
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
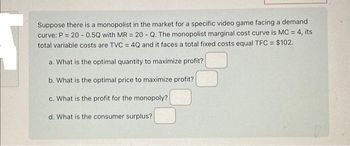
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose there is a monopolist in the market for a specific video game facing a demand
curve: P = 20-0.5Q with MR = 20 - Q. The monopolist marginal cost curve is MC = 4, its
total variable costs are TVC = 4Q and it faces a total fixed costs equal TFC = $102.
a. What is the optimal quantity to maximize profit?
b. What is the optimal price to maximize profit?
c. What is the profit for the monopoly?
d. What is the consumer surplus?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 12 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A Moving to another question will save this response. Question 15 Steve is the only seller of water in town. The market for water is characterized by the following: Demand: P = 100 - 2Q Marginal Revenue: MR = 100 - Q Marginal Cost: MC = 20 +Q %3D What is the Monopolist equilibrium price and quantity? P= 40; Q= 30 P = 80; Q = 30 P= 40; Q = 70 P= 80; Q = 40 A Moving to another question will save this response. 45,055 HORDA tvarrow_forwardThe following table shows a monopolist’s demand curve and cost information for the production of its good. What price will it charge? Quantity Price per Unit Total Cost 25 $5 $110 30 $10 $125 35 $14 $130 40 $15 $140 Question 7 options: $13 $15 $11 $12arrow_forwardConsider a monopolist with the following demand curve. Price: 24, 22 , 20, 18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6 Quantity Demanded: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 [All answers are integers with no units.] 1.If this firm has a marginal cost of $12 per unit, how many will they produce? 2.What will their profit be? 3.What will consumer surplus be? (Rectangle method!) 4.What is the efficient quantity?arrow_forward
- At an output of 1,000 units, a monopoly firm’s average revenue is $40, its marginal revenue is $30, its marginal cost is $30, its average variable cost is $35, and fixed costs are $5,000. Given this information, we can conclude that the monopolist: a. is earning zero economic profit. b. is earning an economic profit equal to $5,000. c. is making an economic loss and should shut down. d. should increase output to maximize profit.arrow_forwarda monopolist finds the demand curve to be linear, containing data points (q,p) of (100,125) and (20,165). a. how many items can he expect to sell, if the price p is $100? b. what price should he charge to maximize the revenue?arrow_forwardThe monopolist faces the following demand curve: Price $20 Quantity 15 $19.50 16 $19 17 $18.50 18 $18 19 $17.50 20 $17 21 $16.50 22 $16 23 If the monopolist has total fixed costs of $40 and a constant marginal cost of $10, how much profit can the firm earn at the profit-maximizing level of output?arrow_forward
- Suppose that a monopolist faces inverse demand given by P = 100 - 10Q and marginal cost given by MC = 20. 1. What is the profit function? 2. What is the marginal revenue function? 3. What is the equilibrium quantity? 4. What is the equilibrium markup?arrow_forwardExercise 3.3. Suppose a profit-maximizing monopolist is producing 800 units of output and is charging a price of $40 per unit. a. If the elasticity of demand for the product is -2, find the marginal cost of the last unit produced. b. What is the firm's percentage markup of price over marginal cost? c. Suppose that the average cost of the last unit produced is $15 and the firm's fixed cost is $2000. Find the firm's profit.arrow_forwardIn the following situation, what should the monopolist do to maximize profit? Select the best answer. A monopolist is currently producing a level of output such that marginal revenue is $143 and marginal cost is $109. The monopolist then sets a price based on demand for the current level of output. Answer 2 Points Keyboard Shortcuts The monopolist should decrease output and decrease price. The monopolist should increase output and increase price. The monopolist should incs The monopolist should decrease output and increase price.arrow_forward
- In the figure below, the competitive price will be, lower than the monopolistic price, and the monopolist causes a loss in social welfare. 100 80 MC 60 40 20 MR Price and coste (cents per bottle]arrow_forwardExercise 3.8. Dayna's Doorstops, Inc. (DD) is a monopolist in the doorstop industry. Its cost is C = 100 - 5Q + Q², and demand is P = 55 - 2Q. a) What price should DD set to maximize profit? What output does the firm produce? How much profit and consumer surplus does DD generate? b) What would output be if DD acted like a perfect competitor and set MC = P? What profit and consumer surplus would then be generated? c) What is the deadweight loss from monopoly power in part (a)? d) Suppose the government, concerned about the high price of doorstops, sets a maximum price at $27. How does this affect price, quantity, consumer surplus, and DD's profit? What is the resulting deadweight loss? e) Now suppose the government sets the maximum price at $23. How does this decision affect price, quantity, consumer surplus, DD's profit, and deadweight loss? f) Finally, consider a maximum price of $12. What will this do to quantity, consumer surplus, profit, and deadweight loss?arrow_forwardSuppose a monopolist's profit-maximizing output is 400 units per week and that the firm sells its output at a price of $40 per unit. The firm has total costs of $8,000 per week. Assume the monopolist is maximizing its profit and earns $20 per unit from the sale of the last unit produced each week. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. a. What are the firm's weekly economic profits? b. What is the firm's marginal cost? c. What is the firm's average total cost? Aarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education