
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A cylinder of mass M and radius R is rotated in a uniform V groove
with constant angular speed ω. The coefficient of friction between
the cylinder and each surface is μ. What torque must be applied to
the cylinder to keep it rotating?
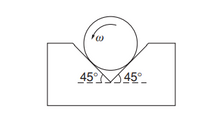
Transcribed Image Text:45° 45°
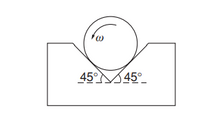
Transcribed Image Text:45° 45°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please show all work and diagrams! Anything is helpful.arrow_forward8. The 20 kg uniform disk of radius r= 0.4 m is at rest on the incline (0 = 20°) when a constant force T= 200 N is applied as shown pulling the cord that is securely wrapped around the rim of the disk. If the coefficients of friction on the incline are u, = 0.3 and u, = 0.2, determine the friction force between the disk and the incline, the angular acceleration of the disk, and the acceleration at the mass center G. F (magnitude and direction) - T a (magnitude and direction) =. ac (magnitude and direction) = Garrow_forwardThe 29-kg wheel is rolling under the constant moment of M = 85 N·m. The wheel has radius r = 0.57 m, has mass center at point G, and the radius of gyration is kg = 0.25 m. The coefficients of friction between the wheel and the ground is g = 0.37 and μk = 0.16. If the wheel rolls while slipping, determine the magnitude of the linear acceleration of point G (in m/s²). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². M Your Answer: Answerarrow_forward
- The 16-kg wheel is rolling under the constant moment of M = 60 N-m. The wheel has radius r= 0.50 m, has mass center at point G, and the radius of gyration is kg = 0.23 m. The coefficients of friction between the wheel and the ground is ls = 0.28 and Uk = 0.14. If the wheel rolls without slipping, determine the angular acceleration of the wheel (in rad/s?). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. Marrow_forwardThe cylinder is uniform and has a mass of 5.00 kg. It is released from rest.a) Calculate the least coefficient of friction between the cylinder and the plane for which the cylinder will roll without slipping.b) Calculate the acceleration of the center of mass G of the cylinder if it rolls without slipping.arrow_forwardProblem #4) The extremities of a 4-ft rod weighing 50lb (1.5528slugs) can move freely and with no friction along two straight tracks. The rod is released with no velocity from the position shown, resulting in the rod to slide down the incline. The angular acceleration of the rod is a = +2.30k rad/s² and the linear acceleration at point A is 12.5674ft/s² to the right. Determine (a) ao, the linear acceleration at point G, and (b) RA and RB, the normal reaction forces at point A and B. Include and present the Free Body Diagram and Inertial Response Diagram as part of the solving process. B B=45° 4 ft G O D 30°1 Aarrow_forward
- The 30-kg wheel is rolling under the constant moment of M = 84 N.m. The wheel has radius r = 0.48 m, has mass center at point G, and the radius of gyration is kg = 0.24 m. The coefficients of friction between the wheel and the ground is μ = 0.39 and k=0.10. If the wheel rolls without slipping, determine the angular acceleration of the wheel (in rad/s²). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². M Your Answer: Answer G 1arrow_forwardPlease answer quickly. Thanksarrow_forwardThe roller is pushed forward with a force of 200 N when the handle is at 45°. The friction coefficients between the roller and the ground are μ = 0.12 and k = 0.1. If the roller has a mass of 80 kg and a moment of inertia of 2.45 kg m² about its center of mass, calculate the magnitude of the angular acceleration of it. Present your answer in rad/sec² using 3 significant figures. MARANANLA G 45° 200 mm A 200 Narrow_forward
- A tire has a weight of 55 lb and a radius of gyration of kg=0.6 ft. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the tire and plane are µs=0.2 and Hk=0.15, a) Draw the FBD and KD of the tirearrow_forwardThe system shown below consists of a uniform disk D that has a mass of mp = 3.0 kg and a radius of r = 1.0 meters. The disk is connected by a massless cable to a block. The system is released from rest and the disk starts rolling without sliding with the angular acceleration of a = rad 30 s2 in the clockwise direction. Determine the magnitude of the friction force (in Newtons) developed between the disk and the inclined surface at this instant. Consider 0 = 40° and g = 10 m. mparrow_forwardA box with mass m = 2.75 kg rests on the top of a table. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the table is μs = 0.71 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.34. Write an expression for Fm the minimum force required to produce movement of the box on the top of the table. Solve numerically for the magnitude of the force Fm in Newtons. Write an expression for a, the box's acceleration, after it begins moving. (Assume the minimum force, Fm, continues to be applied.) Solve numerically for the acceleration, a in m/s2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY