
Concept explainers
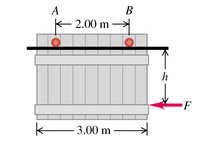
A garage door is mounted on an overhead rail. The wheels at A and B have rusted so that they do not roll, but rather slide along the track. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.55. The distance between the wheels is 2.00 m, and each is 0.50m from the vertical sides of the door. The door is uniform and weighs 850 N. It is pushed to the left at constant speed by a horizontal force F⃗, that is applied as shown in the figure.
If the distance h is 1.60 m, what is the vertical component of the force exerted on the wheel A by the track?
If the distance h is 1.60 m, what is the vertical component of the force exerted on the wheel B by the track?
Find the maximum value hh can have without causing one wheel to leave the track.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

- Part B and Carrow_forwardFind the rato of masses m1/m2arrow_forwardA 2.2-kg sphere S is being moved in a vertical plane by a robotic arm. When the angle is 36°, the angular velocity of the arm about a horizontal axis through O is 45 deg/s clockwise and its angular acceleration is 176 deg/s² counterclockwise. In addition, the hydraulic element is being shortened at the constant rate of 550 mm/s. Determine the necessary minimum gripping force P if the coefficient of static friction between the sphere and the gripping surfaces is 0.58. Compare P with the minimum gripping force P, required to hold the sphere in static equilibrium in the 36° position. 1.0 m $ Answers: P= Ps= i i N Narrow_forward
- The uniform cylindrical drum D weighs 42.0 lb. The coefficient of static friction at all surfaces is 0.600, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.500 at all surfaces. The cylinder is pushed by force P applied to a pad as shown, and it is intended for the cylinder to translate horizontally without rotation. a) Calculate the minimum force P required.b) Calculate the acceleration of the drum.arrow_forwardLost on this one, any help would be appreciated. Check all possible motionsarrow_forwardA pile-driver hammer has a mass of 300 kg and is to be raised 16 m in 4 sec. The total friction on the guides is constant at 400 N. What constant pull must be exerted on the cable?arrow_forward
- 2. A 250-lb block Is initially at rest on a flat surface that is inclined at 30°. If the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.30 and the coefficient of static friction is 0.40, find the force required to start the block moving up the plane. 250 1b. 30°arrow_forwardProblem No. 1 A 200-kg block rests on a horizontal plane. Find the magnitude of the force P required to give the block an acceleration of 1.80 m/s² to the right. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane is 0.25. P 30°arrow_forward3. A vehicle, mass 1400 kg, passes a bend at a speed of 54 km/hr. The radius of curvature of the road is 60 m. Determine the minimum coefficient of static friction between the car tires and the road, so that the car can pass through corners safely.arrow_forward
- Please illustrate the Free Body Diagram of each blocks. Show me the derivation of the equations(Summation X and Y) Thanks in advance Keep Safe!arrow_forwardConstants The disk weighs 11 lb and its radius is 6 in. It is stationary on the surface when the force F = 13 lb is applied. Part A If the disk rolls on the surface, what is the acceleration of its center? Express your answer with the appropriate units. HẢ ? ft a = 38.05 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 6 attempts remaining Figure Part B What minimum coefficient of static friction necessary for the disk to roll instead of slipping when the force is applied? (Figure 1) να ΑΣφ ? vec Hs = Submit Request Answer P Pearsonarrow_forwardA tire has a weight of 55 lb and a radius of gyration of kg=0.6 ft. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the tire and plane are µs=0.2 and Hk=0.15, a) Draw the FBD and KD of the tirearrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





