
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
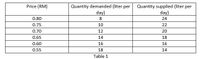
Suppose that the demand and supply of liter of petrol are given in table 1 below:
|
|
Quantity demanded (liter per day) |
Quantity supplied (liter per day) |
|
0.80 |
8 |
24 |
|
0.75 |
10 |
22 |
|
0.70 |
12 |
20 |
|
0.65 |
14 |
18 |
|
0.60 |
16 |
16 |
|
0.55 |
18 |
14 |
Table 1
What is the
Transcribed Image Text:Price (RM)
Quantity demanded (liter per
Quantity supplied (liter per
day)
day)
0.80
8.
24
0.75
10
22
0.70
12
20
0.65
14
18
0.60
16
16
0.55
18
14
Table 1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 6 Suppose the yearly demand and supply curves for Purebread Organic Dog Biscuits is given by the following table: Price ($) Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied 1.00 3500 300 1.50 3200 500 2.00 2800 800 2.50 2200 1200 3.00 1600 1600 3.50 900 1800 What is the equilibrium price? Group of answer choices $2.00 $2.50 $3.00 $3.50arrow_forwardThe following graph shows two known points (X and Y) on a demand curve for apples. PRICE (Dollars per pound) 10 9 8 1 0 0 Slope: -0.05 I Demand 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 QUANTITY (Thousands of pounds of apples) 90 100arrow_forwardDemand and supply often shift in the retail market for gasoline. Here are two demand curves and two supply curves for gallons of gasoline in the month of May in a small town in Maine. Some of the data are missing.Using the table, answer the following questions: Quantities Demanded Quantities Supplied Price D1 D2 S1 S2 $7.00 5,000 7,500 9,000 9,500 6,000 8,000 8,000 9,000 5.00 8,500 8,500 9,000 5,000 Use the following facts to fill in the missing data in the table. If demand is D1 and supply is S1, the equilibrium quantity is 7,000 gallons per month. When demand is D2 and supply is S1, the equilibrium price is $6.00 per gallon. When demand is D2 and supply is S1, there is an excess demand of 4,000 gallons per month at a price of $4.00 per gallon. If demand is D1 and supply is S2, the equilibrium quantity is 8,000 gallons per month. b. Compare the two equilibriums: In the first,…arrow_forward
- no handwritten notesarrow_forwardAssume that the equilibrium price is at $3 and equilibrium quantity is at 40 units of a product. Then, imagine that suddenly any of determinants of demand, other than the price of the product, caused demand to increase while, at the same time, one of determinants of supply, other than the price of the product, caused supply to decrease. TASK: First, draw the demand and supply graph to show the original equilibrium price at $3 and equilibrium quantity at 40 units. Second pick ONE specific DETERMINANT of DEMAND and ONE specific DETERMINANT of SUPPLY Third, show in the graph what it looked like if demand increased and supply decreased (select where you think that the new price and quantity would change to), what the new equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity would be, after both changes in demand and supply occurred. Fourth, in a couple of words, write down what would be YOUR new equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity. [That is, tell us that the original equilibrium price…arrow_forwardWhats the market equilibrium price and the graph?arrow_forward
- I am stuck on this problem, I don't know where to start. Could you give a step by step on how to figure this problem out. Thank you. There is an increase in demand of 100 units at each price and a decrease in supply of 100 units at each price. In the graph below, draw the new demand and supply lines. Instructions: Use the graphing tools, 'D2', 'S2', to plot the new demand and supply lines on the figure and then use the grid lines to determine the new equilibrium price and quantity.arrow_forwardThe following table shows the annual demand and supply in the market for shoes in Miami. Price (Dollars per pair of shoes) 20 40 60 80 PRICE (Dollars per pair of shoes) 120 100 20 On the following graph, plot the demand for shoes using the blue point (circle symbol). Next, plot the supply of shoes using the orange point (square symbol). Finally, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for shoes. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. 0 100 0 Quantity Demanded (Pairs of shoes) 1,100 900 800 200 600 500 400 600 800 QUANTITY (Pairs of shoes) Quantity Supplied (Pairs of shoes) 200 400 500 900 1000 1,200 1200 O Demand Supply Equilibriumarrow_forwardSuppose both the demand for olives and the supply of olives decline by equal amounts over some time period. Use graphical analysis to show the effect on equilibrium price and quantity. Instructions: On the graph below, use your mouse to click and drag the supply and demand curves as necessary. D1 Quantity of olives Price of olivesarrow_forward
- TTT 1. The table below displays information pertaining to the market for milk: TABLE 1 Cartons Per Day Price (dollars per carton) Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied 1.00 200 110 1.25 175 130 1.50 150 150 1.75 125 170 2.00 100 190 In this space, please illustrate the market for milk, with both the supply curve and demand curve graphed on the same graph, making sure you label each component and put the correct variables on the x- and y-axis. The equilibrium price for milk is $ and the equilibrium quantity of milk produced and sold in the market is a. cartons. b. If the market price of milk suddenly rises to $1.75, the milk market will suddenly be faced with a or excess which means the quantity is greater than the quantity Numerically, the excess equals cartons of milk. с. Now assume better feeds increase milk production. When this happens within the above milk market, the curve will shift to the which will the price of milk and the quantity of milk produced and sold.arrow_forwardPlease provide an explanation so I can do it my own. Thanks!arrow_forwardSupply and Demand Problem Set[1] Use the following graph to answer questions 1 through 3: Plot the following Price and Quantity combinations: (4, 8), (1, 2), (5, 10) Is your graph more likely to be a demand curve or a supply curve? Why? Using the equation of a line, and P for price and Q for quantity, what is the algebraic formula of this curve? Use the following graph to answer questions 4 and 5: Plot the following Price and Quantity combinations. Note that the points are given in the format (Quantity, Price).(0, 50), (2, 40), (4, 30), (6, 20), (8, 10) Using the equation of a line, what is the algebraic formula of this demand curve? Use the following information to answer questions 6 through 10: Suppose the equation of the line changes to . Compute the quantity demanded at each indicated price. Price: $50, Quantity: Price: $40, Quantity: Price: $30, Quantity: Price: $20, Quantity: Price: $10, Quantity: Use the following graph to answer questions 11…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education