
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
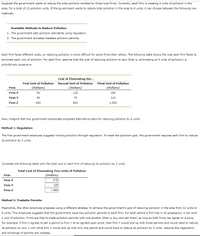
Suppose the government wants to reduce the total pollution emitted by three local firms. Currently, each firm is creating 4 units of pollution in the area, for a total of 12 pollution units. If the government wants to reduce total pollution in the area to 6 units, it can choose between the following two methods:
| Available Methods to Reduce Pollution | |
| 1. | The government sets pollution standards using regulation. |
| 2. | The government allocates tradable pollution permits. |
Each firm faces different costs, so reducing pollution is more difficult for some firms than others. The following table shows the cost each firm faces to eliminate each unit of pollution. For each firm, assume that the cost of reducing pollution to zero (that is, eliminating all 4 units of pollution) is prohibitively expensive.
|
Firm
|
Cost of Eliminating the...
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
|
First Unit of Pollution
|
Second Unit of Pollution
|
Third Unit of Pollution
|
|
|
(Dollars)
|
(Dollars)
|
(Dollars)
|
|
| Firm X | 90 | 125 | 180 |
| Firm Y | 55 | 70 | 110 |
| Firm Z | 650 | 800 | 1,500 |
Now, imagine that two government employees proposed alternative plans for reducing pollution by 6 units.
Method 1: Regulation
The first government employee suggests limiting pollution through regulation. To meet the pollution goal, the government requires each firm to reduce its pollution by 2 units.
Complete the following table with the total cost to each firm of reducing its pollution by 2 units.
|
Firm
|
Total Cost of Eliminating Two Units of Pollution
|
|---|---|
|
(Dollars)
|
|
| Firm X |
|
| Firm Y |
|
| Firm Z |
|
Method 2: Tradable Permits
Meanwhile, the other employee proposes using a different strategy to achieve the government's goal of reducing pollution in the area from 12 units to 6 units. This employee suggests that the government issue two pollution permits to each firm. For each permit a firm has in its possession, it can emit 1 unit of pollution. Firms are free to trade pollution permits with one another (that is, buy and sell them) as long as both firms can agree on a price. For example, if firm X agrees to sell a permit to firm Y at an agreed-upon price, then firm Y would end up with three permits and would need to reduce its pollution by only 1 unit while firm X would end up with only one permit and would have to reduce its pollution by 3 units. Assume the negotiation and exchange of permits are costless.
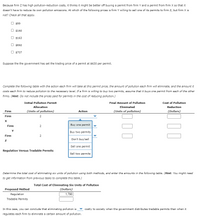
Because firm Z has high pollution-reduction costs, it thinks it might be better off buying a permit from firm Y and a permit from firm X so that it doesn't have to reduce its own pollution emissions. At which of the following prices is firm Y willing to sell one of its permits to firm Z, but firm X is not? Check all that apply.
$99 ?
$160 ?
$163 ?
$692 ?
$707 ?
Suppose the the government has set the trading price of a permit at $630 per permit.
Complete the following table with the action each firm will take at this permit price, the amount of pollution each firm will eliminate, and the amount it costs each firm to reduce pollution to the necessary level. If a firm is willing to buy two permits, assume that it buys one permit from each of the other firms. (Hint: Do not include the prices paid for permits in the cost of reducing pollution.)
|
Firm
|
Initial Pollution Permit Allocation
|
Action
|
Final Amount of Pollution Eliminated
|
Cost of Pollution Reduction
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(Units of pollution)
|
(Units of pollution)
|
(Dollars)
|
||
| Firm X | 2 |
|
|
|
| Firm Y | 2 |
|
|
|
| Firm Z | 2 |
|
|
Regulation Versus Tradable Permits
Determine the total cost of eliminating six units of pollution using both methods, and enter the amounts in the following table. (Hint: You might need to get information from previous tasks to complete this table.)
|
Proposed Method
|
Total Cost of Eliminating Six Units of Pollution
|
|---|---|
|
(Dollars)
|
|
| Regulation |
|
| Tradable Permits |
|
In this case, you can conclude that eliminating pollution is costly to society when the government distributes tradable permits than when it regulates each firm to eliminate a certain amount of pollution.
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the government wants to reduce the total pollution emitted by three local firms. Currently, each firm is creating 4 units of pollution in the
area, for a total of 12 pollution units. If the government wants to reduce total pollution in the area to 6 units, it can choose between the following two
methods:
Available Methods to Reduce Pollution
1. The government sets pollution standards using regulation.
2. The government allocates tradable pollution permits.
Each firm faces different costs, so reducing pollution is more difficult for some firms than others. The following table shows the cost each firm faces to
eliminate each unit of pollution. For each firm, assume that the cost of reducing pollution to zero (that is, eliminating all 4 units of pollution) is
prohibitively expensive.
Cost of Eliminating the...
First Unit of Pollution Second Unit of Pollution Third Unit of Pollution
(Dollars)
Firm
(Dollars)
(Dollars)
Firm X
90
125
180
Firm Y
55
70
110
Firm Z
650
800
1,500
Now, imagine that two government employees proposed alternative plans for reducing pollution by 6 units.
Method 1: Regulation
The first government employee suggests limiting pollution through regulation. To meet the pollution goal, the government requires each firm to reduce
its pollution by 2 units.
Complete the following table with the total cost to each firm of reducing its pollution by 2 units.
Total Cost of Eliminating Two Units of Pollution
Firm
(Dollars)
Firm X
215
Firm Y
125
Firm Z
1,450
Method 2: Tradable Permits
Meanwhile, the other employee proposes using a different strategy to achieve the government's goal of reducing pollution in the area from 12 units to
6 units. This employee suggests that the government issue two pollution permits to each firm. For each permit a firm has in its possession, it can emit
1 unit of pollution. Firms are free to trade pollution permits with one another (that is, buy and sell them) as long as both firms can agree on a price.
For example, if firm X agrees to sell a permit to firm Y at an agreed-upon price, then firm Y would end up with three permits and would need to reduce
its pollution by only 1 unit while firm X would end up with only one permit and would have to reduce its pollution by 3 units. Assume the negotiation
and exchange of permits are costless.
Transcribed Image Text:Because firm Z has high pollution-reduction costs, it thinks it might be better off buying a permit from firm Y and a permit from firm X so that it
doesn't have to reduce its own pollution emissions. At which of the following prices is firm Y willing to sell one of its permits to firm z, but firm X is
not? Check all that apply.
O $99
O $160
$163
$692
$707
Suppose the the government has set the trading price of a permit at $630 per permit.
Complete the following table with the action each firm will take at this permit price, the amount of pollution each firm will eliminate, and the amount it
costs each firm to reduce pollution to the necessary level. If a firm is willing to buy two permits, assume that it buys one permit from each of the other
firms. (Hint: Do not include the prices paid for permits in the cost of reducing pollution.)
Initial Pollution Permit
Final Amount of Pollution
Cost of Pollution
Allocation
Eliminated
Reduction
(Units of pollution)
(Units of pollution)
(Dollars)
Firm
Action
Firm
2
Buy one permit
Firm
Y
Buy two permits
Firm
2
Don't buy/sell
Sell one permit
Regulation Versus Tradable Permits
Sell two permits
Determine the total cost of eliminating six units of pollution using both methods, and enter the amounts in the following table. (Hint: You might need
to get information from previous tasks to complete this table.)
Total Cost of Eliminating Six Units of Pollution
Proposed Method
(Dollars)
Regulation
1,790
Tradable Permits
In this case, you can conclude that eliminating pollution is
costly to society when the government distributes tradable permits than when it
regulates each firm to eliminate a certain amount of pollution.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 40 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The town has a kayak rental and visitors use the lake for recreation. The town also has a chemical lab that dumps industrial waste into the lake. This pollutes the lake and makes it a less desirable vacation destination. That is, the chemical lab's waste decreases the kayak rental's economic profit. Suppose that the chemical lab could use a different production method that involves recycling water. This would reduce the pollution in the lake to levels safe for recreation, and the kayak rental would no longer be affected. If the chemical lab uses the recycling method, then the chemical lab's economic profit is $900 per week, and the kayak rental's economic profit is $2,600 per week. If the chemical lab does not use the recycling method, then the chemical lab's economic profit is $1,600 per week, and the kayak rental's economic profit is $1,500 per week. These figures are summarized in the following table. Complete the following table by computing the total profit (the chemical lab's…arrow_forwardSuppose that speeding imposes externalities on other people resulting in a social cost of $50. A town is considering hiring an extra police officer to give out speeding tickets. If we want to maximize social welfare (absent enforcement costs), which of the following statements are true? (Assume risk neutral drivers.) What happens to the socially optimal cost of the speeding ticket if the town decides to hire the police officer? a) It goes down b) It goes up c) The amount that it goes down depends on salary of the police officer d) The amount if goes up depends on the salary of the police officer e) None of the abovearrow_forwardSuppose a municipality votes to reduce the combined pollution introduced by three local companies. Presently, each firm creates 4 units of pollution in the area, for a total of 12 pollution units. The government can reduce total pollution in the area to 6 units by choosing between the following two methods: Methods to Reduce Pollution 1. The government imposes pollution standards using regulation. 2. The government issues tradable pollution permits. The costs faced by each firm are different, so it is more difficult for some firms to reduce pollution than others. The following table shows the cost faced by each firm to eliminate each unit of pollution. Assume that the cost of eliminating all 4 units of pollution (that is, reducing pollution to zero) is prohibitively expensive for all three firms. Firm Firm A Firm B Firm C First Unit of Pollution (Dollars) 80 550 75 Cost of Eliminating the... Second Unit of Pollution Third Unit of Pollution (Dollars) 210 1,075 130 (Dollars) 130 700 90…arrow_forward
- See below for three parts of Scenario 2 Scenario 2A. There are three firms, A;B; and C that produce electricity. The first two firms have the same per-megawatt cost of production equal to $2, while firm C has a per-megawatt cost of $1. The firms differ, however, in their pollution. Firms A;B; and C produce respectively 1, 2, and 3 cubic feet of carbon monoxide per megawatt produced. A cubic foot of carbon monoxide pollutes the environment, and has a social cost of $2.5. The demand for electricity is represented by the inverse demand function P (Mw) =100 - Mw, where Mw represents the megawatts consumed by the public. Suppose firms are not held accountable for the pollution they produce. Scenario 2B. Suppose now that the government can measure the amount of pollution issued by each firm, and suppose that the government constrains each firm to emit no more than 9 cubic feet of carbon monoxide. Scenario 2C Suppose that government allows firms to trade their permits to emit carbon…arrow_forwardConsider a market with the following supply and demand. (It may help to draw a graph for these questions.) P 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QS 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 QD 800 750 700 650 600 550 500 450 400 350 If there is an external cost of $3, what is the efficient quantity? If there is an external benefit of $3, what is the efficient quantity? For the remaining questions assume that there is a $3 external COST. If the government wants to get the efficient quantity with a per/unit tax, how much should the tax be? Now imagine that they use tradable allowances. If they cap the quantity at 400 what would the value of these allowance be in the market? (Assume the market is perfectly competitive and that "one allowance" lets you…arrow_forwardTwo MSU fraternities, Phi Kappa Sigma and Phi Kappa Tau, are accustomed to each having 6 parties a month. Phi Kappa Sigma and Phi Kappa Tau are located close to each other on Bogue Street. These parties impose a negative externality on their other neighbors on Bogue Street. Suppose President Stanley decides that the socially optimal total number of parties on Bogue Street is 8 parties a month. The total benefits each fraternity derives from having a certain number of parties a month are given in the table below. Number of Parties 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Phi Kappa Sigma's Total Benefits 0 300 500 650 700 740 775 Phi Kappa Sigma's Marg. Benefits Phi Kappa Tau's Total Benefits 0 250 475 650 750 825 850 Phi Kappa Tau's Marg. Benefits a) Suppose President Stanley decides to limit the total number of parties to 8 by issuing Phi Kappa Sigma 6 rights and Phi Kappa Tau 2 rights. Each right allows the fraternity to have one party. If these rights are allowed to be traded, how many rights will be sold? Who…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education