the spring force + gravity will overtake the force Fo, and the disc will then decelerate). gravity Fo= 30 N 30° no frictionarrow_forwardCan anyone help me with this questionarrow_forward
- The 10 kg slender bar AB, shown in the figure, has a length of 2 m. A blockof negligible mass, pinned freely to end A, is confined to move along the smooth circular groove with its centre at O. End B rests on the floor for which the coefficient of kinetic friction, µk = 0.4. If the bar is released from rest when θ = 30 degreesa) identify the type of ensuing motion of the bar,b) draw the free body, kinematic and kinetic diagrams for the bar, c) set up a global reference axes system, and write down the relevantkinetic and kinematic relationships with respect to reference axes system, andd) determine the angular acceleration of the bar and the reaction forces at ends A and B.arrow_forwardIn The mass of block A is 60 kg. Neglect the weightof the 5 wedge. The coefficient of kinetic frictionbetween the contacting surfaces of the block A, thewedge, the table, and the wall is ?? = 0.4 . The pitchof the threaded shaft is 5 mm, the mean radius of thethread is 15 mm, and the coefficient of kineticfriction between the thread and the mating groove is0.2. What couple must be exerted on the threadedshaft to raise the block A at a constant rate?arrow_forwardRequired information NOTE: This is a multi-part question. Once an answer is submitted, you will be unable to return to this part. A uniform 4-kg cylinder A, of radius r= 150 mm, has an angular velocity wo = 52 rad/s when it is brought into contact with an identical cylinder B, which is at rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction at the contact point Dis uk. After a period of slipping, the cylinders attain constant angular velocities of equal magnitude and opposite direction at the same time. Consider that cylinder A executes three revolutions before it attains one revolution before it attains a constant angular velocity. constant angular velocity and cylinder Bexecutes Determine the final angular velocity of each cylinder. The final angular velocities of cylinders A and B are |rad/s (Click to select) and rad/s (Click to select) + , respectively.arrow_forward
- A bar of mass mb is to be released from rest at the position shown. Three possible designs use rollers differently. All rollers have the same identical masses m, and radii r. Each can be approximated as cylinders. After dropping a distance h, which would move the fastest, and which the slowest. Quantify your answer with an equation of v for each case. The designs will be made to allow no slipping and make any bracket weight negligible. HH Q Search A B (a) A THE B (b) O O |-----| O A al p BCD ESP |--| x Oarrow_forwardSolve it correctly. I ll ratearrow_forwardReview The 25-kg roll of paper has a radius of gyration kA = 90 mm about an axis passing through point A. It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets AB. The roll rests against a wall for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is pe = 0.3. Neglect the mass of paper that is removed. (Eigure 1) Part A Determine the magnitude of the constant vertical force F that must be applied to the roll to pull off 1 m of paper in t = 3 s starting from rest Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figurearrow_forward
- A tire has a weight of 55 lb and a radius of gyration of kg=0.6 ft. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the tire and plane are µs=0.2 and Hk=0.15, a) Draw the FBD and KD of the tirearrow_forwardA homogeneous cylinder weighing 32.2 Ib has a narrow slot cut in it as shown. A force of 12 Ib is exerted on a string wrapped in the slot. If the cylinder rolls without slipping, determine the acceleration of its mass center and the frictional force F. Neglect the effect of the slot.arrow_forwardPart A The 21-kg roll of paper has a radius of gyration kA = 90 mm about an axis passing through point A. It is pin supported at both ends by two brackets AB. The roll rests against a wall for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is u = 0.2. Neglect the mass of paper that is removed. (Figure 1) Determine the magnitude of the constant vertical force F that must be applied to the roll to pull off 1 m of paper in t = 3 s starting from rest. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. TH HẢ ? F = Value Units Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback Figure < 1 of 1 300 mm 125 mmarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY